- All instances in the same availability zone for ultra-fast communication.
- Instances spread across different availability zones for high redundancy.
- A combination where clusters of systems are distributed over multiple availability zones (for example, replicating a database cluster across three availability zones in Virginia).
Cluster Placement Group
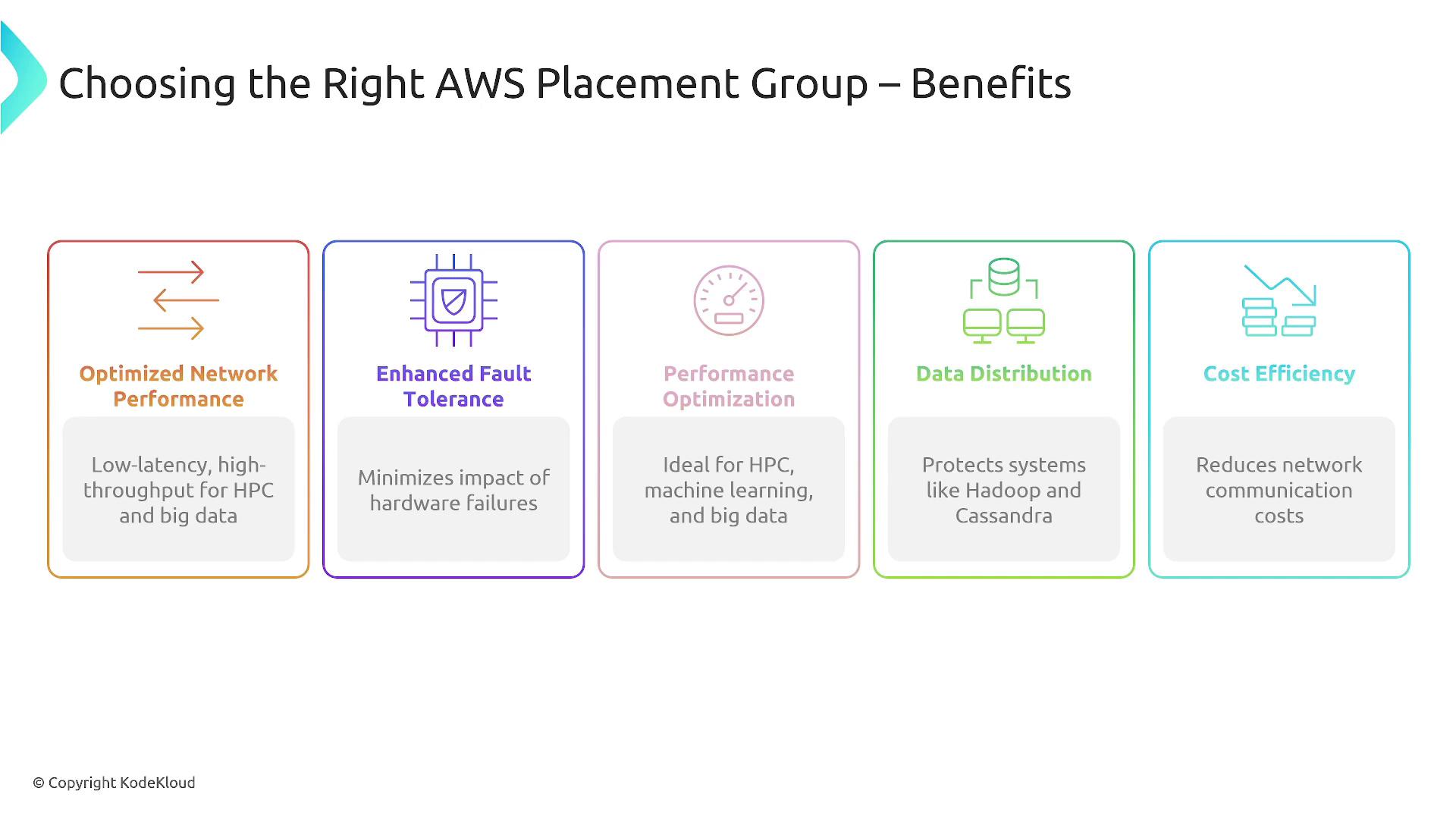
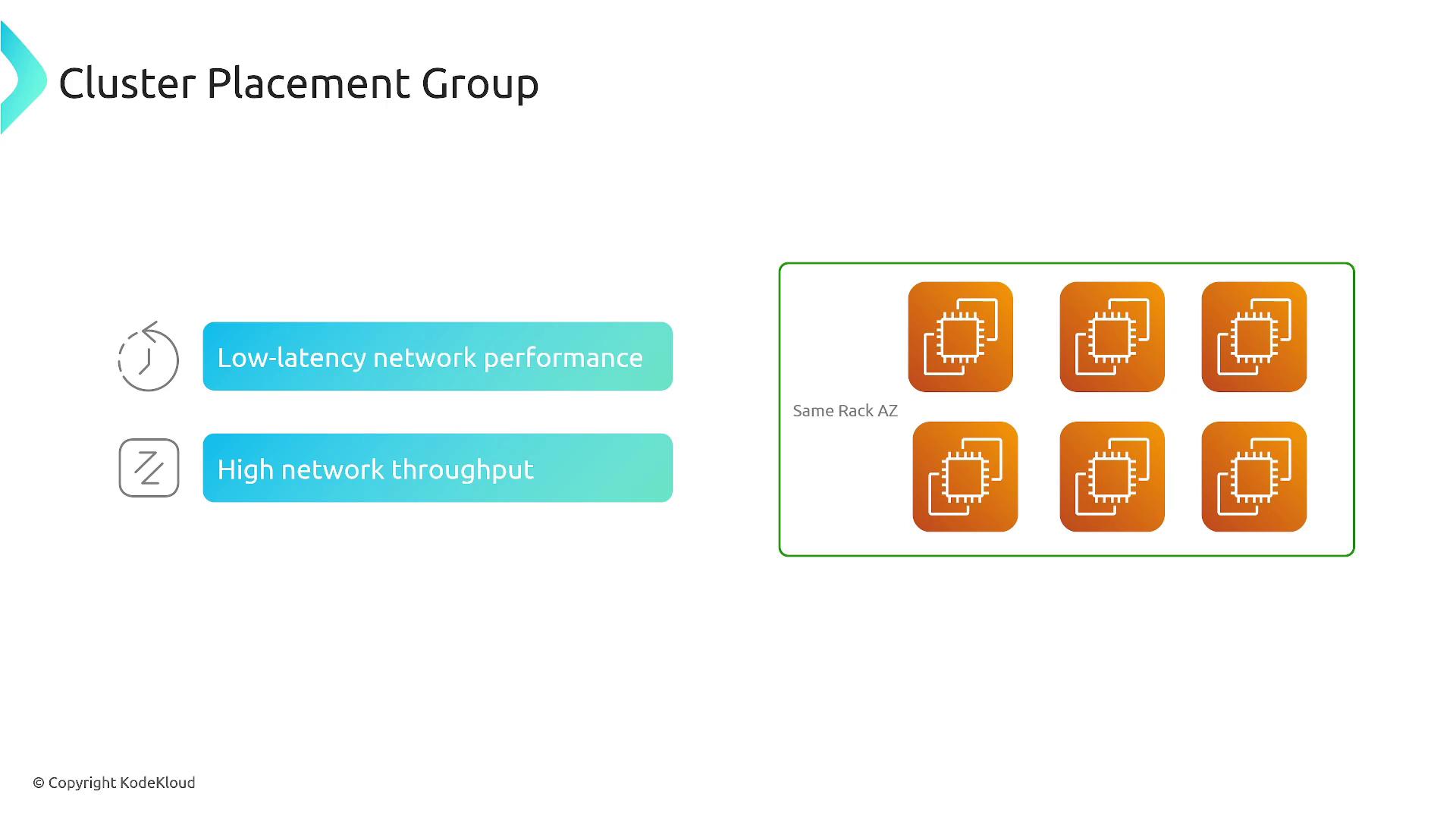
A cluster placement group is optimized for low latency and high throughput workloads. It packs instances as closely as possible—typically within a single availability zone and even on the same physical server—to maximize network performance for high-performance computing, big data analytics, and applications requiring rapid inter-instance data exchanges.
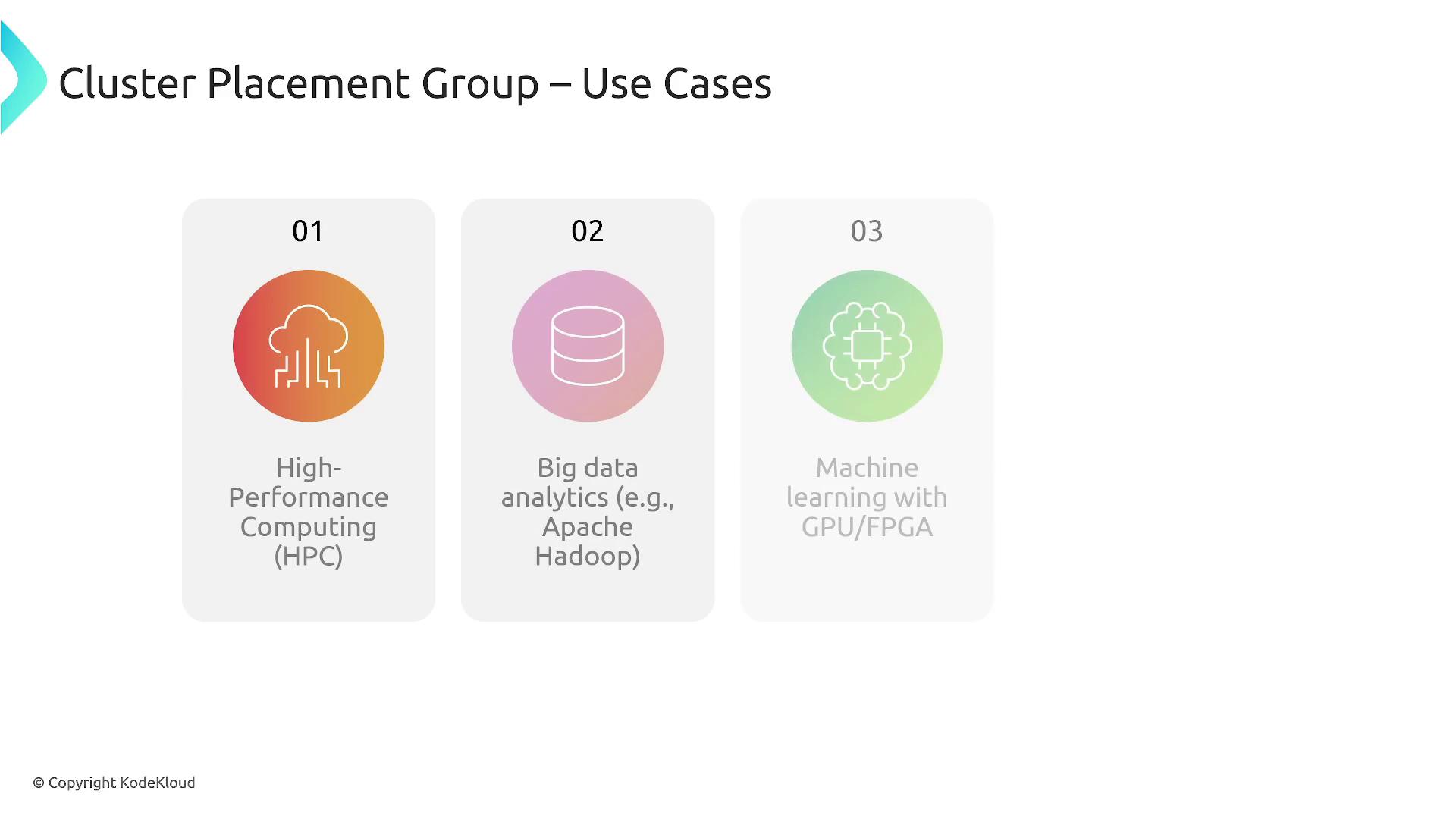
- High-performance computing
- Big data analytics
- Machine learning applications
Keep in mind the following limitations when using a cluster placement group:
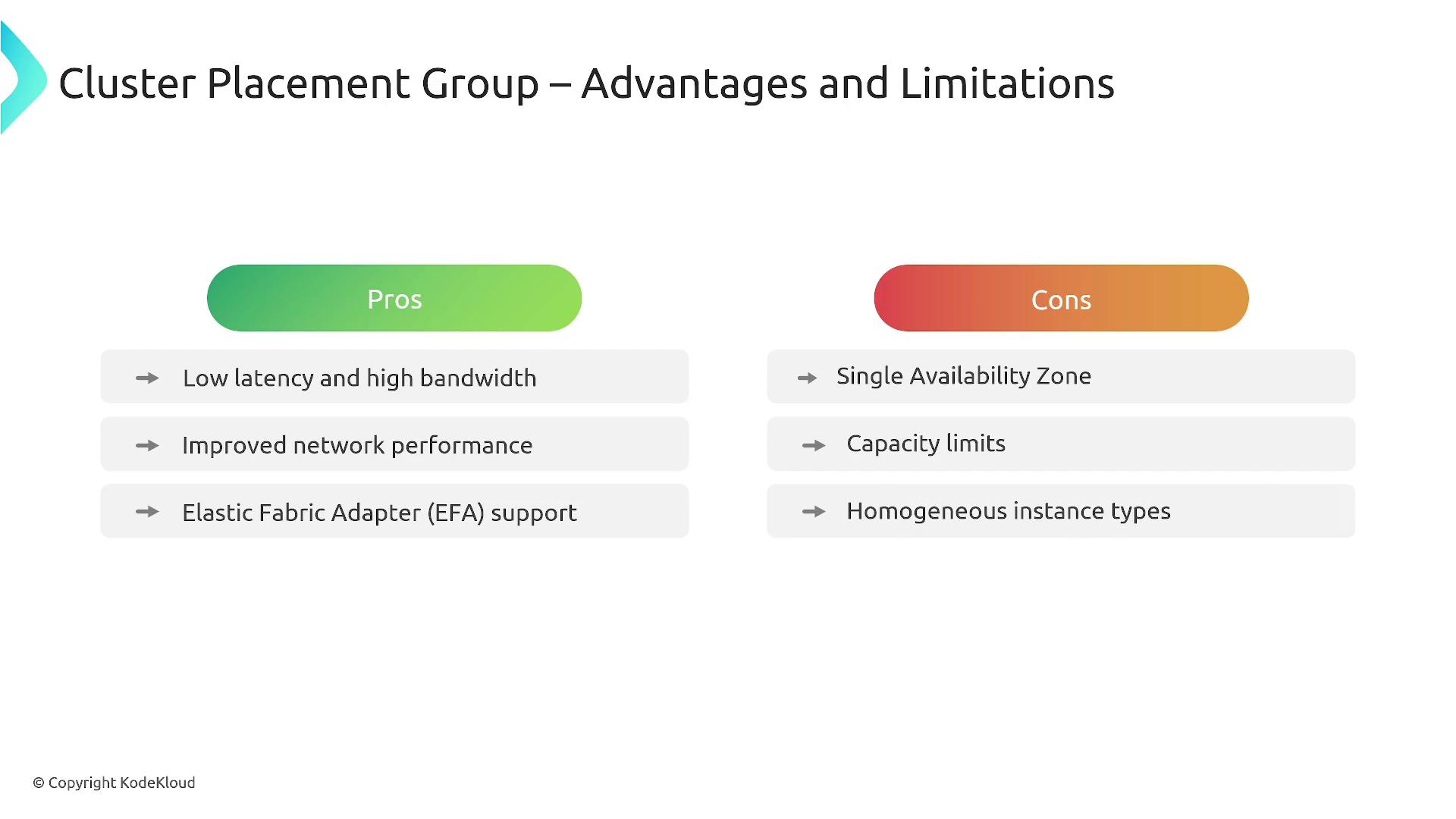
- A limited number of instances per group.
- Restricted to a single availability zone.
- Network throughput is constrained by the slowest instance type.
- Enhanced networking can help overcome some performance limits.
- It is recommended to use uniform instance types along with the necessary capacity reservations.

Partition Placement Group
A partition placement group isolates instances by assigning them to distinct logical partitions, ensuring that instances in different partitions do not share the same underlying hardware. This approach isolates hardware failures, as each partition resides on its own set of racks with separate networking and power sources. It is an excellent choice for large-scale workloads such as distributed databases or high-availability applications.
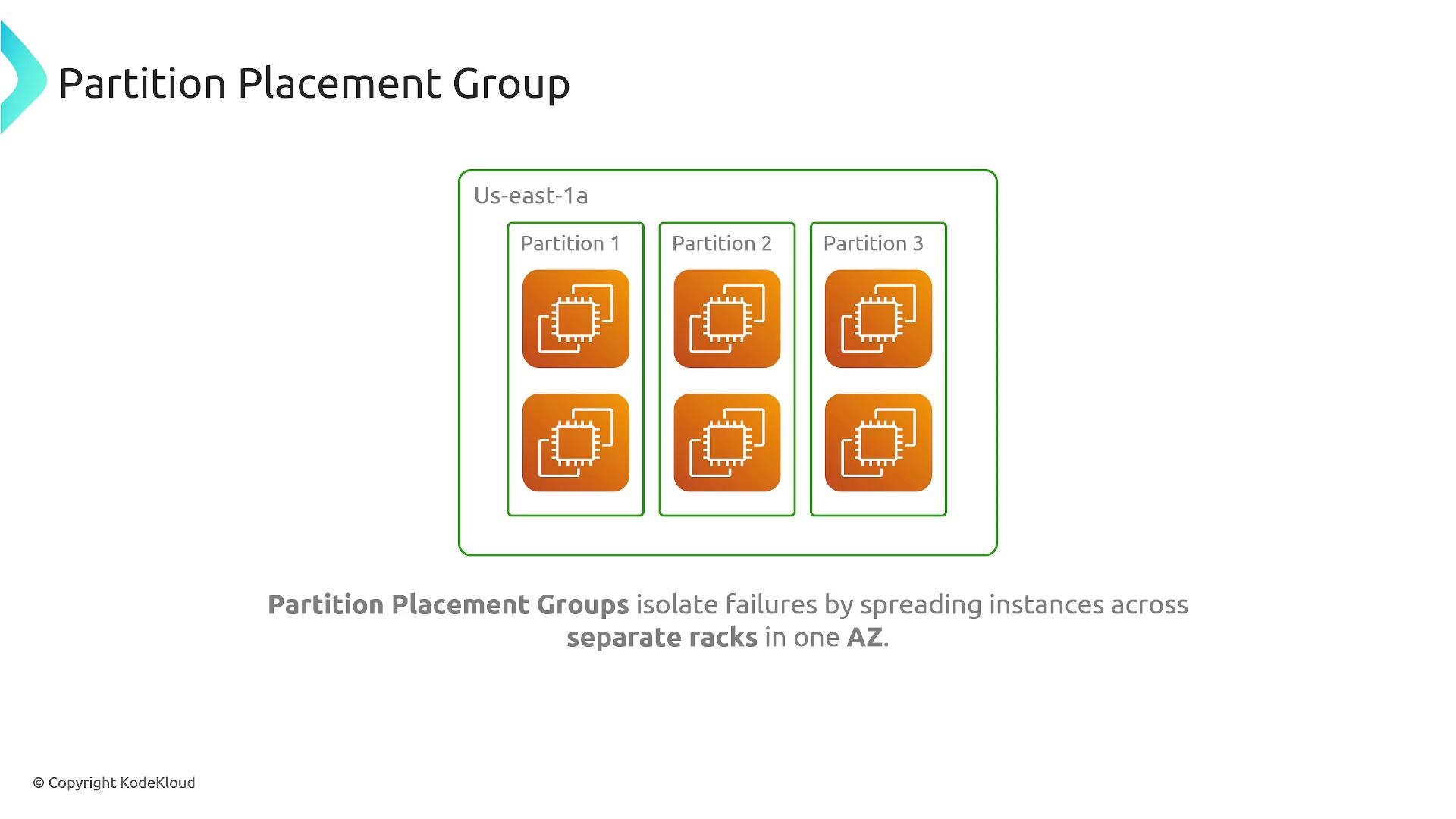
- Up to seven partitions per availability zone per region by default.
- Instance limits vary depending on your account.
- Dedicated instances support only two partitions.
- Capacity reservations used for clusters cannot be applied to partition placement groups.

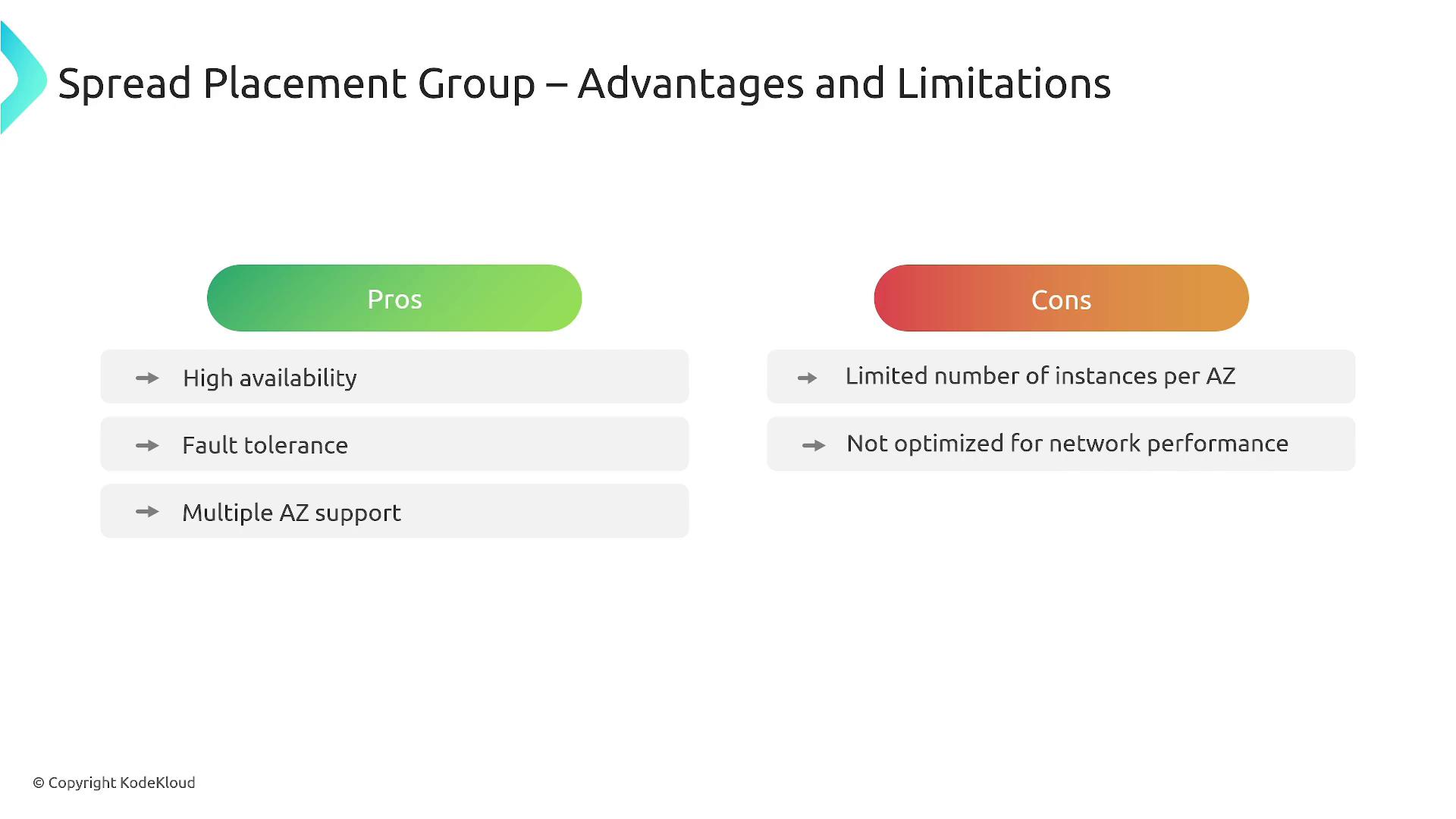
Spread Placement Group
The spread placement group is designed for maximum isolation. Each instance is placed on distinct underlying hardware, reducing the risk that a single hardware failure will affect multiple instances. This configuration is ideal for mission-critical workloads that require high fault tolerance, such as highly available microservices or isolated virtual machines required for compliance.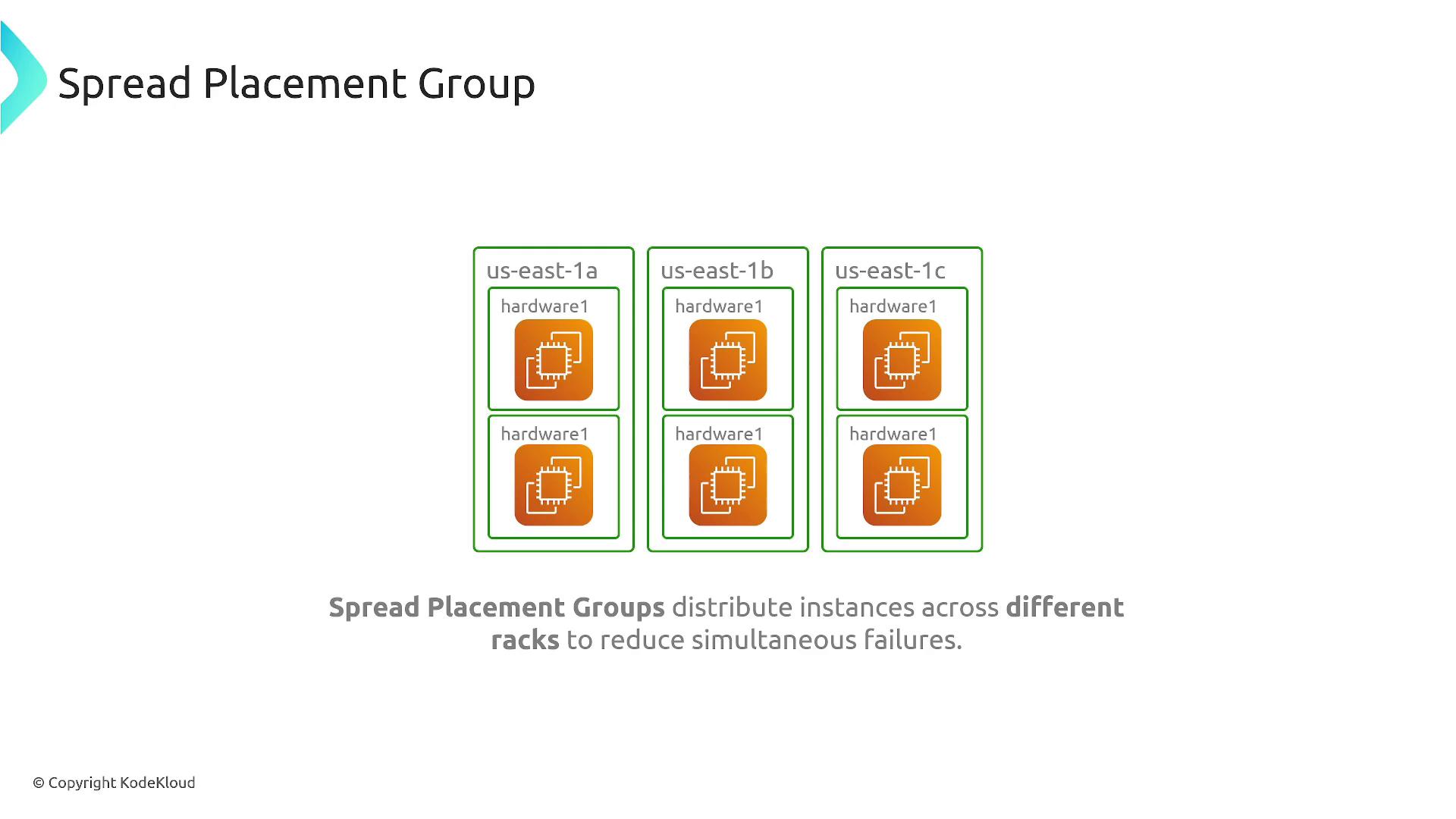
- Support up to seven instances per availability zone.
- To deploy more instances, you must create multiple groups.
- Dedicated instances are not supported.
- Compared to cluster placement groups, the network performance may be lower due to greater separation of hardware.

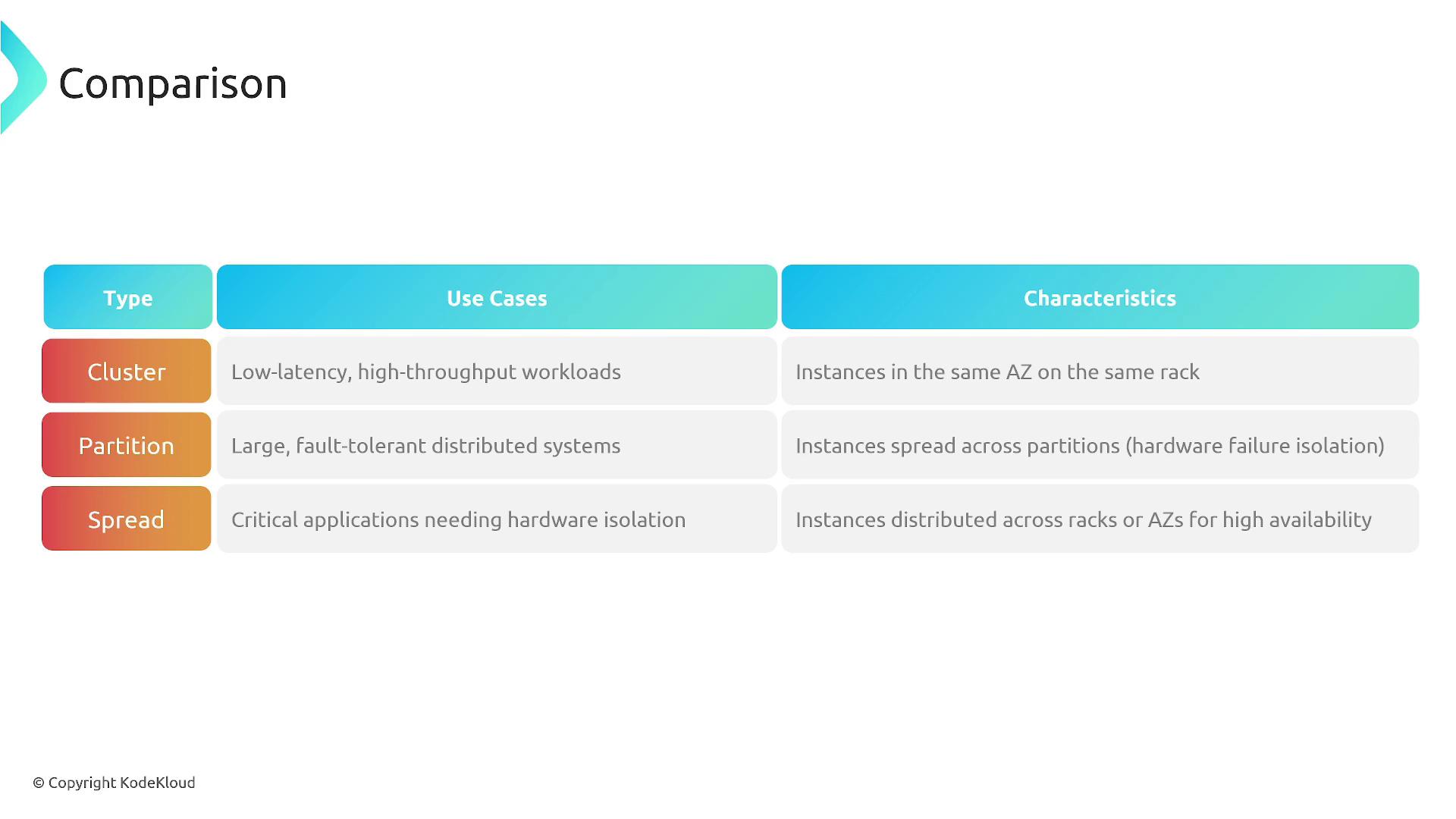
Comparison Overview
Each placement group type is tailored for specific infrastructure requirements:| Placement Group Type | Best For | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster Placement Group | Low latency, high throughput workloads | Enhanced network performance, ideal for HPC and big data scenarios |
| Partition Placement Group | Fault-tolerant setups with hardware isolation | Isolation of hardware failures across partitions, suitable for distributed databases and high-availability apps |
| Spread Placement Group | Critical applications requiring maximum isolation | Maximum fault tolerance through isolated hardware, ideal for compliance and microservices |
- Whether your priority is optimized network performance, enhanced fault tolerance, or strict hardware isolation.
- The instance type uniformity and capacity reservations available.
- Infrastructure requirements such as load, scalability, and cost efficiency.