AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate
Domain 5 Networking and Content Delivery
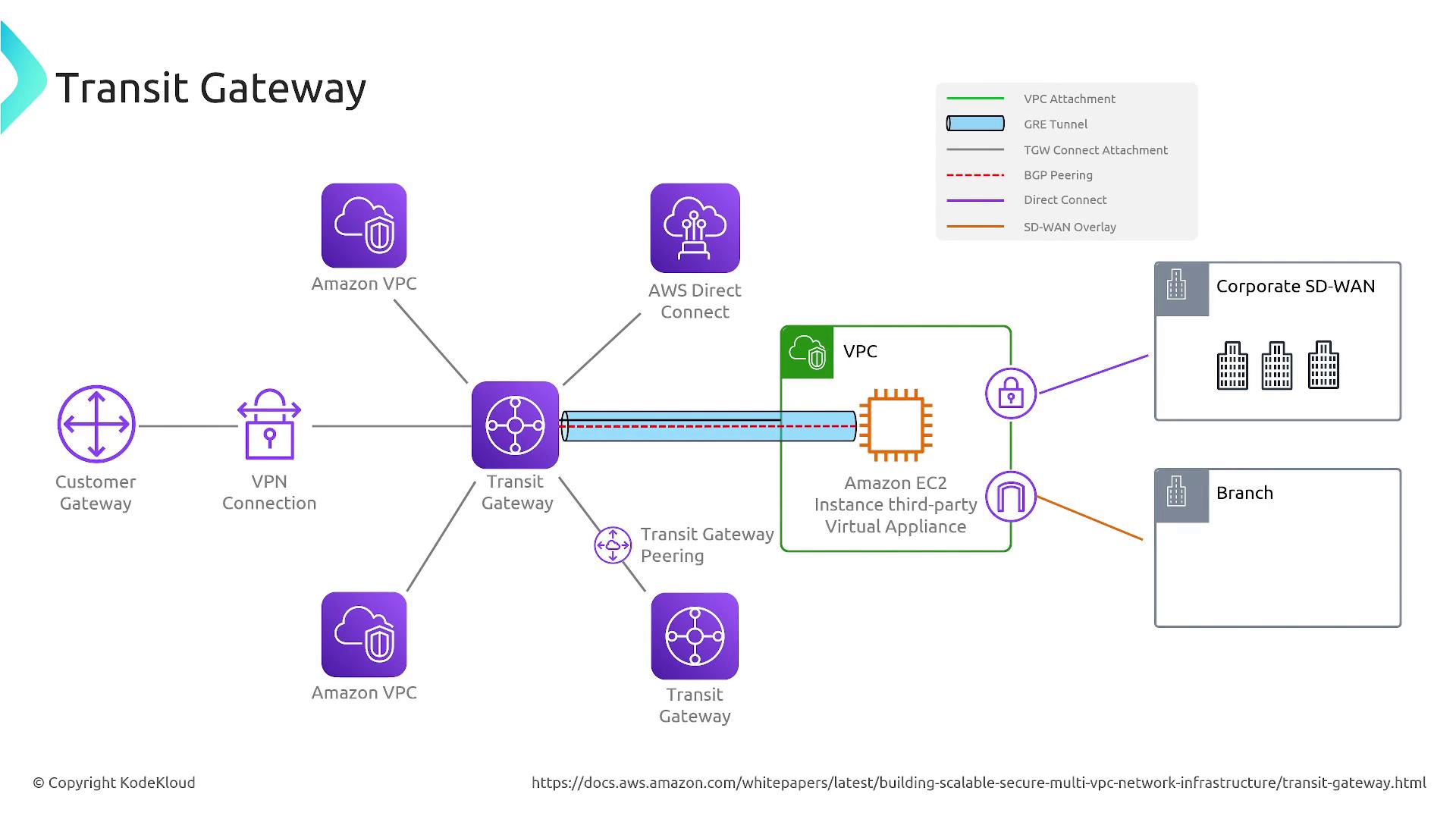
Internal Network to Network Connectivity With Transit Gateway
Welcome back. In this article, we explore how AWS Transit Gateway transforms the way you manage internal network-to-network connectivity. Building on our previous discussion about VPCs, we now dive into how Transit Gateway enhances connectivity, scalability, and security in your AWS environment.
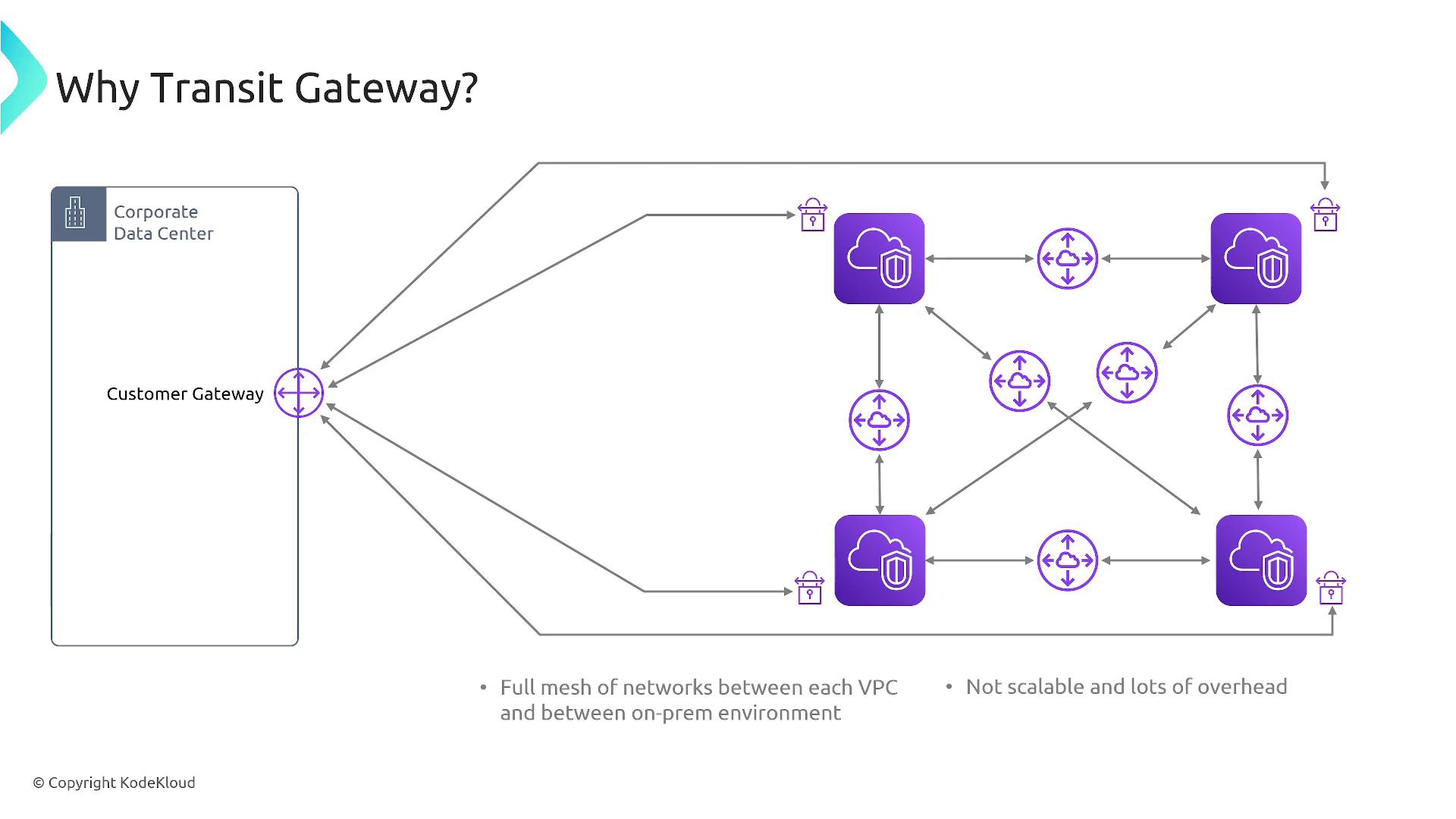
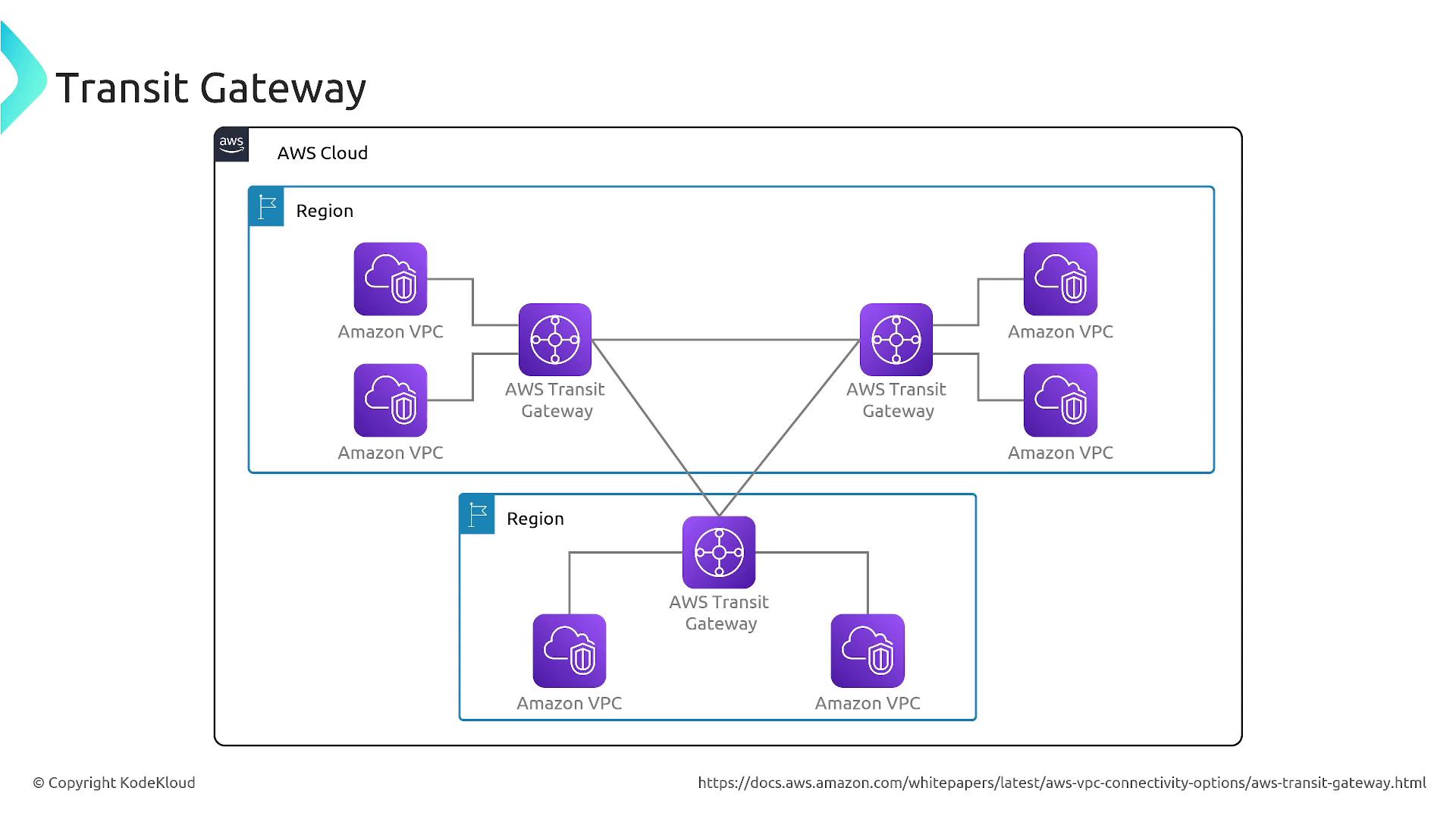
Transit Gateway is designed to overcome the scalability challenges inherent in VPC peering. While VPC peering is effective for a few connections, it quickly becomes unmanageable as you add more VPCs. Acting as a centralized transit hub, Transit Gateway simplifies network routing and security by integrating multiple VPCs, Direct Connect, VPN, and on-premises networks through region peering.
Instead of establishing separate VPC peering connections for every pair of VPCs—resulting in an exponential increase in configurations—Transit Gateway consolidates connectivity by serving as a single routing point. For instance, in a scenario with five VPCs, the mesh of direct peering connections becomes complex and error-prone, whereas Transit Gateway drastically reduces this overhead by linking each VPC to a centralized transit hub.
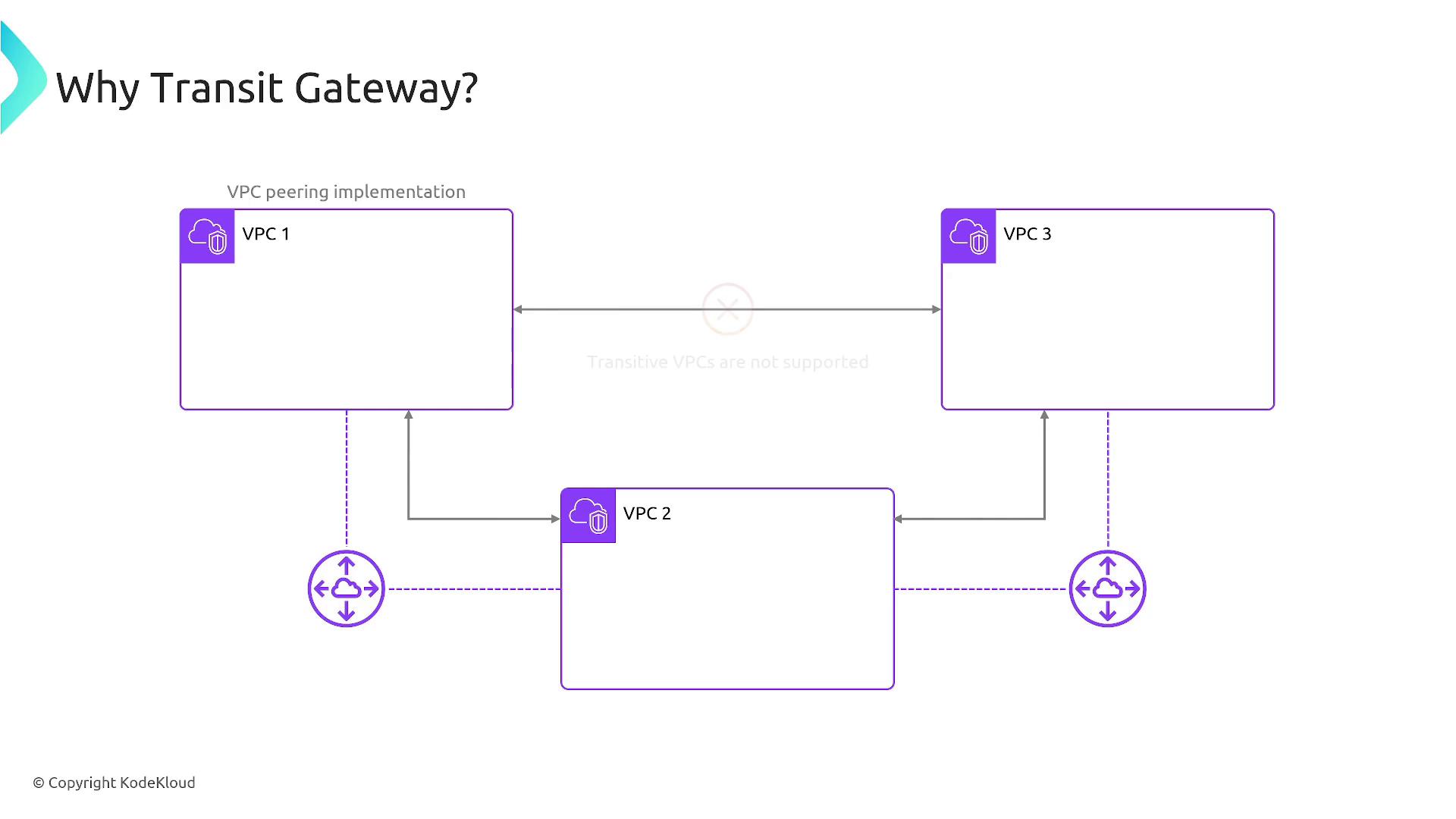
Transit Gateway not only centralizes management but also scales seamlessly as a serverless service. This approach simplifies network topology and provides enhanced control over your security policies, eliminating the complications often encountered in full mesh VPC peering configurations.
Consider the complexity in a full mesh setup: connecting four VPCs through VPC peering requires six separate peering connections. With Transit Gateway, each VPC connects to one transit hub, significantly reducing configuration complexity and enabling efficient management of inter-VPC traffic.
In a multi-region environment, each region operates its own Transit Gateway. You simply attach each VPC, Direct Connect, VPN, or even third-party connection to the gateway. The Transit Gateway then routes traffic based on your defined security policies and routing configurations.
Transit Gateway supports various connection types, enabling centralized routing across your entire network. It manages Direct Connect connections, VPNs, and even links to third-party appliances or customer gateways. The service deploys an Elastic Network Interface in each subnet used for its attachments, acting as a central router.
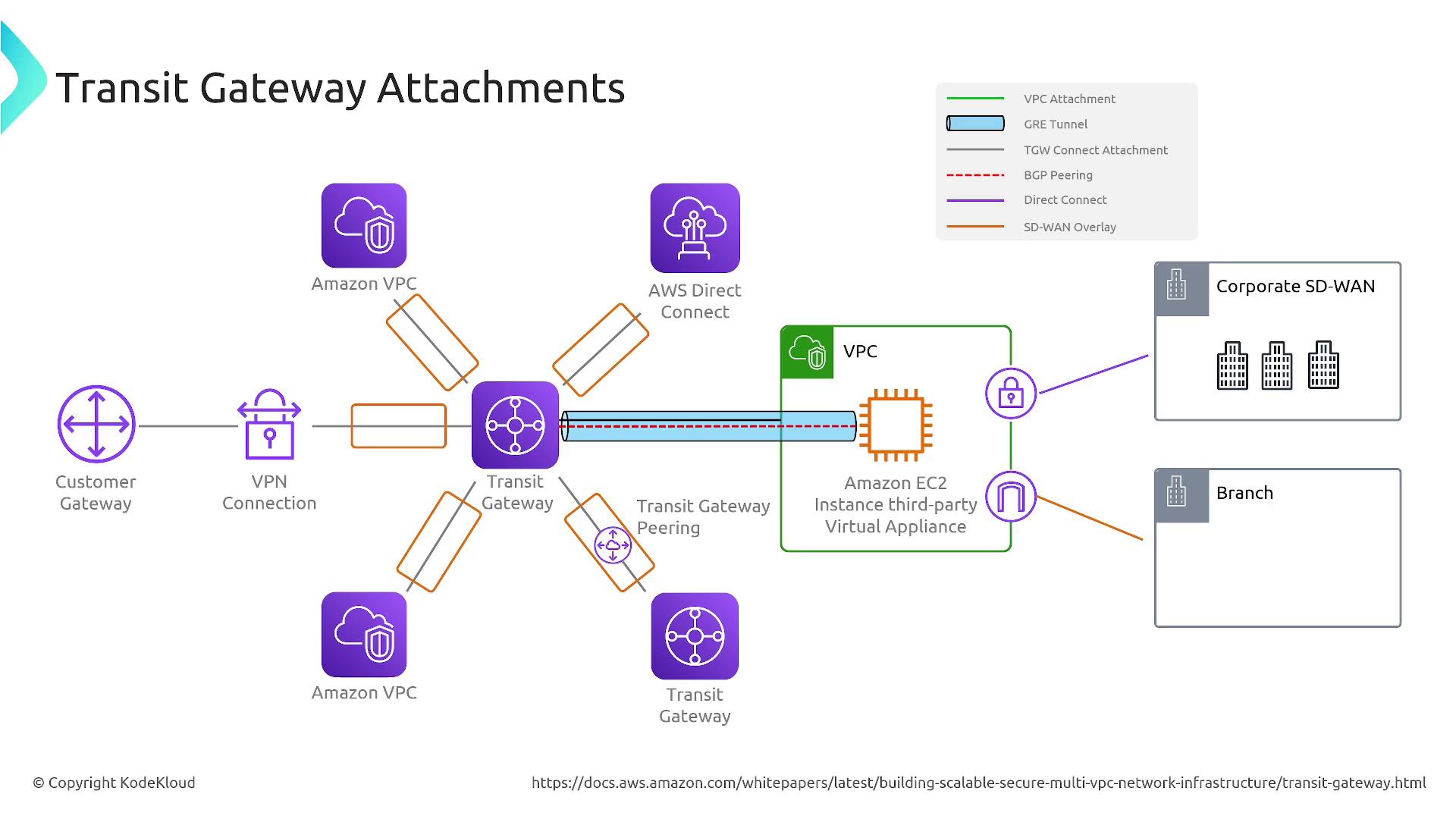
Important MTU Information
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) for Transit Gateway is 8,500 bytes. This adjustment is handled automatically and rarely affects your configuration or exam considerations.
By connecting VPCs, VPNs, or Direct Connect to the Transit Gateway, you can define precise routing rules to control network interconnectivity and enforce security boundaries.
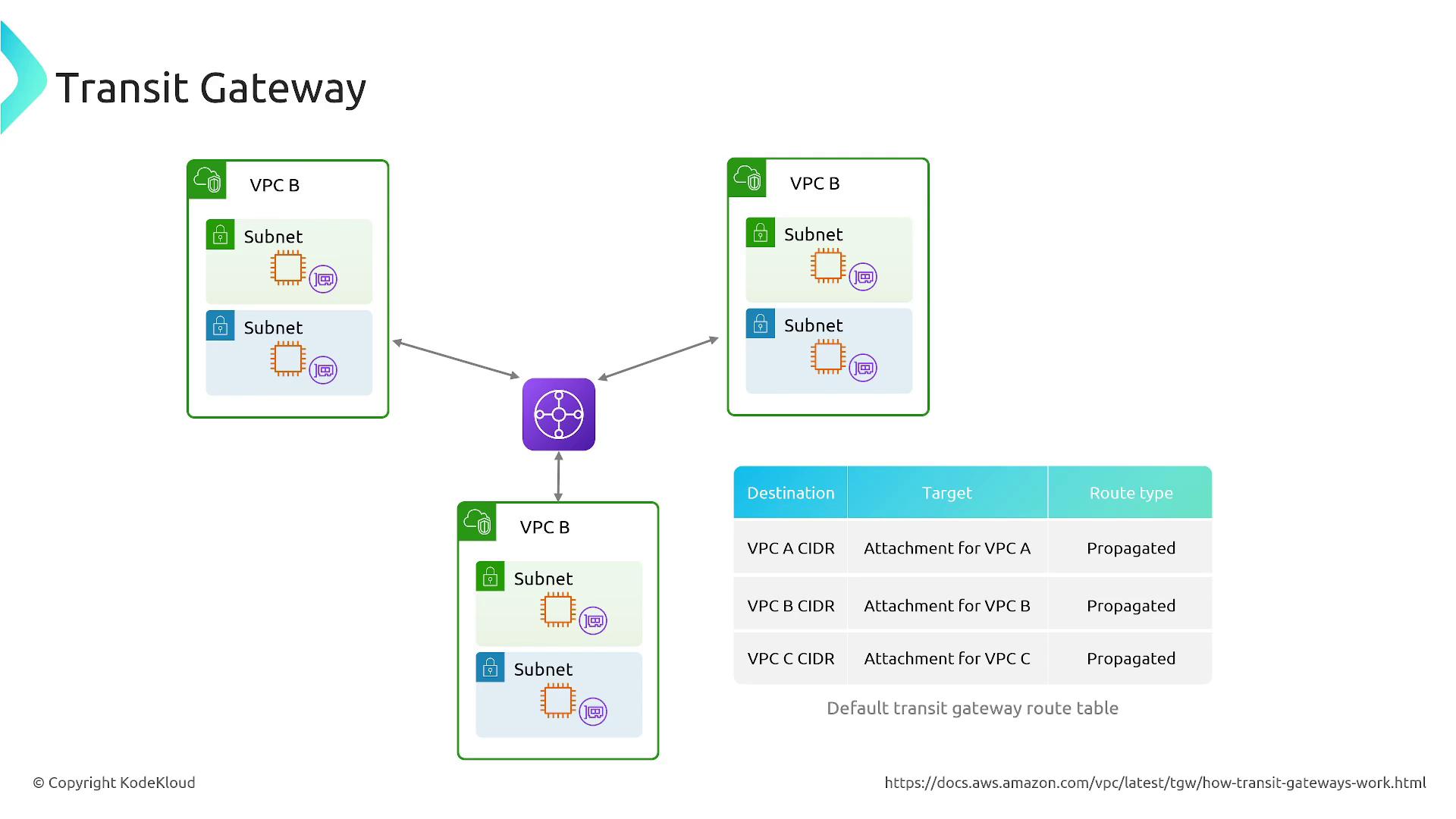
For both public and private subnets, you can specify routing rules that direct traffic to the Transit Gateway, centralizing routing for shared services or outbound internet access. In shared services deployments, Transit Gateway can integrate with appliances or Gateway Load Balancers to inspect and filter traffic, enhancing security further.
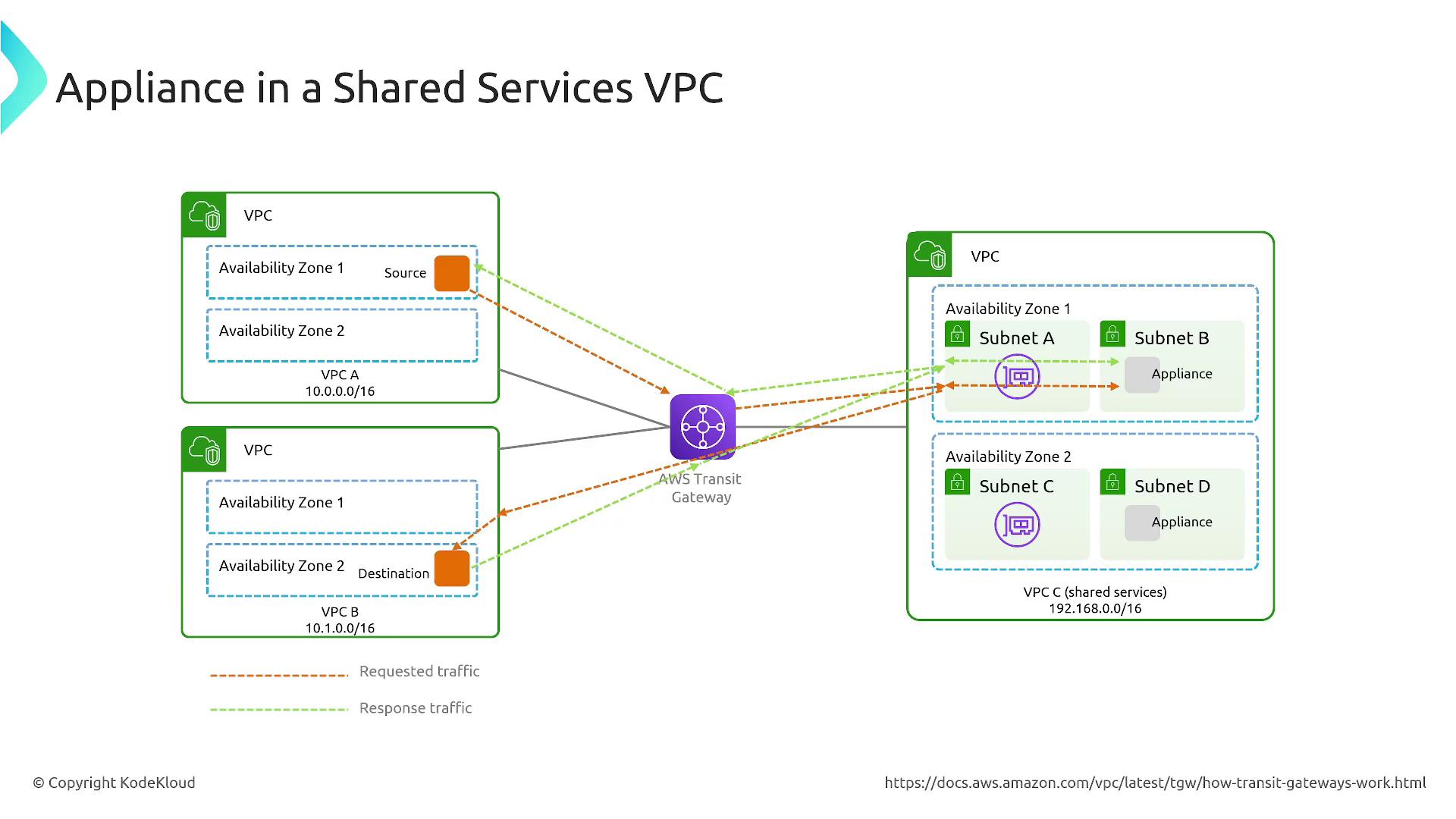
Centralizing outbound routing through Transit Gateway enables you to direct traffic from private subnets to a NAT gateway in a public subnet. This method enhances control and security of internet-bound traffic and supports integration with deep packet inspection and other advanced security appliances.
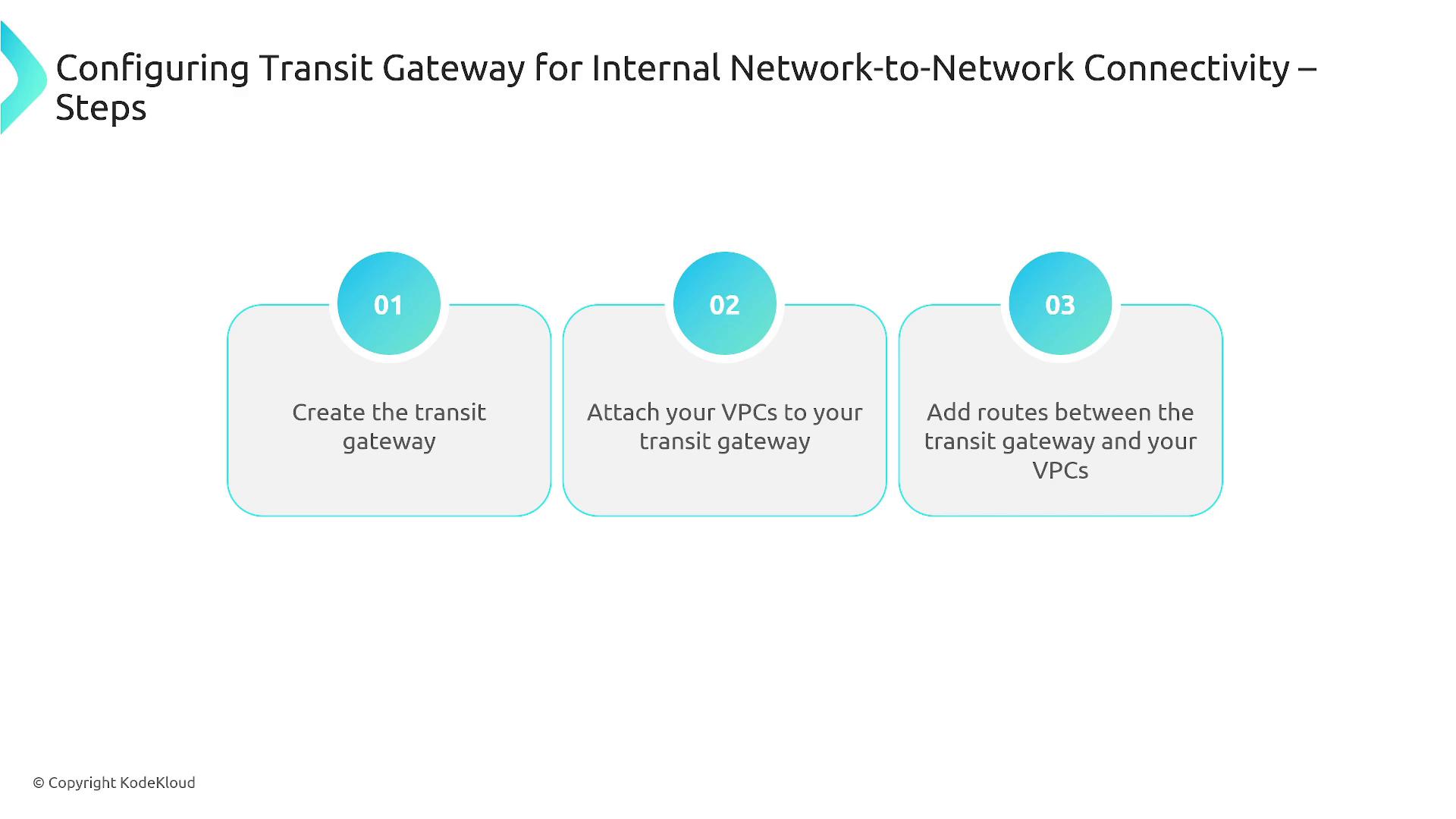
Setting up a Transit Gateway involves these key steps:
- Create the Transit Gateway.
- Attach your VPCs, Direct Connect, virtual private gateways, or customer gateways to the Transit Gateway.
- Add routing rules to control traffic flows between the various attachments.
After your Transit Gateway is set up, you can monitor its performance and traffic using VPC flow logs, Transit Gateway flow logs, and AWS CloudTrail logs. These logging services ensure that your routing policies are enforced correctly and help you troubleshoot any potential issues.
![]()
Key Benefits of Using Transit Gateway
Transit Gateway simplifies your network architecture, scales effortlessly, and enhances security when connecting multiple VPCs, VPNs, Direct Connects, and on-premises networks. For environments with a high number of VPC connections or those requiring advanced routing features, Transit Gateway is the superior choice. However, if you manage only a few VPCs and do not require complex routing, VPC peering can still be an effective solution.
Thank you for reading this in-depth overview of internal network-to-network connectivity using AWS Transit Gateway. For more detailed AWS networking strategies and best practices, be sure to explore additional resources in our AWS Documentation and related technical articles.
Watch Video
Watch video content