Enhancing EC2 Performance
Amazon EC2 is the backbone of many cloud infrastructures, powering services like AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS) and AWS EKS. However, the default configuration may not meet your performance requirements. Similar to fine-tuning a car, tweaking EC2 settings can deliver notable improvements without the need for larger machines.Load Balancing and Auto Scaling
Optimizing EC2 performance starts with integrating load balancing and auto scaling. This duo not only enhances performance and responsiveness but also increases cost efficiency and reliability. Auto Scaling groups dynamically manage failover, ensuring your system remains robust even when individual components fail. For instance, the diagram below demonstrates the architecture of Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) paired with Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC):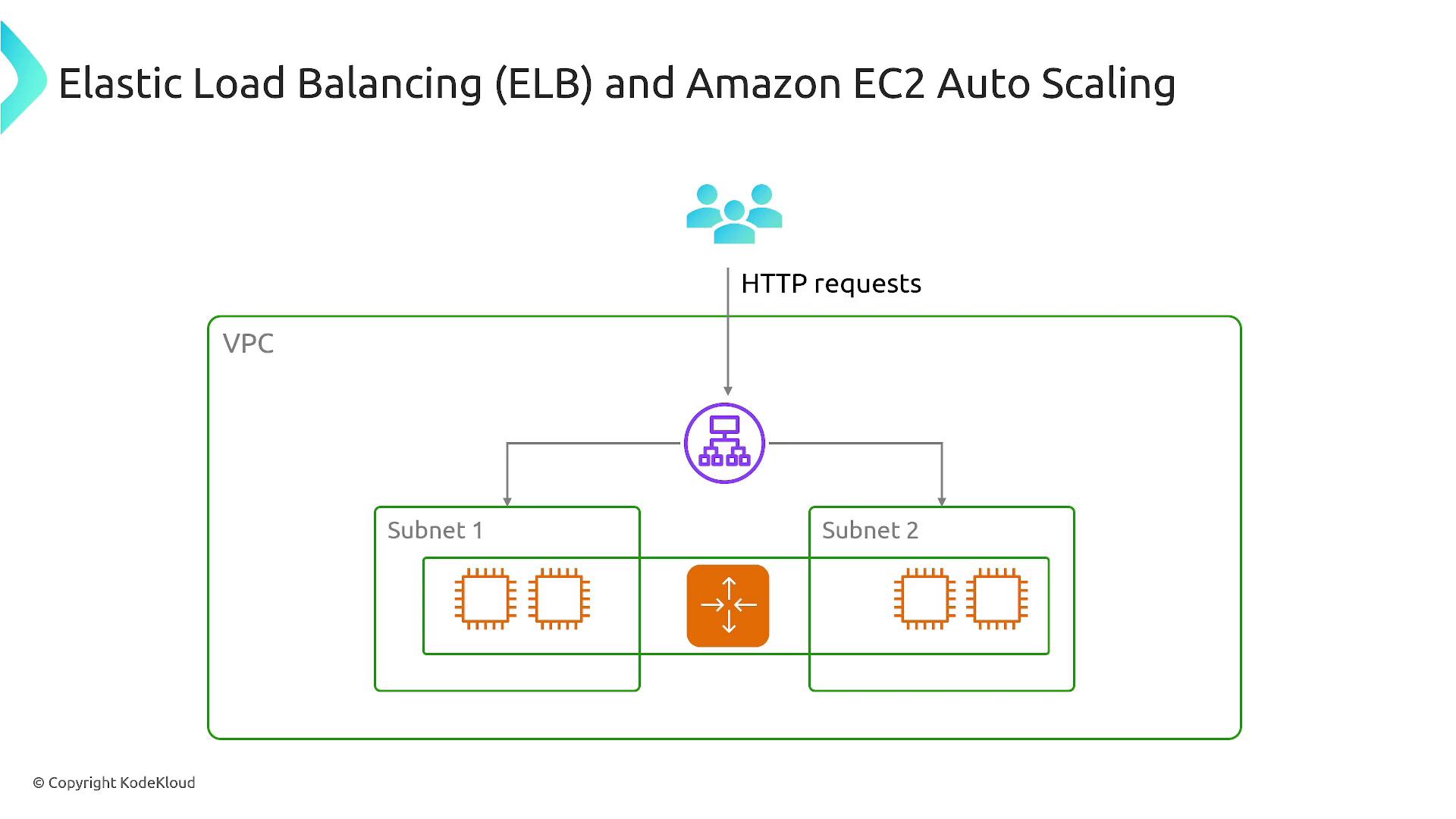
Integrating ELB with Auto Scaling groups creates a robust and elastic AWS environment, essential for handling variable workloads.
Storage Enhancements with EBS
High-performance applications demand optimized storage solutions. Amazon EBS provides multiple volume types tailored to different needs. Besides general-purpose SSDs like GP2 and GP3, you can leverage provisioned IOPS (IO1 and IO2) to guarantee high input/output operations per second. Consider the diagram below, which shows an EC2 instance connected to an EBS volume using Provisioned IOPS for high-demand applications: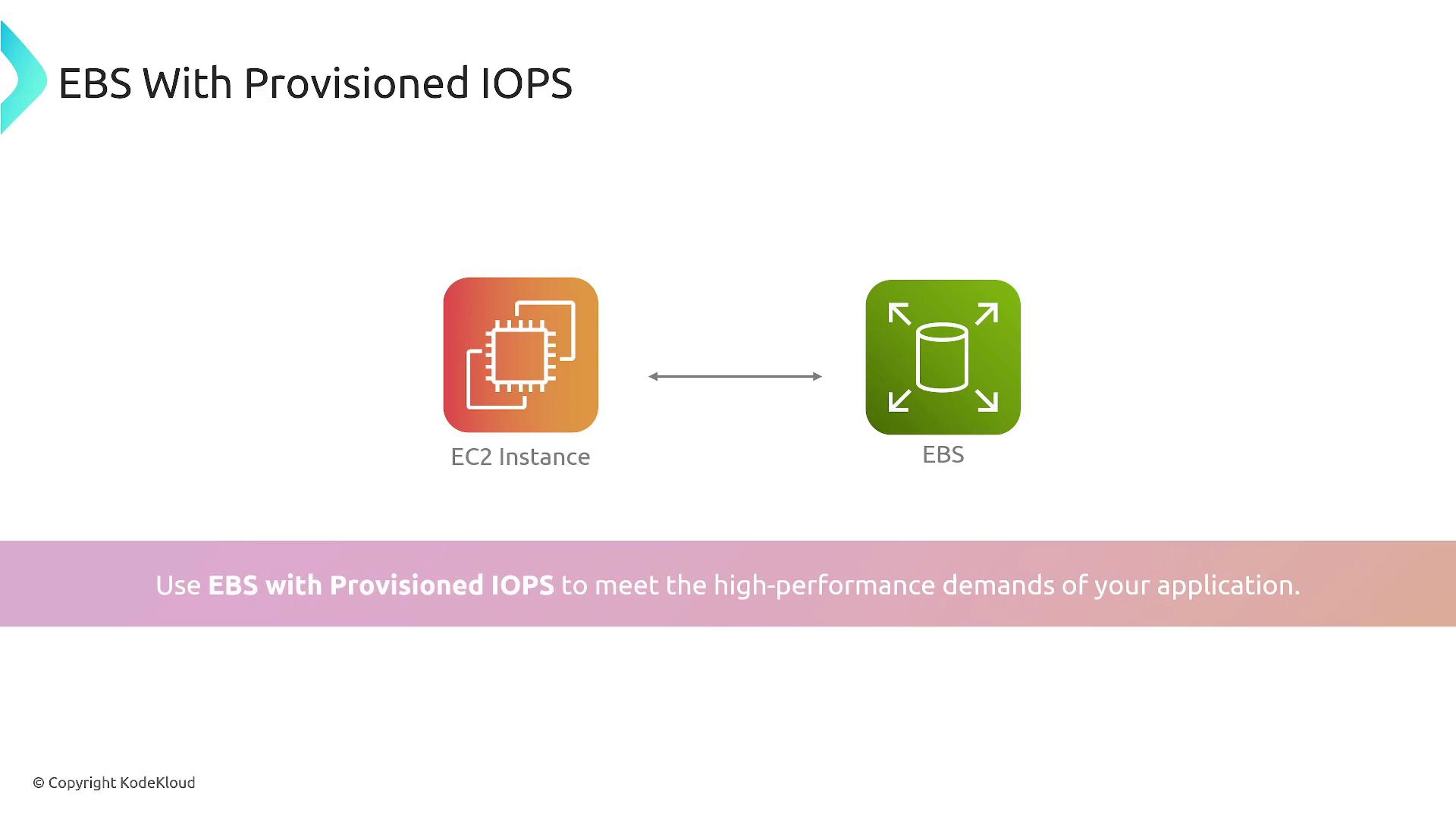
Networking Enhancements
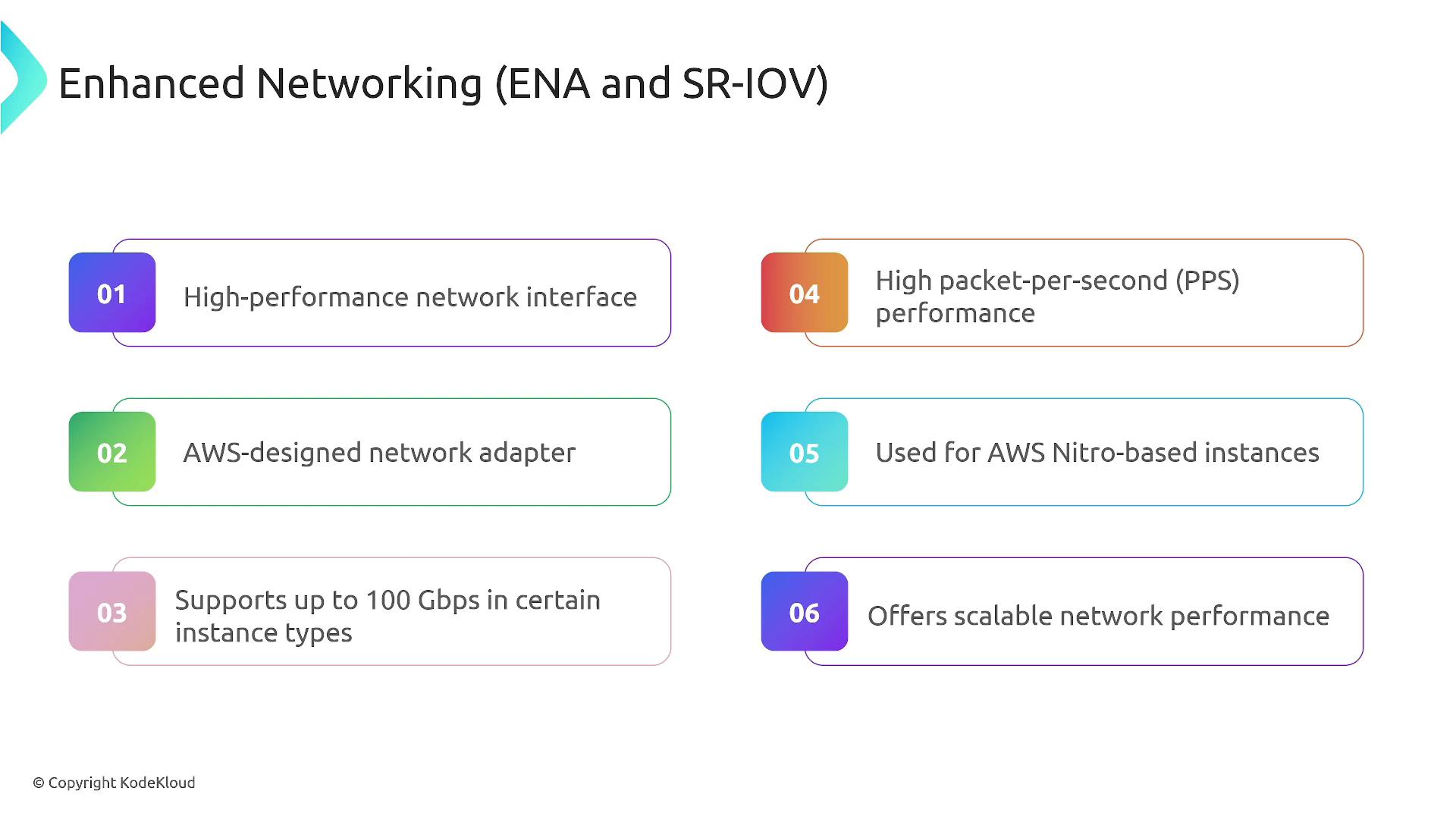
Enhanced networking is crucial for reducing latency and increasing throughput. While the basic Elastic Network Interface (ENI) provides standard connectivity, advanced adapters like the Elastic Network Adapter (ENA) and Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA) offer superior performance:- ENI: The default networking interface.
- ENA: Delivers up to 100 Gbps on select instance types, optimized for scalable network performance.
- EFA: Designed for high-performance computing, capable of speeds up to 400 Gbps, surpassing even ENA performance.
Graviton Processors
AWS Graviton processors present a compelling option for enhancing compute performance and achieving better cost efficiency. Instance families such as T4g utilize these ARM-based processors, offering improved performance relative to AMD or Intel-based instances. When transitioning to Graviton-based instances, ensure that your applications and tooling are ARM-compatible. Real-world benchmarks have shown that Graviton processors achieve a 20% to 40% improvement in price-performance. The diagram below highlights popular EC2 instance types powered by AWS Graviton processors:If your applications support the ARM architecture, leveraging Graviton-based instances can deliver significant performance and cost benefits.
Conclusion
This guide has covered key strategies for enhancing EC2 performance:- Using load balancing and auto scaling for better resource management.
- Optimizing storage performance with EBS and provisioned IOPS.
- Upgrading networking capabilities through advanced ENA and EFA technologies.
- Embracing the cost-effective and high-performance benefits of AWS Graviton processors.