Operational Management and Traffic Handling
Fully managed services simplify operations by having AWS take care of tasks such as handling traffic flow, scaling, and routine maintenance. On the other hand, self-managed services require you to directly configure, maintain, and scale your systems. For example, compare using a custom setup of Amazon EC2 to host your application versus leveraging AWS Lambda. With AWS Lambda, a fully managed service, you trade full control over the infrastructure for ease of use. In contrast, an EC2 instance gives you complete control over the environment—with additional overhead for configuration and maintenance.
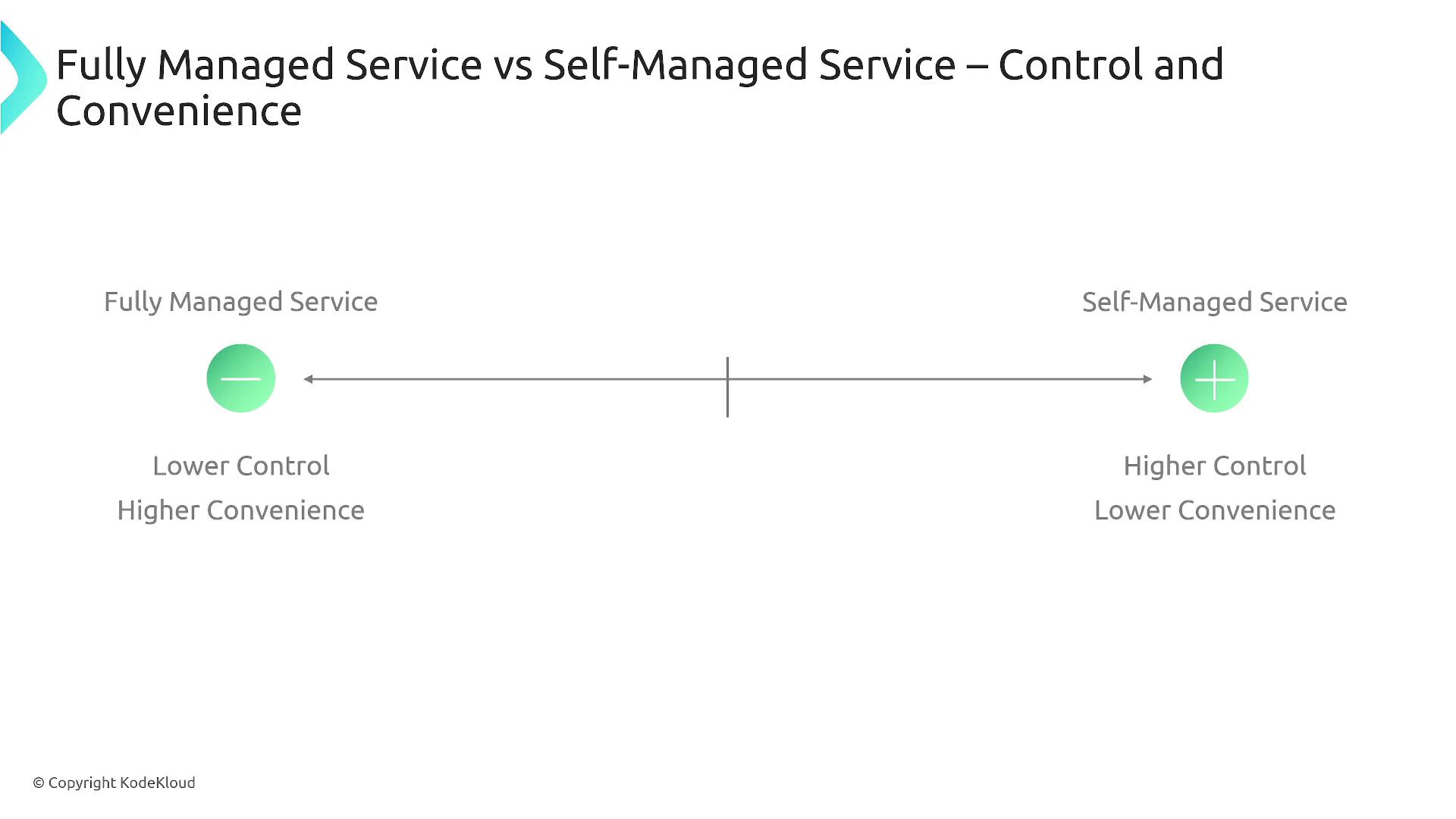
Comparison of Control Levels
The diagram below clearly contrasts fully managed services and self-managed services by showcasing the difference in operational responsibility. Fully managed services offer lower control over the underlying infrastructure, whereas self-managed services provide a significantly higher level of customization and control.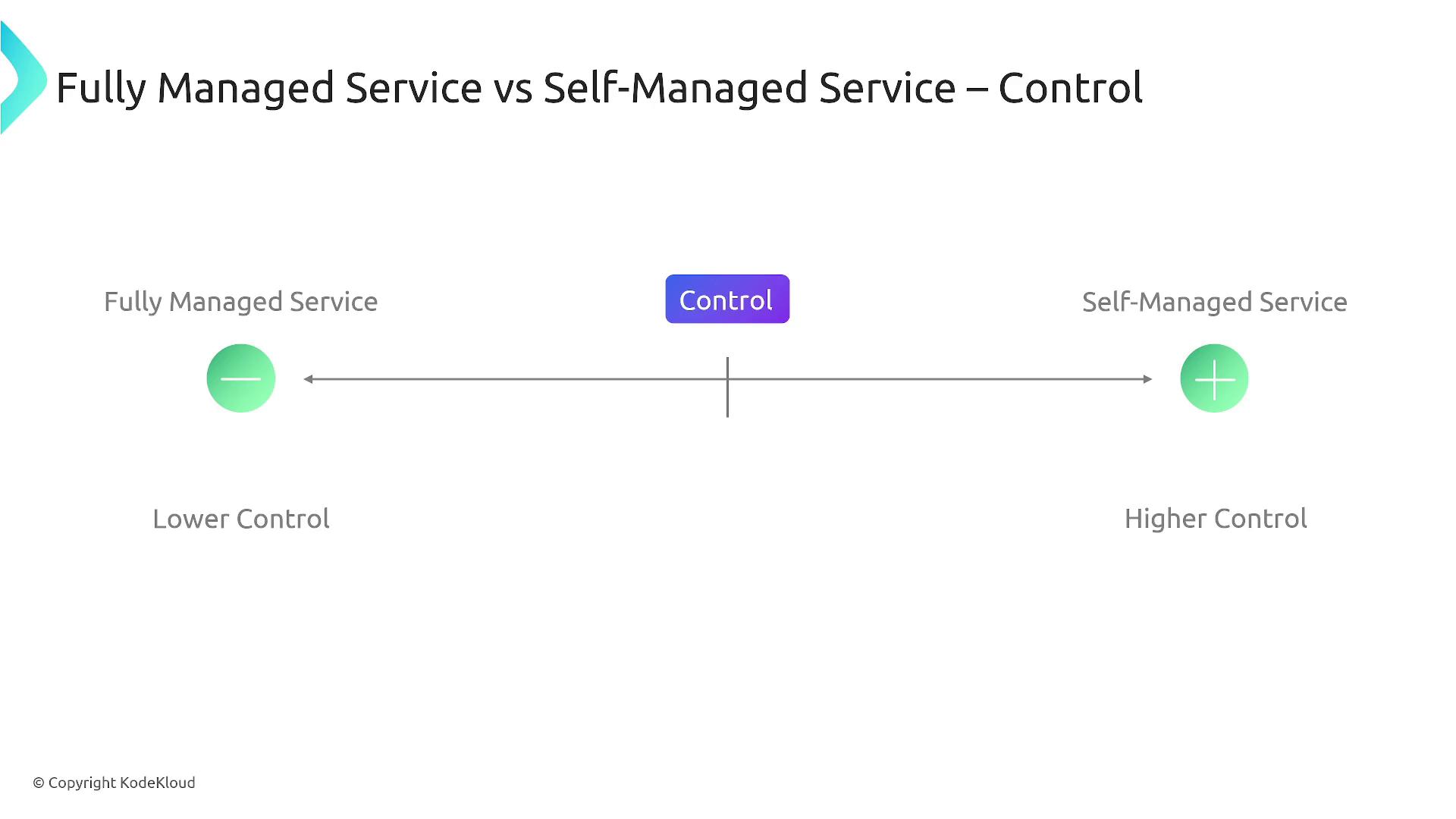
Convenience versus Operational Overhead
When it comes to convenience, fully managed services substantially reduce operational overhead. AWS handles patching, scaling, and other backend issues so you can concentrate on your core business. Conversely, self-managed services require more hands-on management and increase operational responsibility.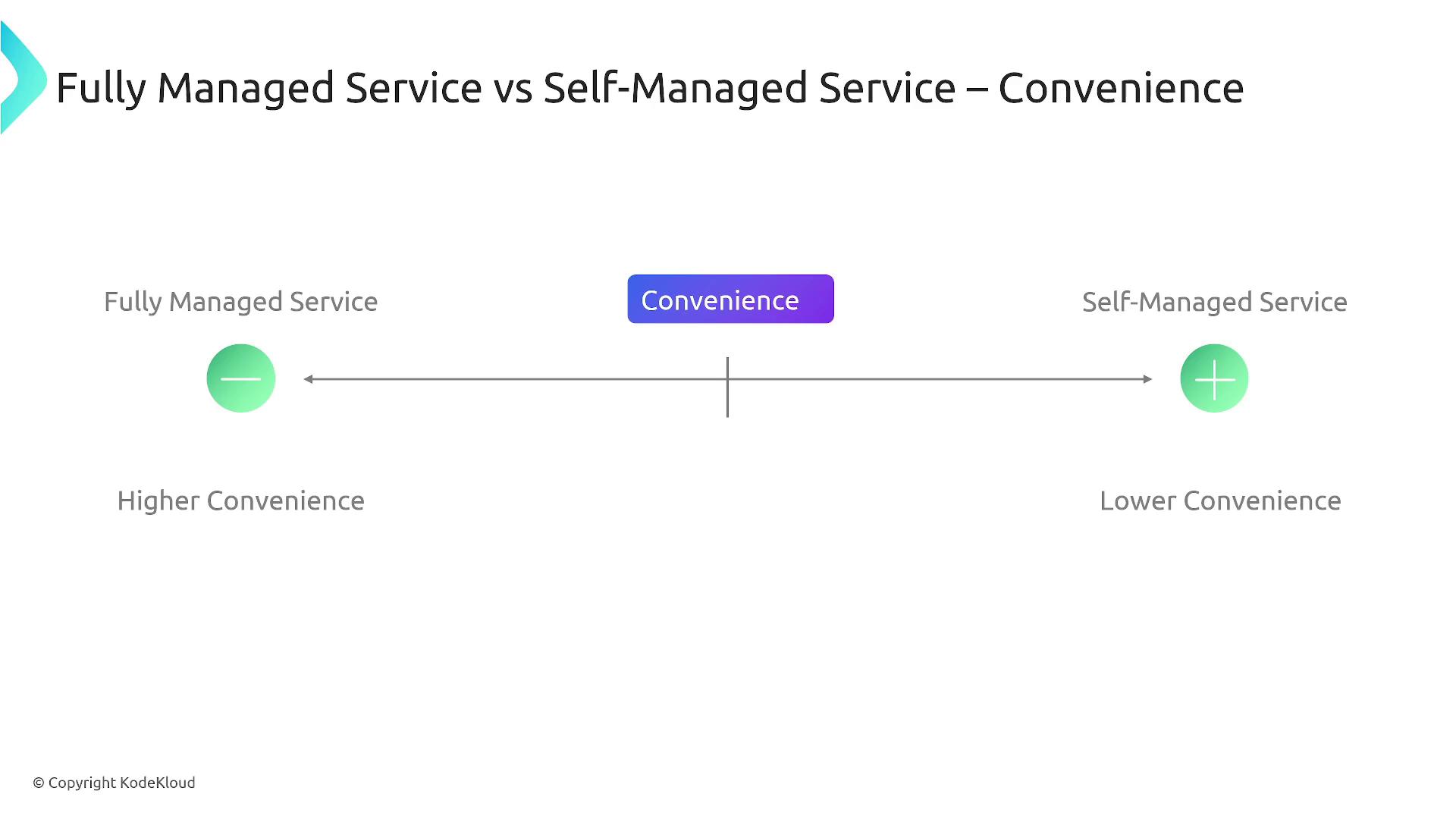
Cost Considerations
Cost efficiency is another critical factor. Fully managed services typically use a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can result in lower costs when scaling dynamically based on demand. Self-managed services, such as provisioning an EC2 instance, commonly involve fixed capacity costs regardless of usage, potentially leading to higher expenses when resources are underused.
Responsibility and Security
A key consideration is the division of security responsibilities. Fully managed services offload much of the security management to AWS, reducing your administrative burden. However, with self-managed services, you are responsible for nearly all aspects of security, maintenance, and operating system setup.
Setup Time and Customization
The time it takes to set up your service is another important differentiator. Fully managed services often allow you to deploy with just a few clicks, ensuring a rapid start. In contrast, self-managed setups require detailed configuration steps, increasing deployment time but allowing for deep customization.
Monitoring and Debugging
Monitoring tools and debugging capabilities can vary significantly. Fully managed services may offer limited insight into lower-level system details, whereas self-managed services provide extensive monitoring options. Integrating additional monitoring tools is often necessary with self-managed services, though the initial setup requires extra effort.
When to Choose Each Approach
Below are some key factors to consider when deciding between fully managed and self-managed services:Fully Managed Services
-
Ideal for Limited Operational Expertise:
Rely on AWS to handle routine management, allowing your team to focus on development. -
Quick Deployment:
Perfect for scenarios requiring rapid deployment of standard workloads. -
Lower Maintenance Overhead:
Benefit from AWS managing patching, scaling, and backend operations.

Self-Managed Services
-
High Customization Needs:
When your business requires specialized infrastructure configuration and advanced security measures. -
Dedicated Management Team:
Suitable if you have a team that can handle in-depth system management and monitoring. -
Avoiding Vendor Lock-In:
Opt for flexibility and control over the environment by managing services independently.

While vendor lock-in is sometimes mentioned as a reason for choosing self-managed services, it is generally not the primary factor. Always align your decision with the operational, security, and customization requirements specific to your business.