1. CloudFormation Template
Ensure that an IAM role named
HelloWorldFunctionRole exists with permissions for Lambda execution and CloudWatch logging. You can define it in this template or create it beforehand.Function Summary
| Function Name | Description | Timeout |
|---|---|---|
| HelloWorldFunction01 | Prints a greeting message | 15 sec |
| HelloWorldFunction02 | Prints a greeting message | 15 sec |
| HelloWorldFunction03 | Prints a greeting after a 5-sec delay | 15 sec |
2. Invocation Script
Generate consistent metrics by invoking each function 50 times. Save the following aslambda_call.sh and make it executable.
3. Deploying the Stack
- Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to CloudFormation.
- Choose Create stack > With new resources (standard).
- Upload the YAML template and click Next.
- Enter a stack name (e.g.,
lambda-insights-demo), acknowledge IAM capabilities, then click Next and Create stack.
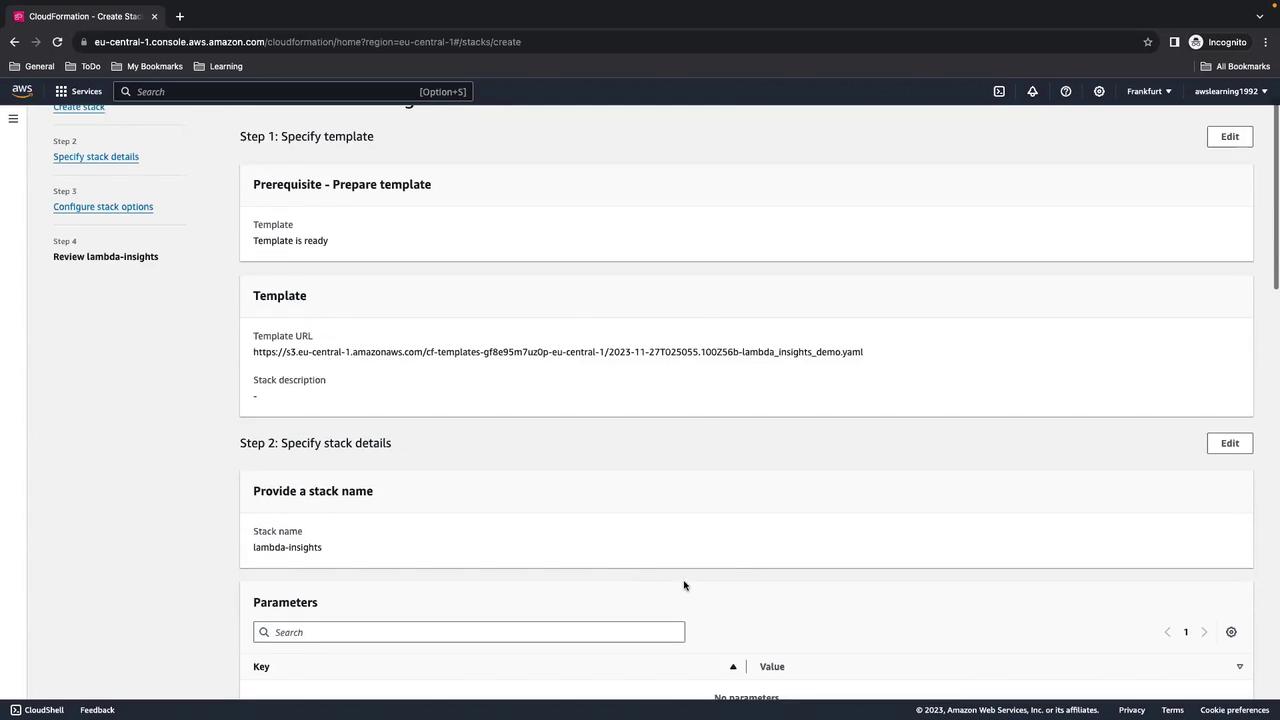
CREATE_COMPLETE.
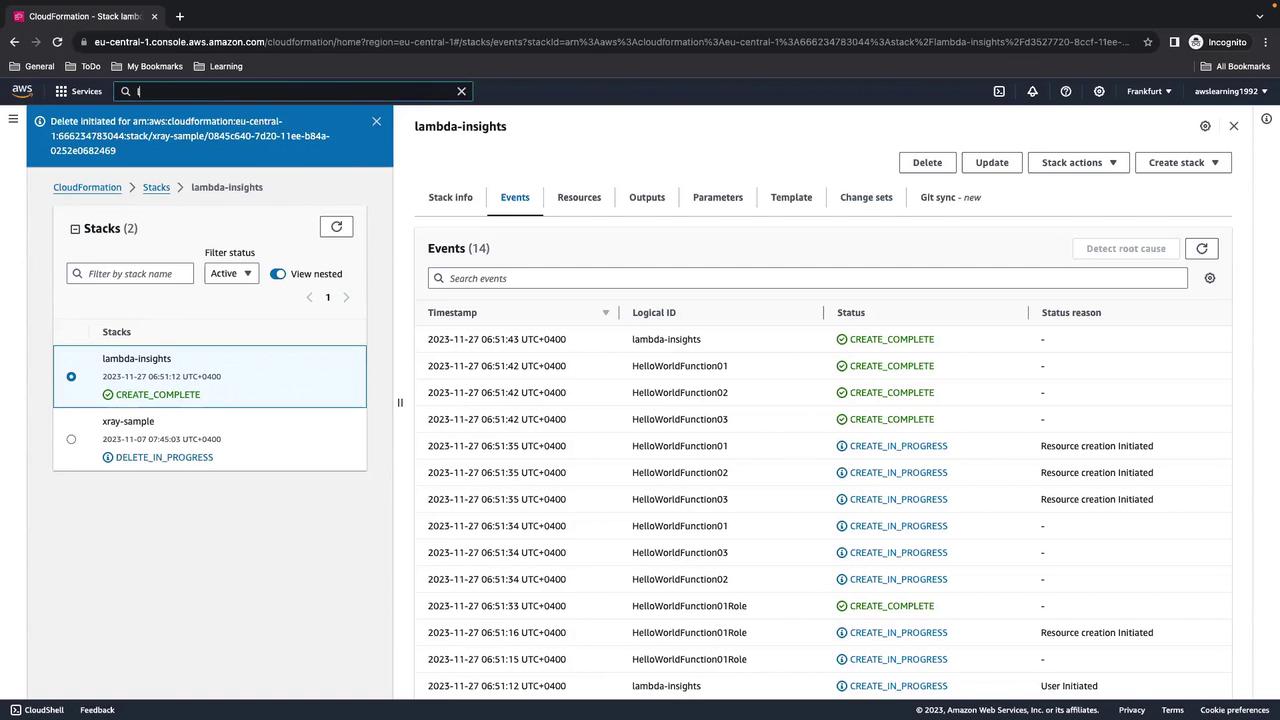
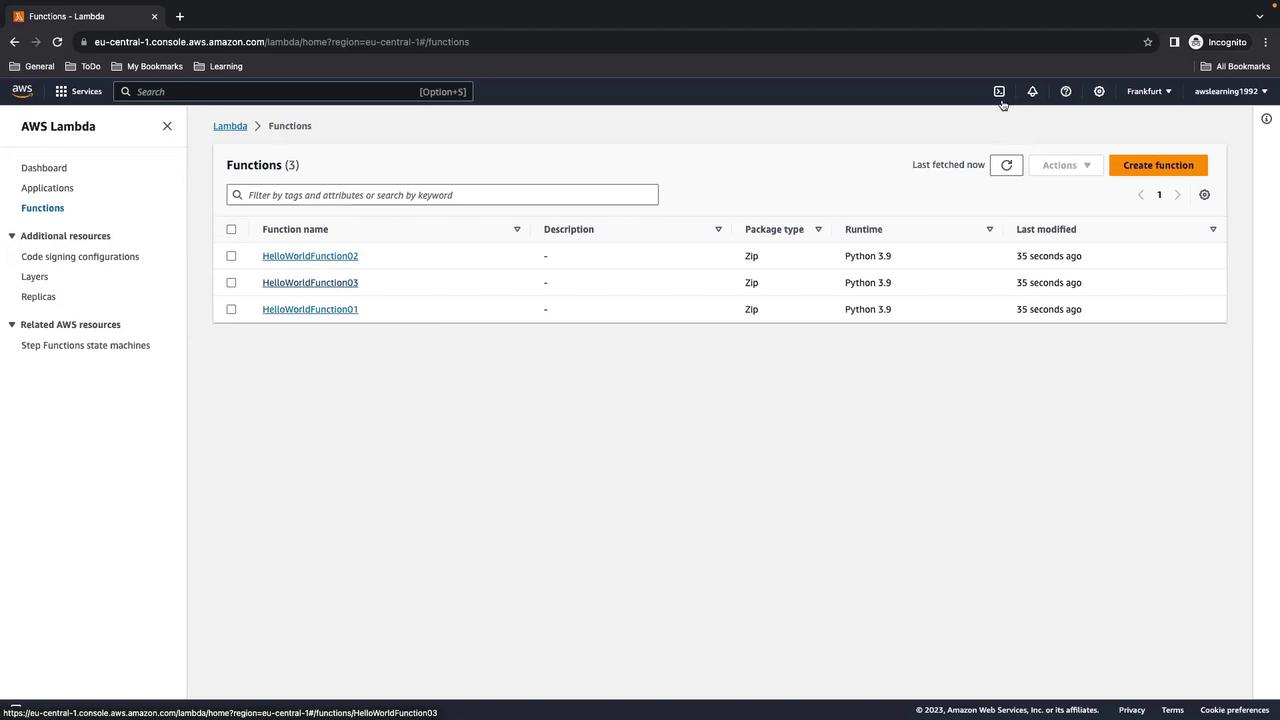
4. Verify Lambda Functions
In the Lambda console, confirm that all three functions (HelloWorldFunction01, HelloWorldFunction02, HelloWorldFunction03) are present and using Python 3.9.
5. Generate Load Using AWS CloudShell
- Open AWS CloudShell from the console toolbar.
-
Upload or paste the
lambda_call.shscript into your home directory. -
Execute:
6. Enabling Lambda Insights
By default, Lambda Insights is off. To enable it:- In the Lambda console, select each function and go to Configuration > Monitoring and operations.
- Click Edit, enable Enhanced monitoring (Lambda Insights), and save.
Enabling Lambda Insights produces extra logs and metrics, which may incur additional charges.
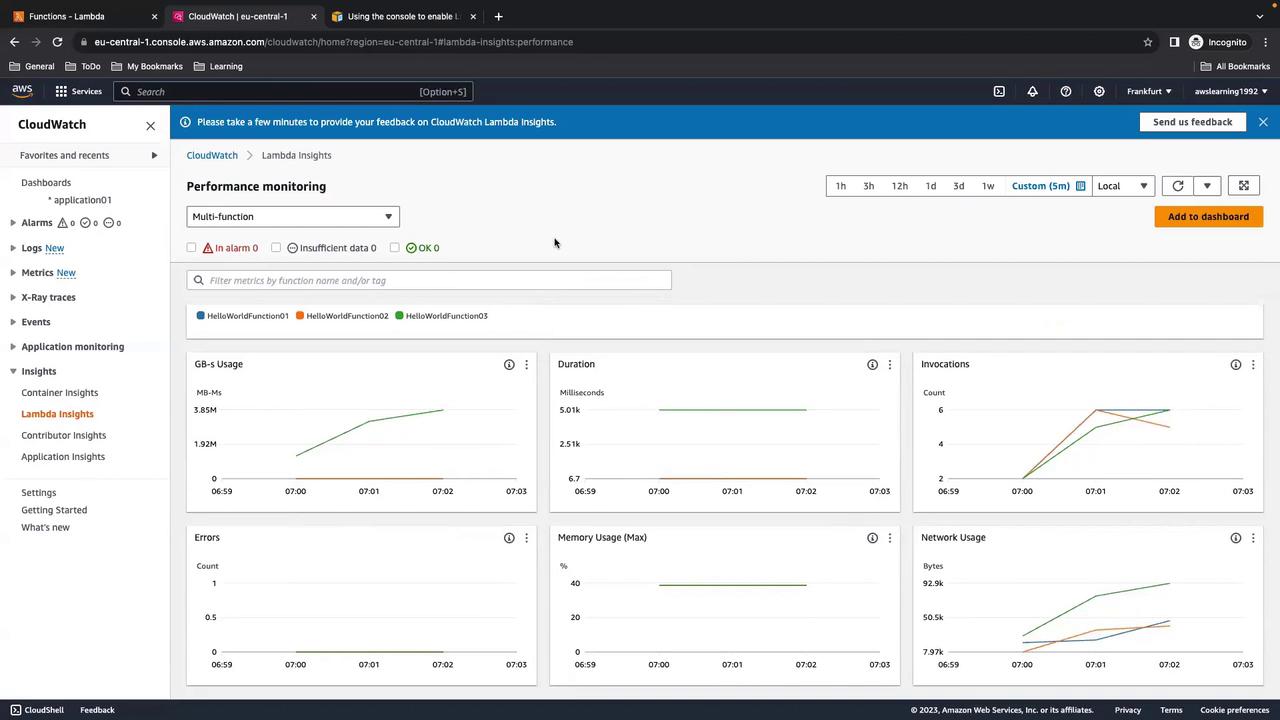
7. Exploring Metrics in CloudWatch
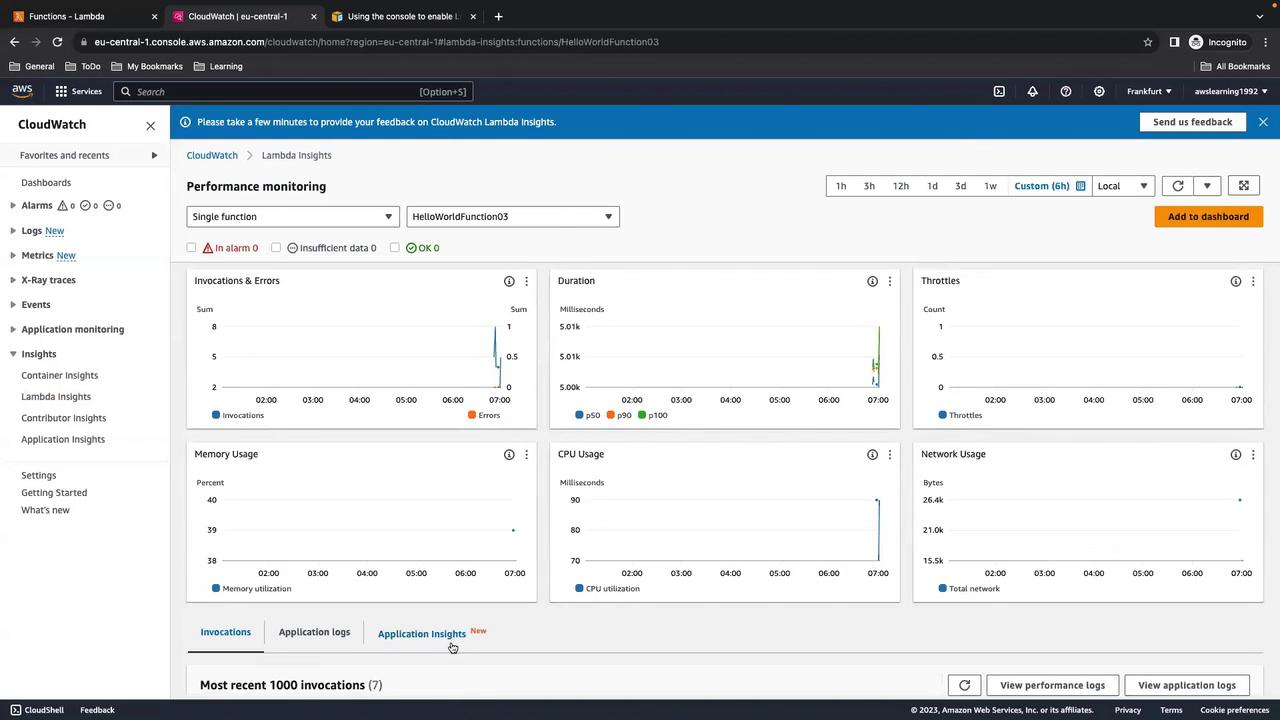
Navigate to CloudWatch > Insights > Lambda Insights to view consolidated metrics across all functions.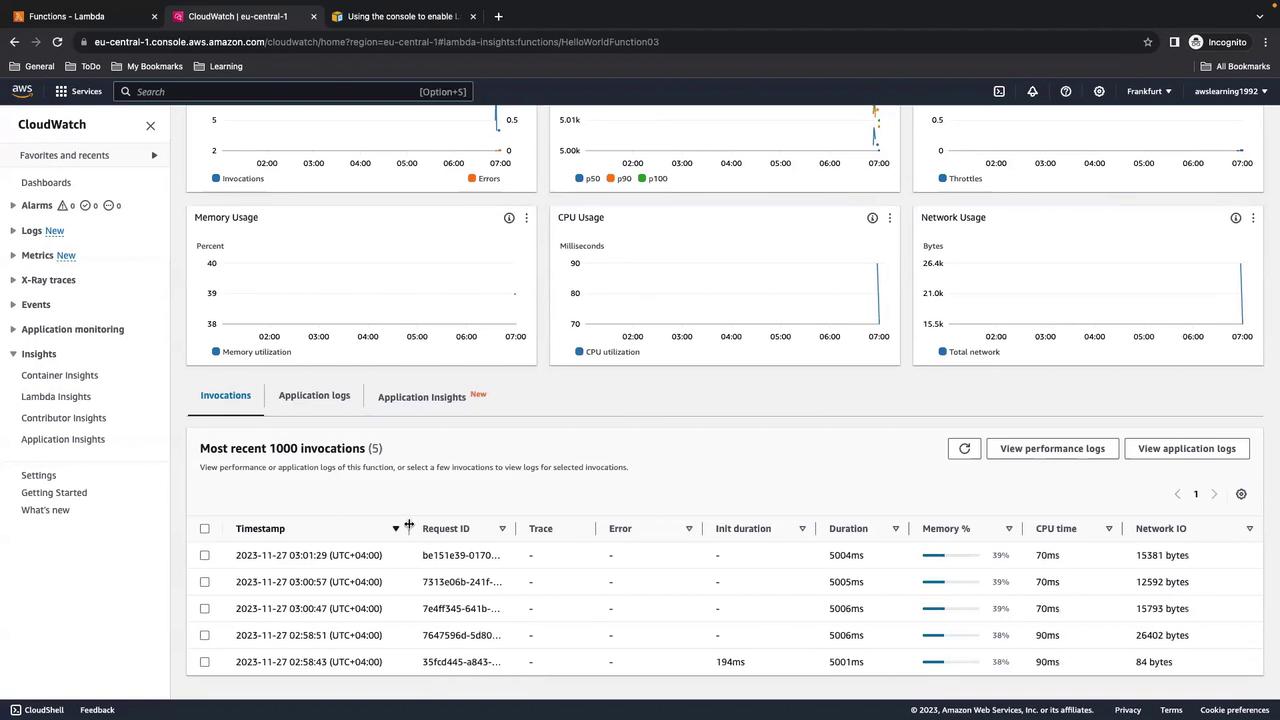
HelloWorldFunction03), select it from the list:
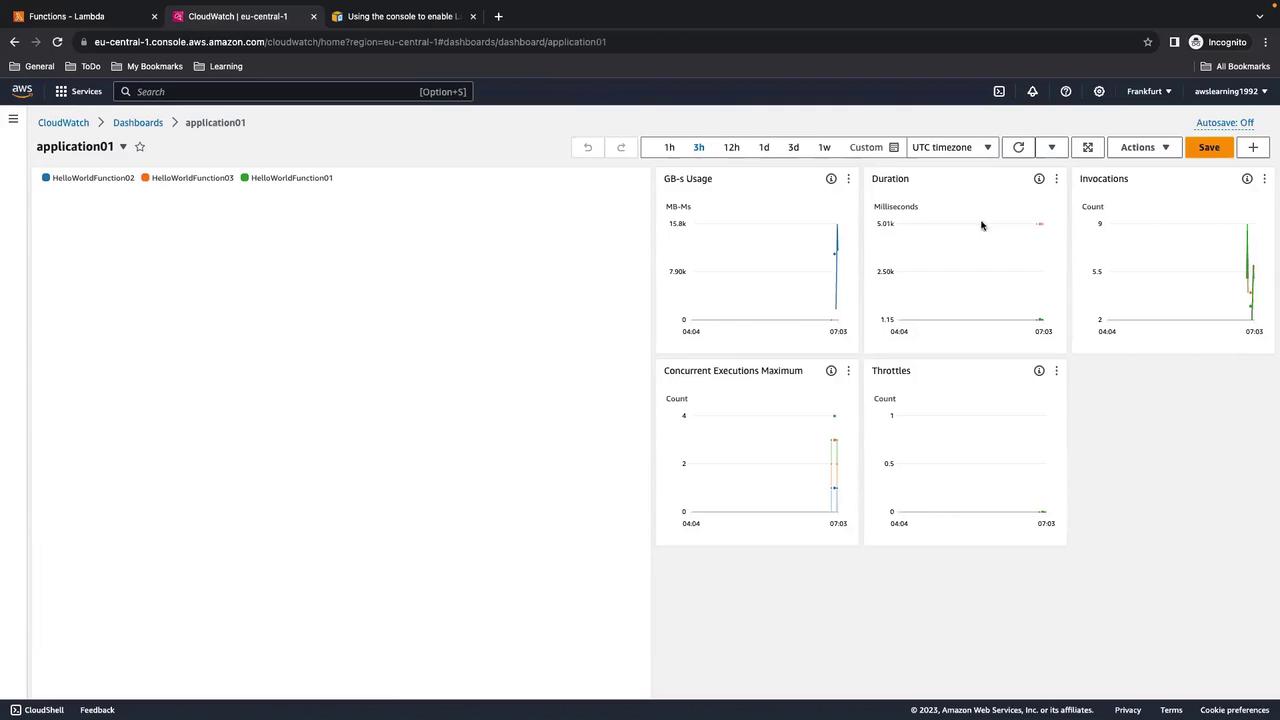
8. Creating a Custom Dashboard
If you manage many functions, a dedicated CloudWatch dashboard helps.- In CloudWatch, go to Dashboards and click Create dashboard.
- Add Lambda Insights widgets and select your functions.
- Customize widgets for GB-s usage, duration, invocations, concurrent executions, and throttles.
Remember to disable Lambda Insights when not troubleshooting to avoid unnecessary costs.
9. Cleanup
- In CloudShell, choose Actions > Restart CloudShell to stop any running processes.
- In CloudFormation, select
lambda-insights-demoand click Delete. - Confirm that the Lambda functions, logs, and IAM roles have been removed.