Overview of Compute Platforms
Choosing the right compute platform depends on your workload and desired performance characteristics. Below is a brief overview of each:- EC2 (Virtual Machines): Provides high control, robust performance, and is ideal for enterprise-grade applications.
- ECS (Container Orchestration): Optimized for containerized applications; supports deployment via EC2 launch types or the serverless Fargate option.
- EKS (Kubernetes-based Orchestration): Designed for Kubernetes users; available with both EC2 and Fargate launch options.
- Lambda (Serverless): Delivers a completely serverless experience. This option may require re-architecting your application and comes with specific resource limitations.
Key Considerations for Platform Selection
When selecting your compute platform, keep the following factors in mind:-
Architecture Requirements:
Lambda is tailored for serverless architectures and may need substantial application redesign, while EC2 supports traditional VM-based deployments. -
Container Orchestration:
Use ECS for container orchestration if you prefer not to manage Kubernetes. If you already rely on Kubernetes, then EKS might be the better choice. -
Launch Types:
Both ECS and EKS offer Fargate (serverless) and EC2 launch types. Although Fargate provides serverless advantages, it has certain resource constraints compared to a direct EC2 deployment (e.g., CPU and memory flexibility).
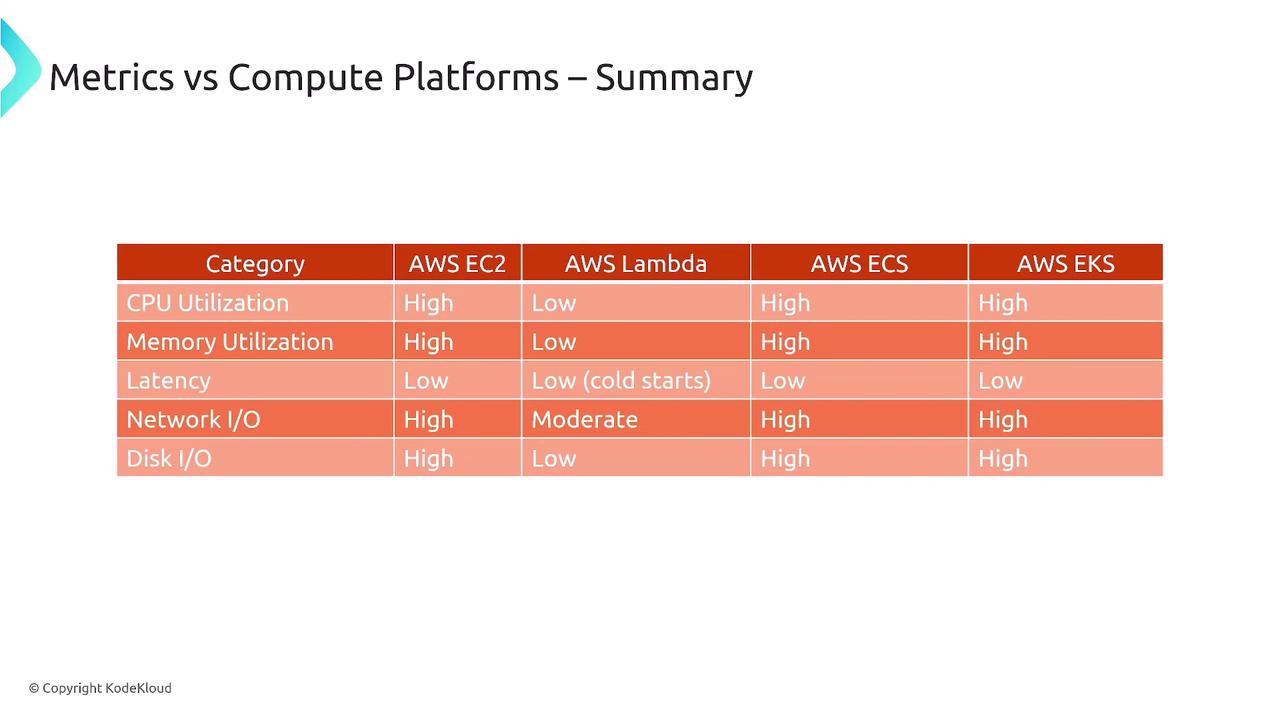
CPU Utilization
CPU performance is crucial when evaluating compute platforms. For CPU-intensive workloads, EC2 (or ECS/EKS with EC2 launch types) offer greater flexibility due to the underlying robust infrastructure.When monitoring CPU metrics, consider factors like CPU credit balance, disk operations, and network throughput—metrics that are more detailed in EC2-based deployments.
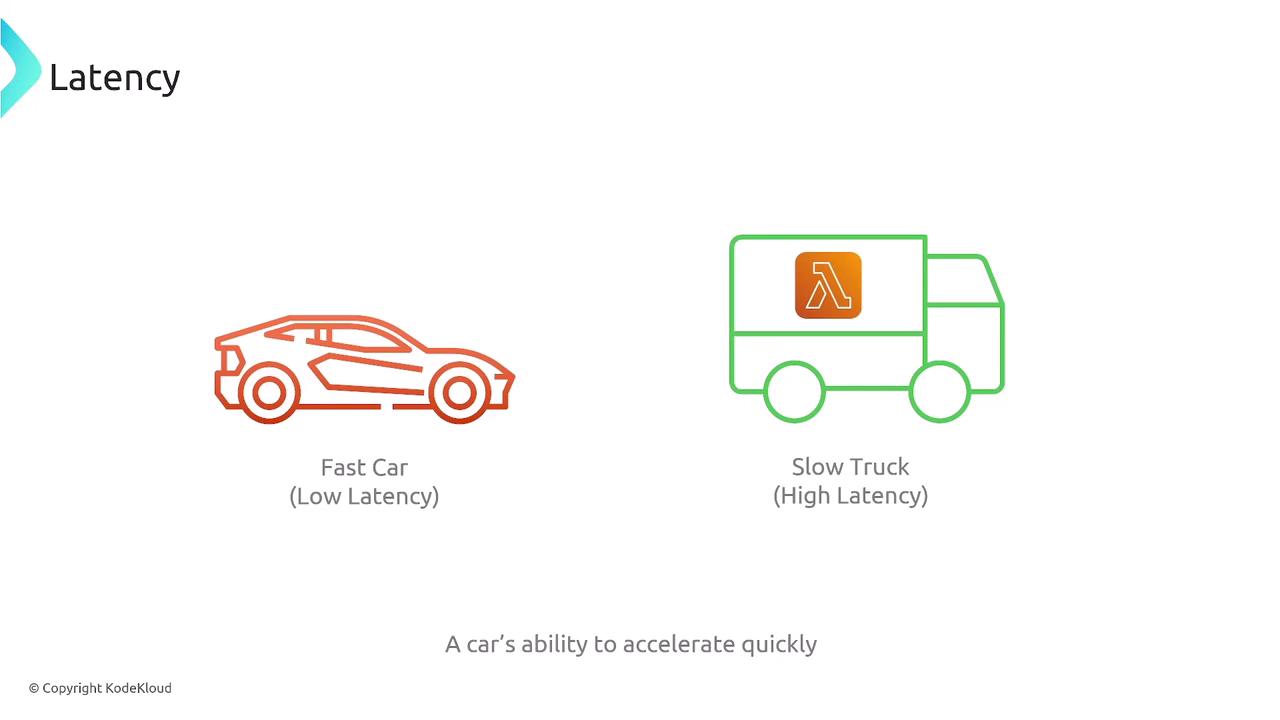
Latency and Throughput
Latency—the time taken between a request and its response—is critical in performance evaluation:- EC2: Offers low latency with rapid response times, especially in high-end instances with substantial processing power and memory.
- Lambda: May experience higher latency due to cold starts and provisioning delays, making it less suitable for low-latency, high-performance applications.
- Fargate: Generally provides faster responses than Lambda; however, its performance may depend on the configured resource limits.
Memory Utilization
Memory capacity is comparable to cargo space in a vehicle. Your application’s memory demands will influence your platform choice:-
High Memory Workloads:
For requirements exceeding 10 GB of memory, EC2-based deployments are preferable since Lambda and Fargate are typically capped at 10 GB. -
Moderate or Low Memory Workloads:
Applications with memory needs within the 10 GB limit can effectively use Lambda or Fargate on ECS/EKS.
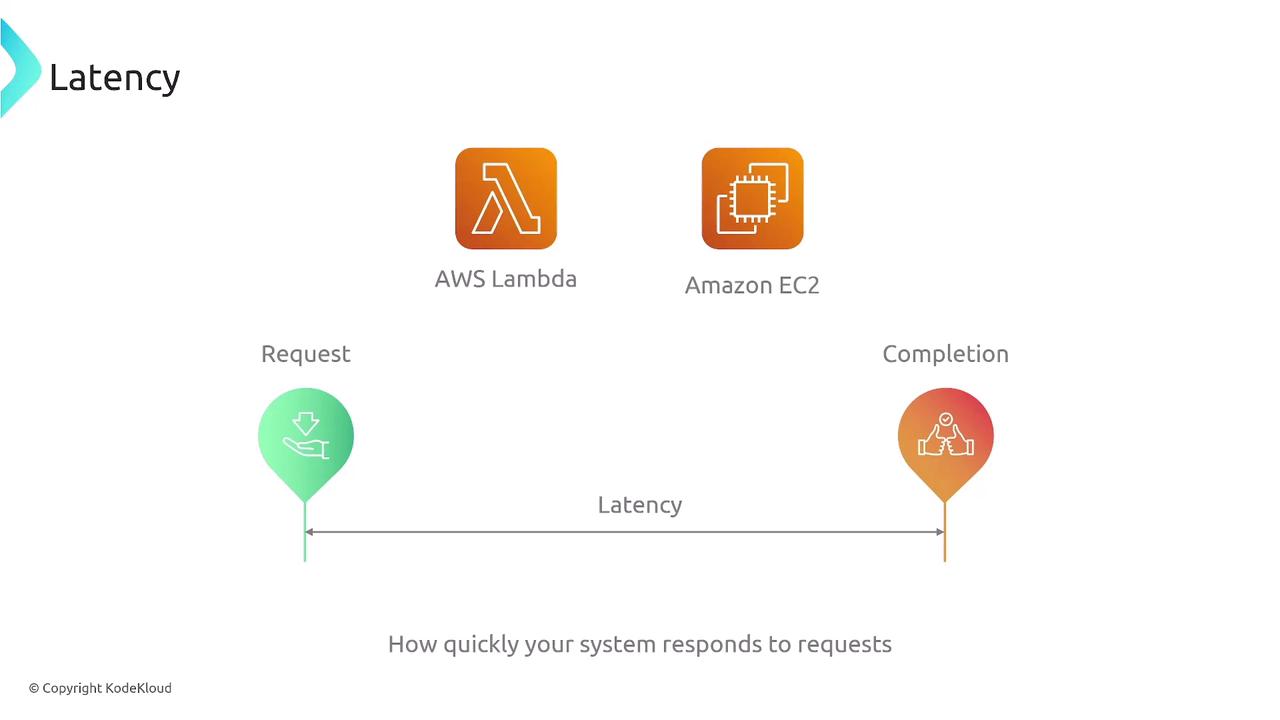
Revisiting Latency
Latency remains a pivotal consideration:- Lambda:
May introduce delay due to necessary pre-provisioning and efforts to keep instances warm. - EC2 and Fargate:
Pre-allocated capacities in EC2 (and to some extent in Fargate) generally result in lower latency.
Network I/O and Disk I/O
Applications with high network or disk I/O requirements may favor specific platforms:-
Network I/O:
Although all platforms offer reliable network performance, EC2-based instances (including EKS/ECS on EC2) are typically superior for sustained, high-throughput scenarios. -
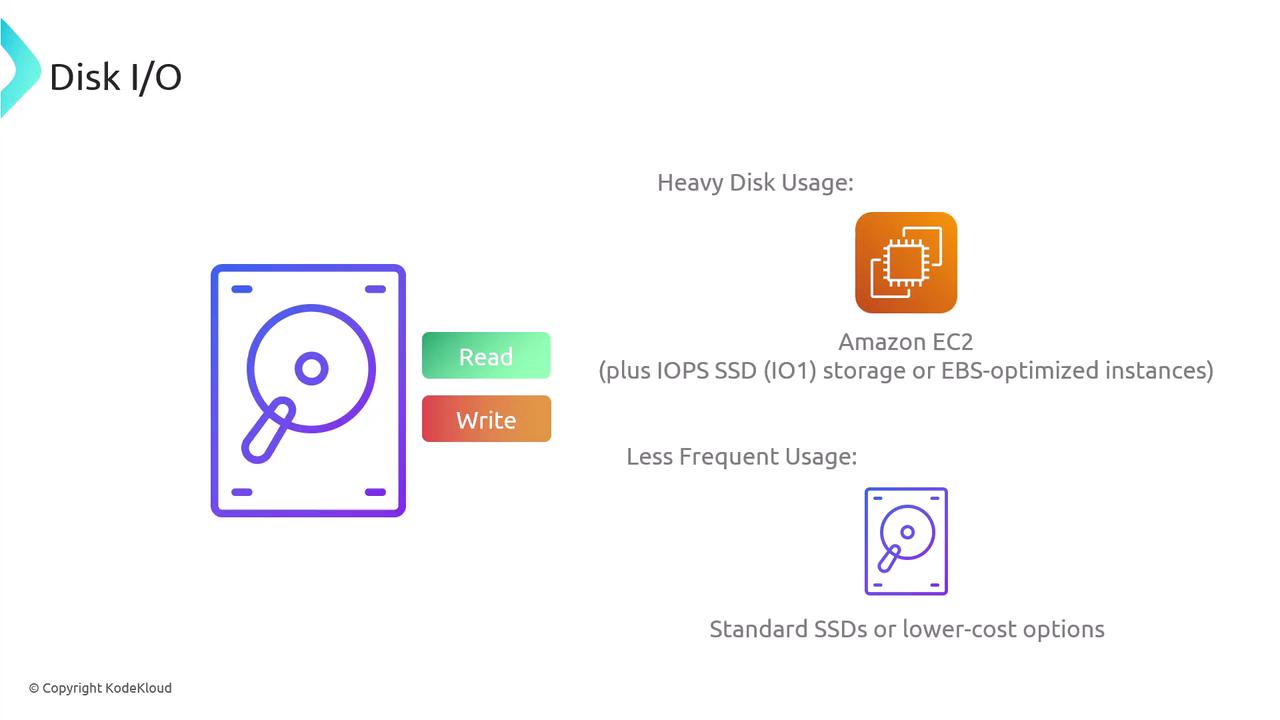
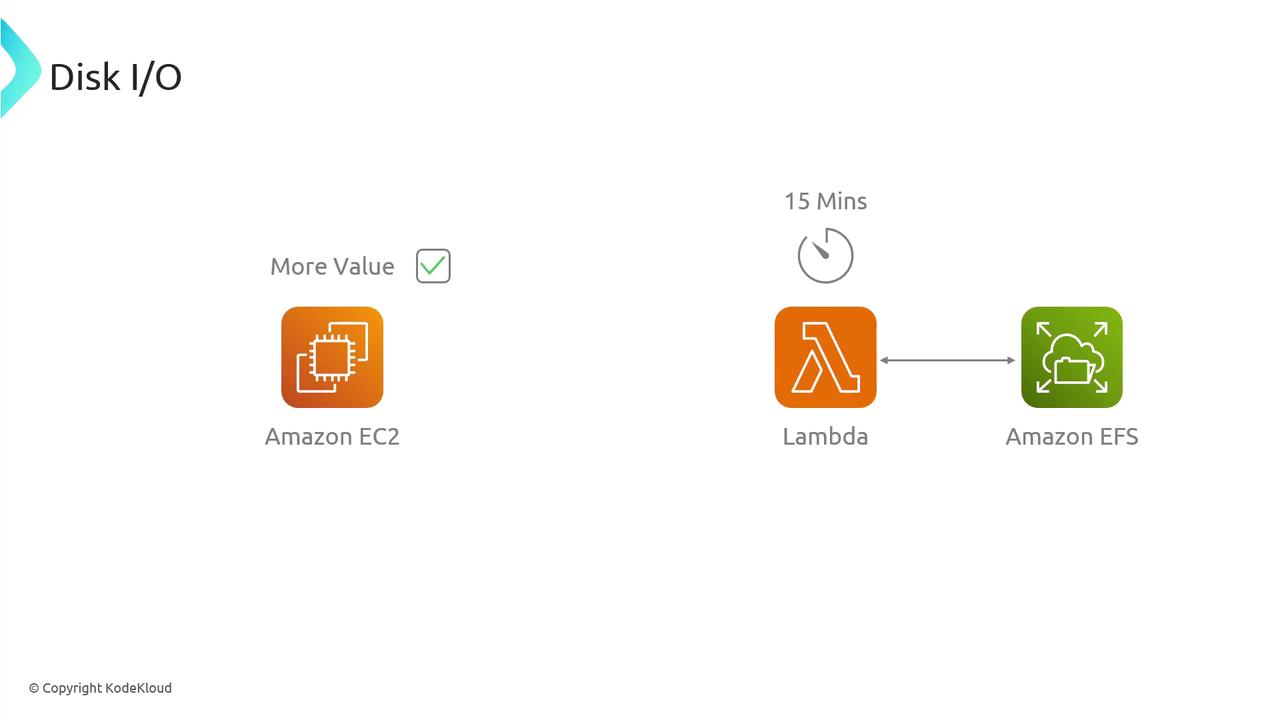
Disk I/O:
EC2 delivers fast, local NVMe storage and offers EBS volumes with provisioned IOPS for high-performance disk operations. While Lambda can integrate with EFS, its 15-minute execution cap makes EC2 a more dependable choice for prolonged, heavy disk I/O needs.
Summary and Recommendations
To summarize, consider the following guidelines when selecting your compute platform:- For High Resource Demands (CPU, Memory, Network, Disk I/O):
- Prioritize EC2, or use ECS/EKS with the EC2 launch type to leverage dedicated hardware capabilities.
- For Lower or Sporadic Workloads:
- Lambda or Fargate on ECS/EKS can be a cost-effective solution if your application’s demands are modest (e.g., under 10 GB of memory) or intermittent.