AWS Cloud Practitioner CLF-C02
Technology Part Two
AWS Database Demo
Welcome back, Cloud Practitioners! In this lesson, we'll walk through a comprehensive demo of the Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS). Our focus is on understanding the key use cases rather than the intricate backend details. By observing practical examples—such as launching a PostgreSQL database—you'll gain insights into how RDS simplifies database management.
Overview
We will create three types of databases:
- A standard PostgreSQL database using the free tier.
- An Aurora PostgreSQL database that automatically provisions a cluster.
- An Aurora Serverless PostgreSQL database that scales dynamically.
Launching a Standard PostgreSQL Database
Start at the RDS console (logged in and with the region set to Ohio). Click on Create Database and select the Easy Create option. Remember, RDS offers two sub-options: standard Aurora and Aurora Serverless. In this section, we are working with the primary RDS option for PostgreSQL.

When creating your first database:
- Select PostgreSQL.
- Choose the free tier to minimize configuration.
- Close the side panel and click Auto-Generate a Password.
- Leave default settings intact (e.g., encryption enabled and the default VPC is used).
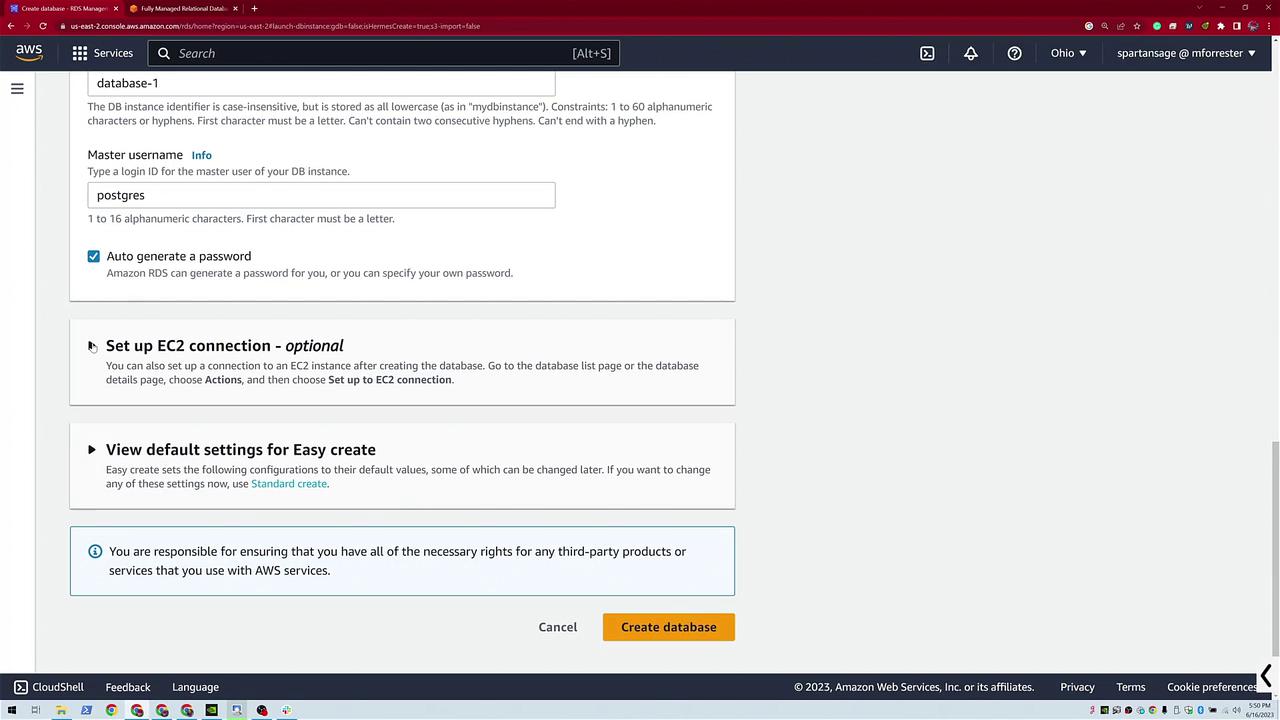
After reviewing your settings:
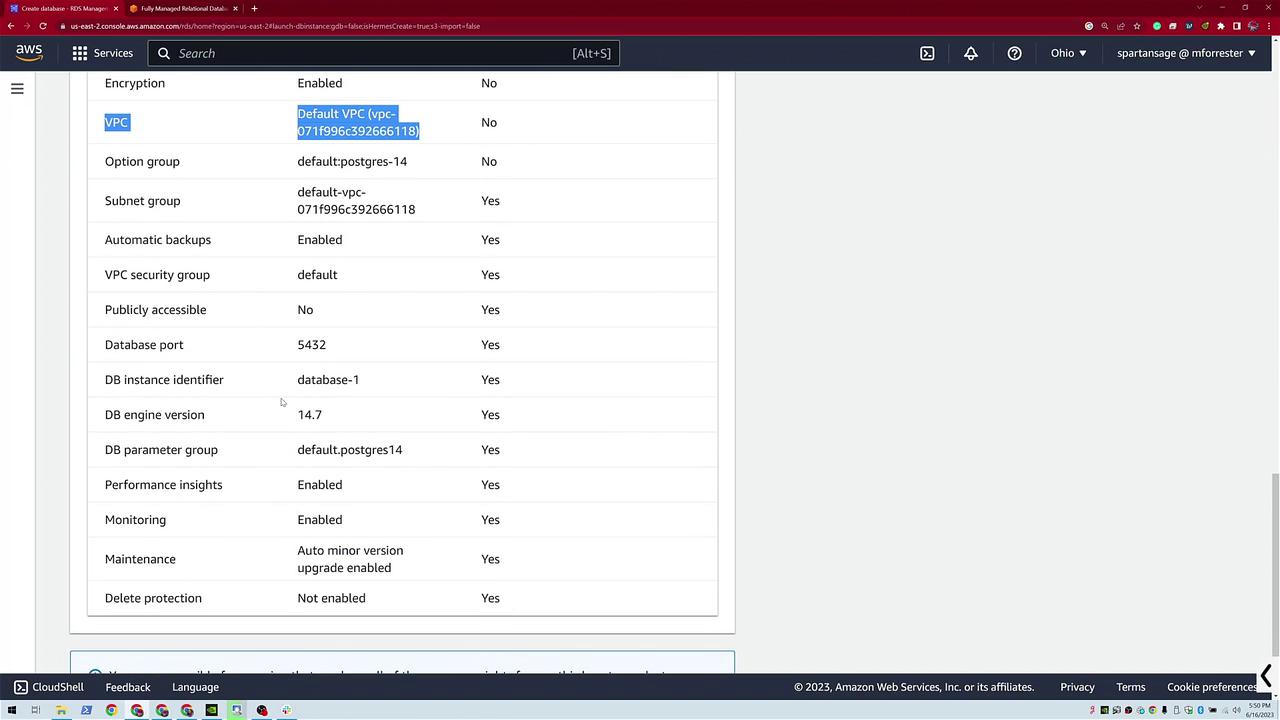
Click Create Database. The system begins provisioning your PostgreSQL database, and you'll see a progress notification at the bottom of the screen. This instance is created as a T3 micro PostgreSQL database. Even though options like restoring a database from S3 exist, in this demo, we are focusing on a basic configuration.
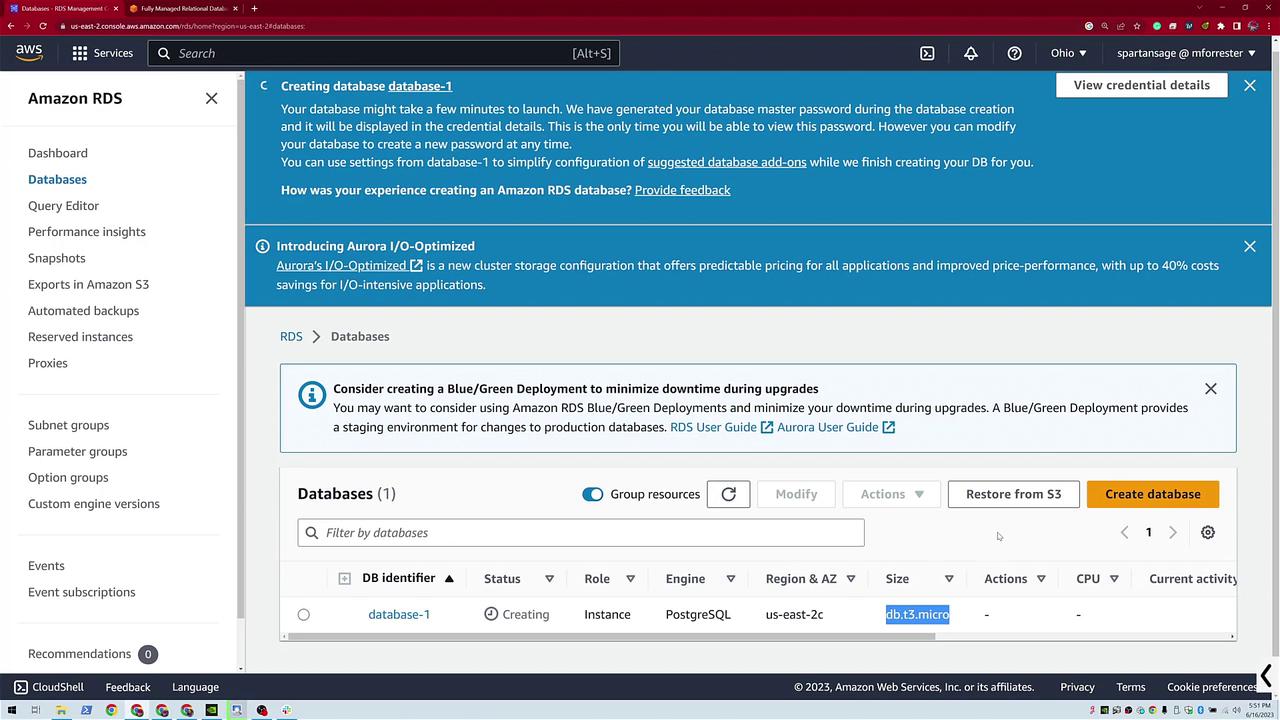
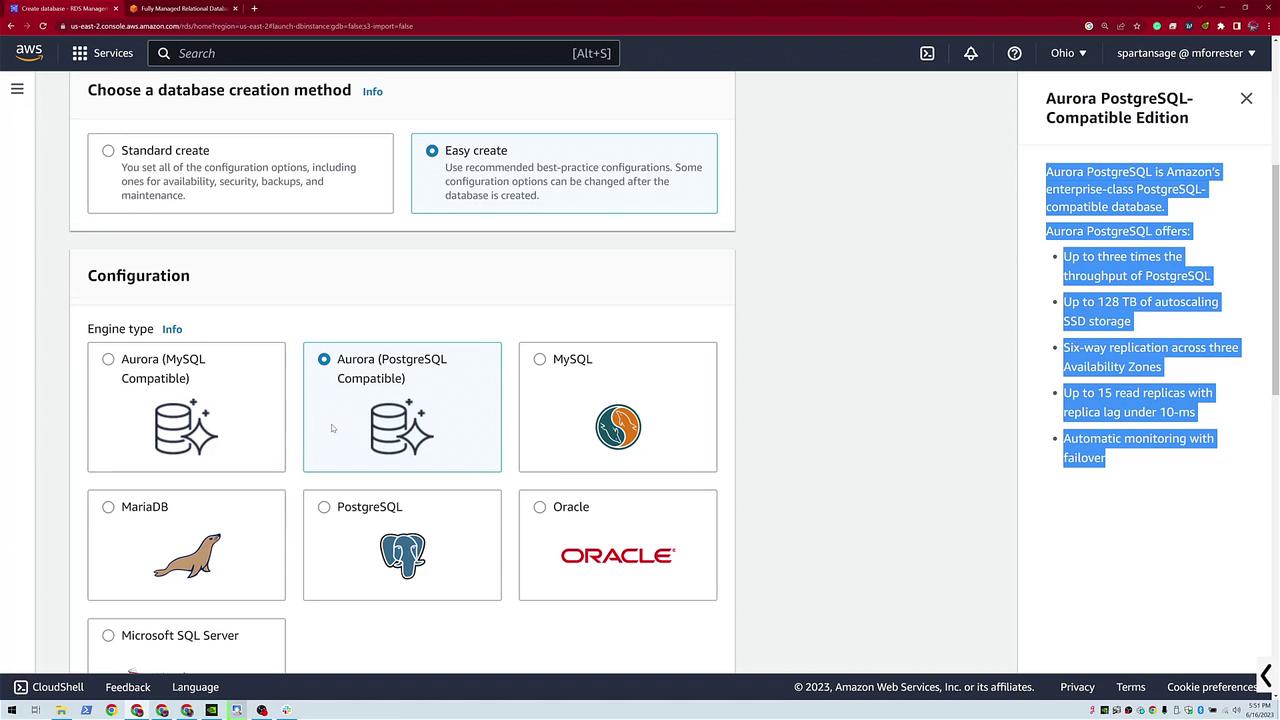
Creating an Aurora PostgreSQL Database
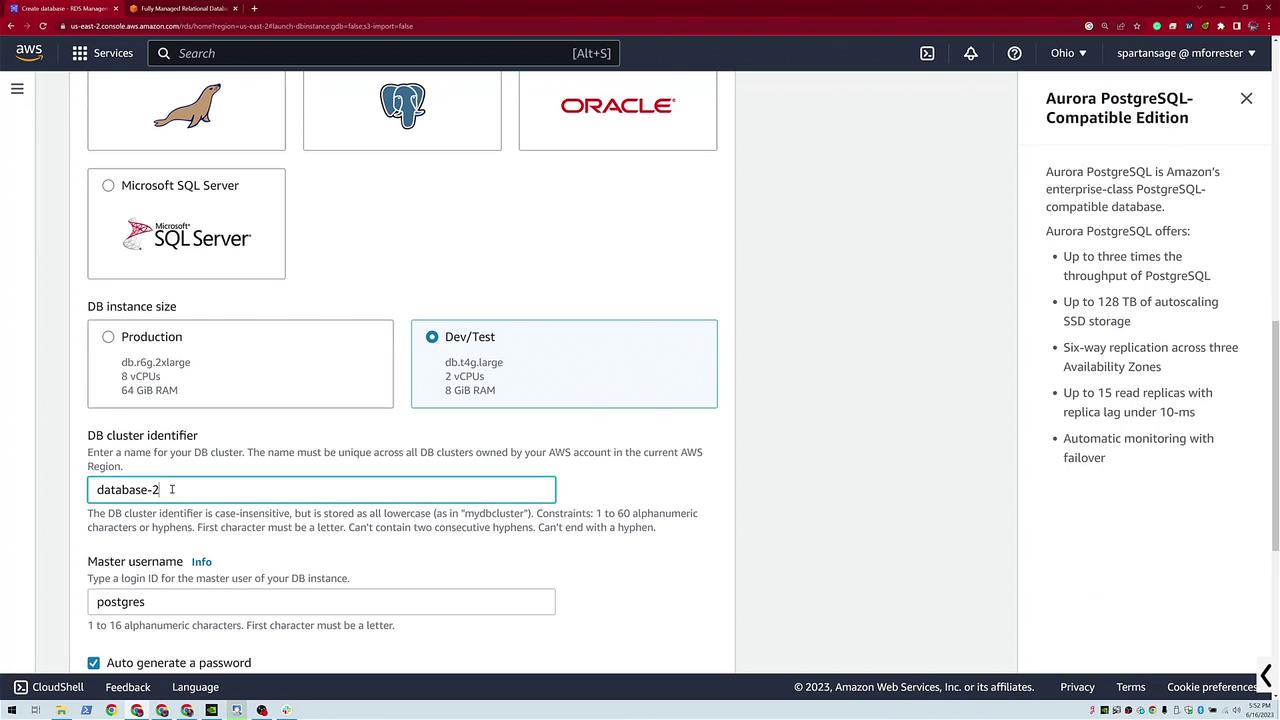
To create the Aurora PostgreSQL database, click Create Database again and choose Easy Create. This time, select Aurora PostgreSQL. Notice the interface differences in the upper right between standard PostgreSQL and Aurora. For this example, use the DevTest mode with default configurations to create "database two."
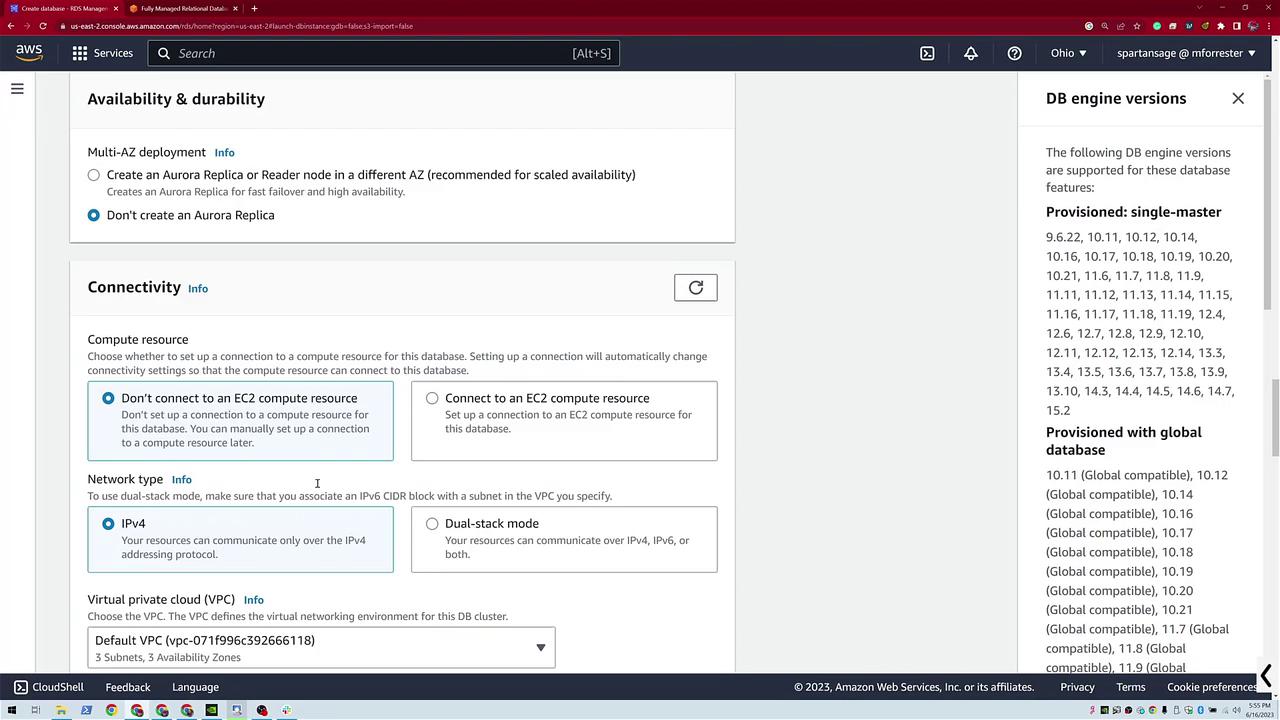
On the Aurora configuration page, you'll configure:
- Instance size.
- DB cluster identifier.
- Master username.
After clicking Create Database, an Aurora cluster is provisioned. Unlike the standard PostgreSQL instance, Aurora instantly creates a database cluster. Initially, the cluster comprises one instance, but you have the flexibility to add more instances later. The dashboard will show the Aurora PostgreSQL instance along with a reader instance.
Deploying an Aurora Serverless PostgreSQL Database
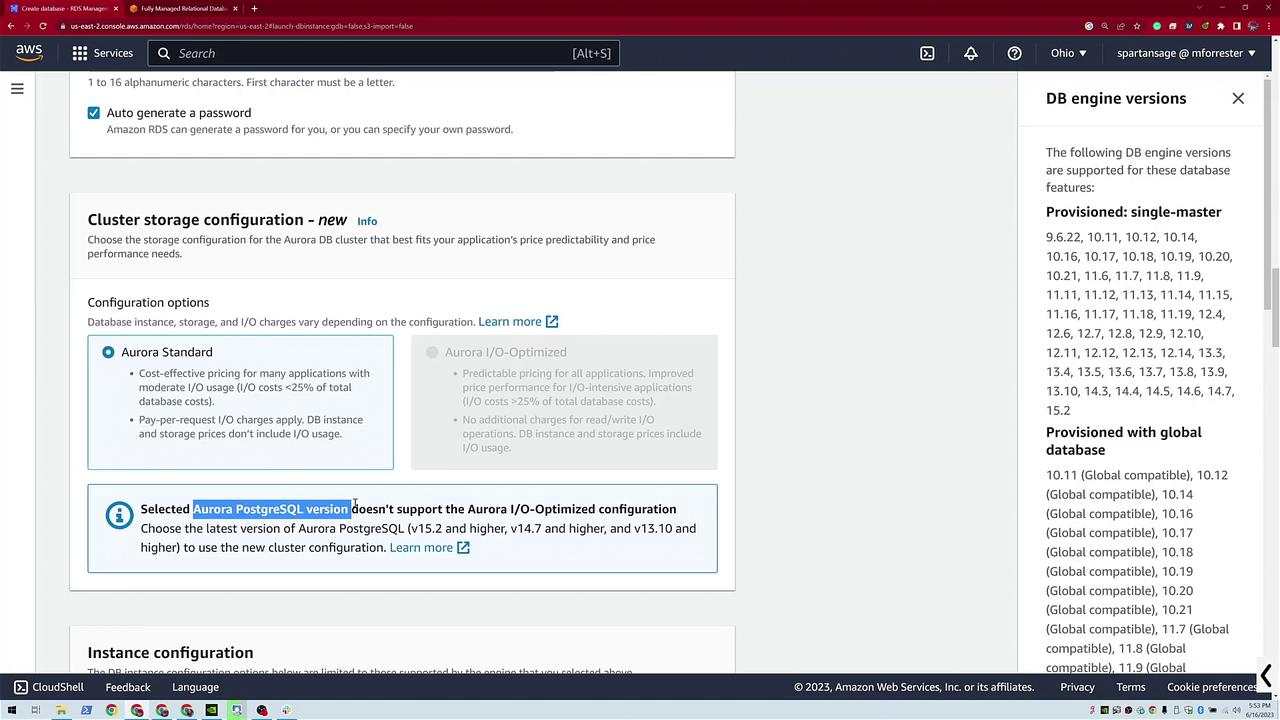
For the third database, click Create Database and choose Standard Create. Select Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition, then pick a version that supports Serverless v2. Enter a database name (for example, "dev-test") and dismiss any pop-up triggers that appear.
During the serverless instance configuration:
- You have the option to auto-generate a password.
- Select between Aurora Standard and Aurora Optimized.
- Configure the compute capacity by choosing a range. Typically, this demo uses a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 4 Aurora Capacity Units (ACUs), with 1 ACU providing 2 GB of memory.
- This configuration ensures that your serverless database scales automatically based on demand.
Additional instance settings include backup configurations, linking Aurora as a replica, and various networking options. In this demo, the default settings are sufficient. After confirming your settings by clicking Create Database, the serverless database is provisioned.
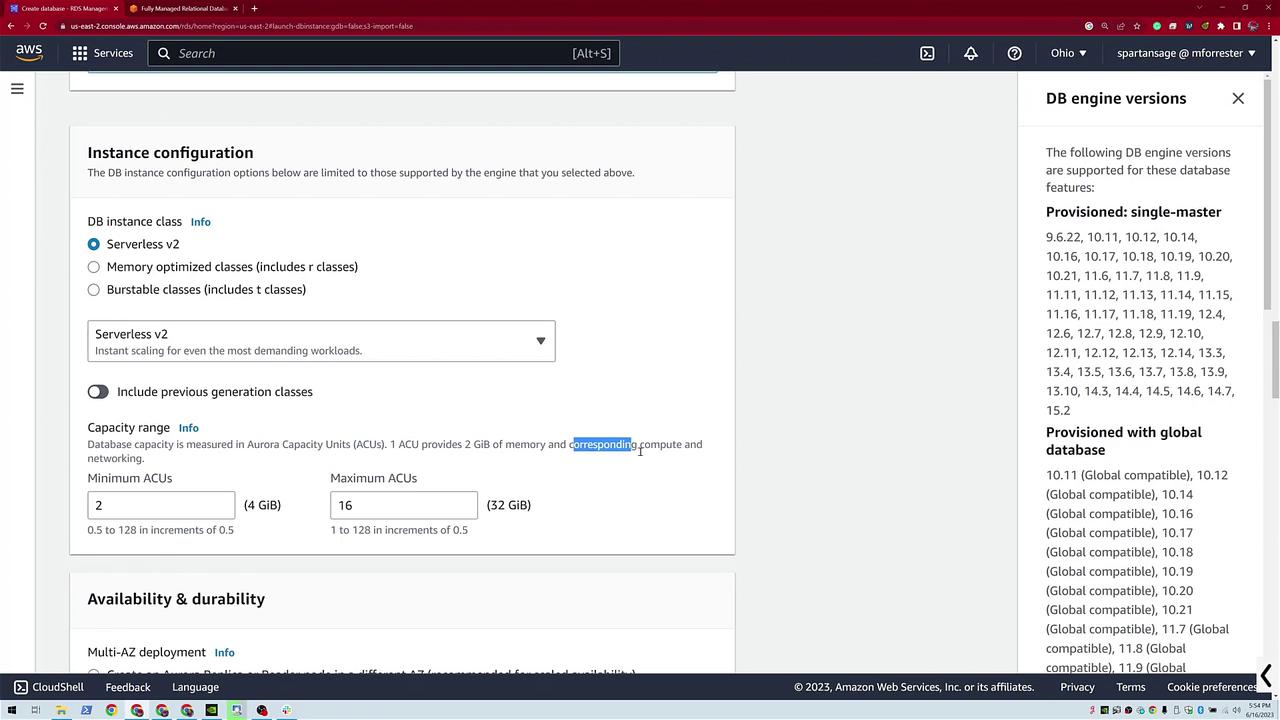
An extra screenshot further details the serverless v2 settings, such as capacity ranges and supported DB engine versions.
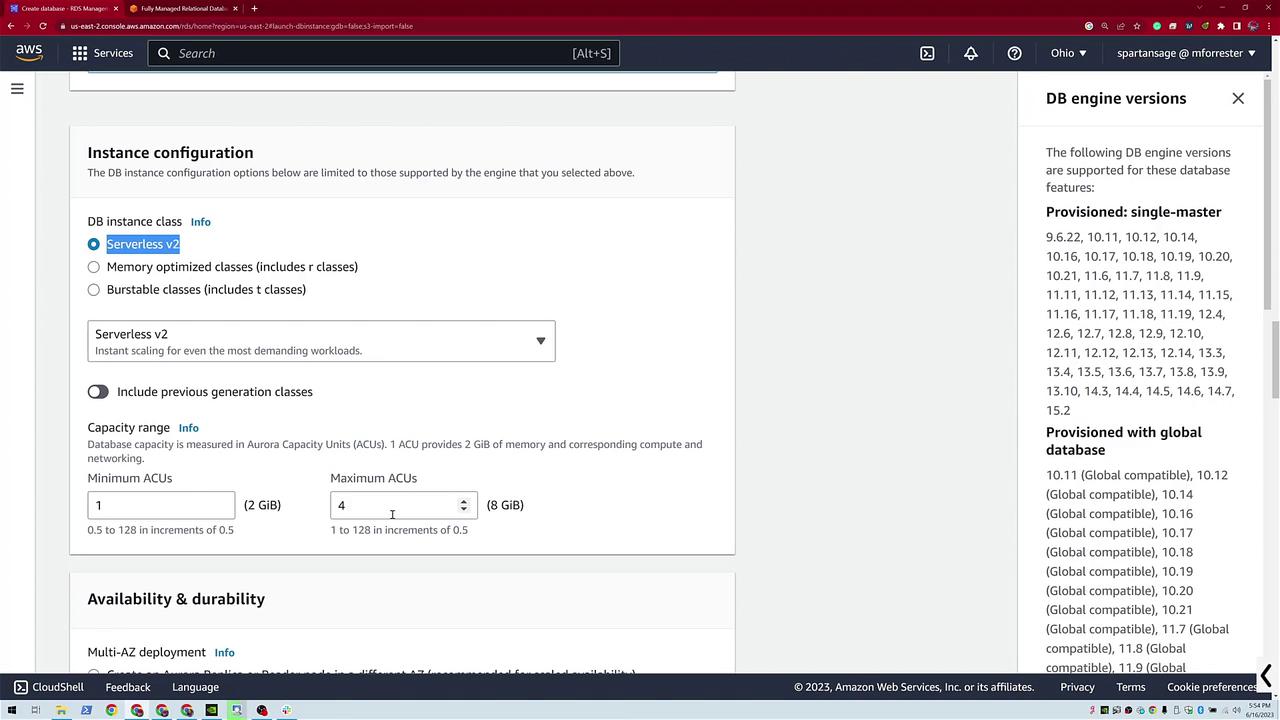
Another diagram illustrates additional networking and availability configurations, including connections to compute resources.
Viewing Your Databases
Once all three databases are created, your dashboard displays:
- A standard PostgreSQL database.
- An Aurora PostgreSQL database (with both instance and cluster details).
- A serverless Aurora PostgreSQL database (showing scaling details from 1 to 4 ACUs).
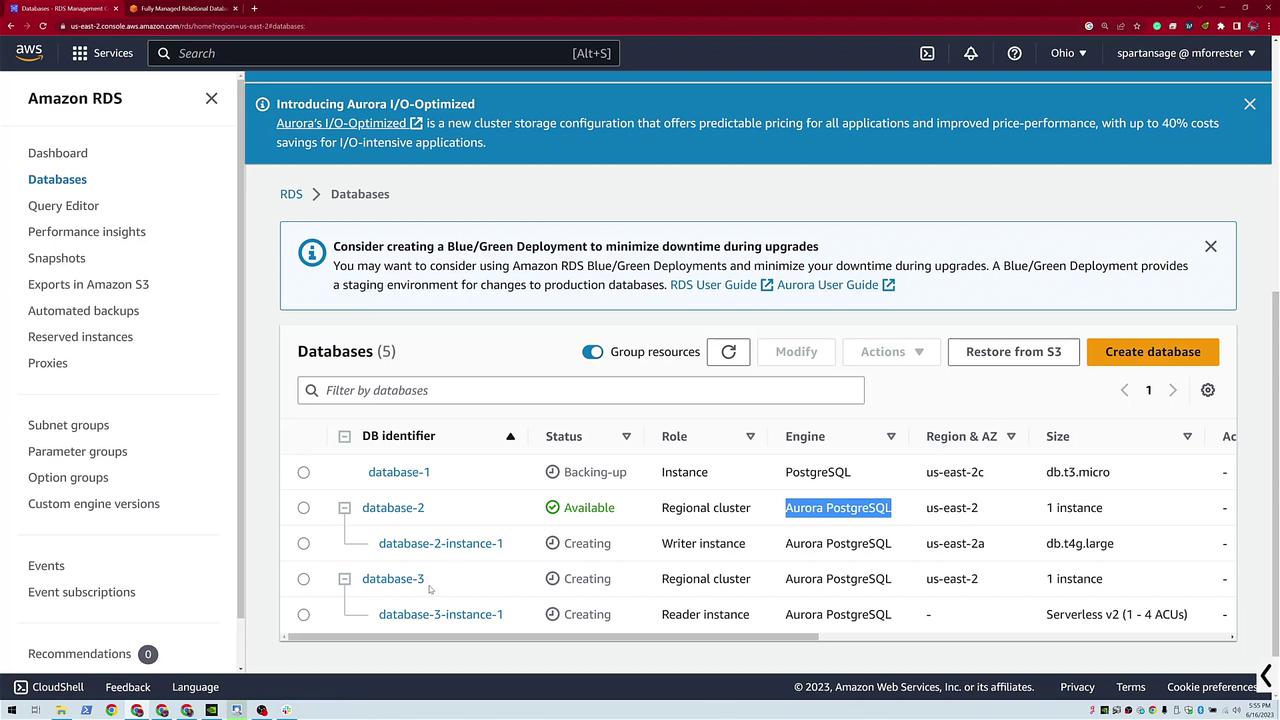
By clicking on the database credentials link, you can connect remotely to any of these databases just as if they were running locally. One of the PostgreSQL instances might display an ongoing backup process on the RDS summary view.

Quick Reference
In this demo, you learned how to launch three unique configurations on AWS RDS:
- A standard PostgreSQL database.
- An Aurora PostgreSQL database (with automatic cluster creation).
- An Aurora Serverless PostgreSQL database with auto-scaling capabilities.
If you have any questions, please feel free to reach out in the forums. We look forward to seeing you in the next lesson!
Further Reading
Watch Video
Watch video content