Pipeline Stages Overview
A robust CI/CD pipeline typically follows four core stages:- Source – Pull code or artifacts from repositories
- Build – Compile, package, and run unit tests
- Test – Execute integration or specialized tests
- Deploy – Release assets to production environments
1. Source Stage Integrations
CodePipeline supports multiple source providers, enabling you to trigger pipelines automatically when changes occur.| Source Type | Integration Method | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon S3 | S3 Event Notifications | Versioned artifacts, static website |
| AWS CodeCommit | Native Git Repository | Private source control on AWS |
| Amazon ECR | Image Push Events | Container images for ECS/EKS |
| GitHub, Bitbucket | CodeStar Connections | Public/third-party Git repositories |
Amazon S3
Amazon S3 offers durable object storage with versioning and event-based triggers. Configure an S3 bucket event to start your pipeline whenever a new object arrives.AWS CodeCommit
Fully managed, scalable Git repositories with branch and commit history. CodePipeline hooks directly into CodeCommit branches for seamless source control.Amazon ECR
Store and manage Docker container images. Usedocker push to upload images—perfect when you deploy to Amazon ECS or EKS.
Third-Party Repositories
Link GitHub or Bitbucket via AWS CodeStar Connections. Grant repository access and select the branch to trigger your pipeline.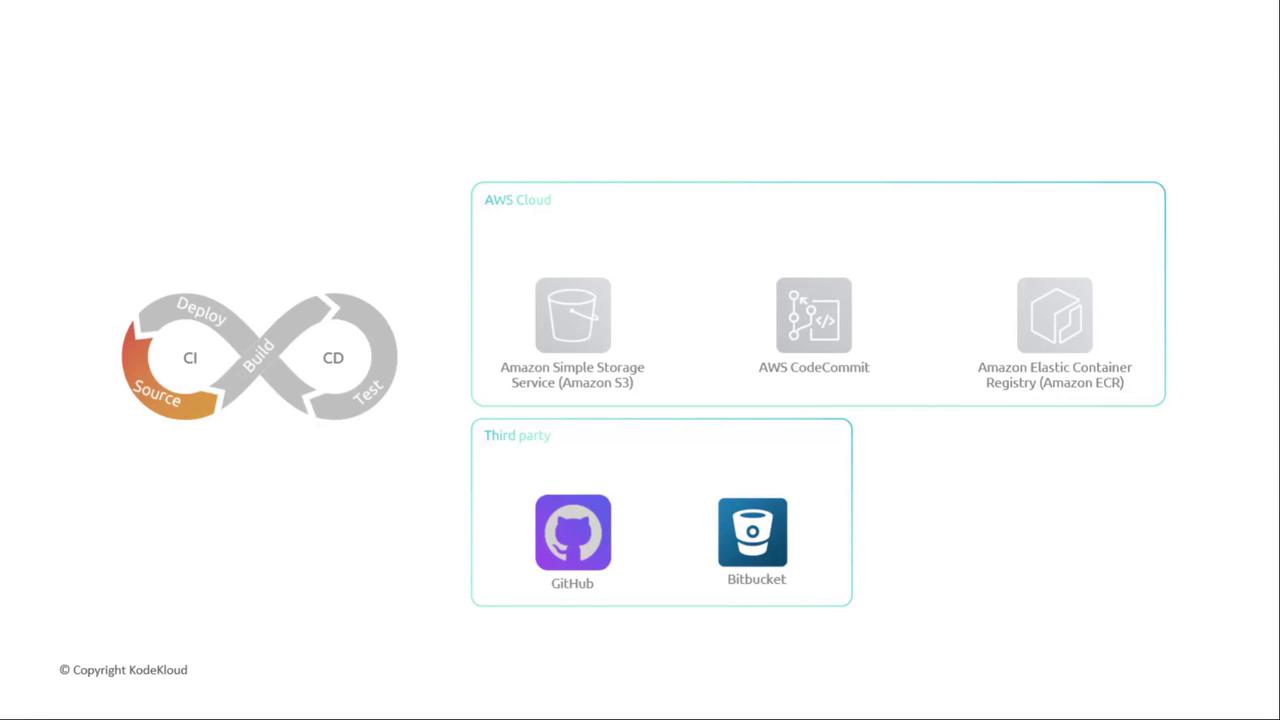
2. Build Stage Integrations
Compile your application, run unit tests, and package artifacts using either AWS-managed or external CI tools.| Provider | Service | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| AWS CodeBuild | Fully managed | Auto-scaling, buildspec support |
| Jenkins | Self-managed | AWS CodePipeline plugin & IAM roles |
| TeamCity | On-prem/Cloud | Custom agent pools |
| CloudBees | SaaS | Pipeline as code |
AWS CodeBuild
A fully managed CI service that scales continuously. Define your build commands in abuildspec.yml.
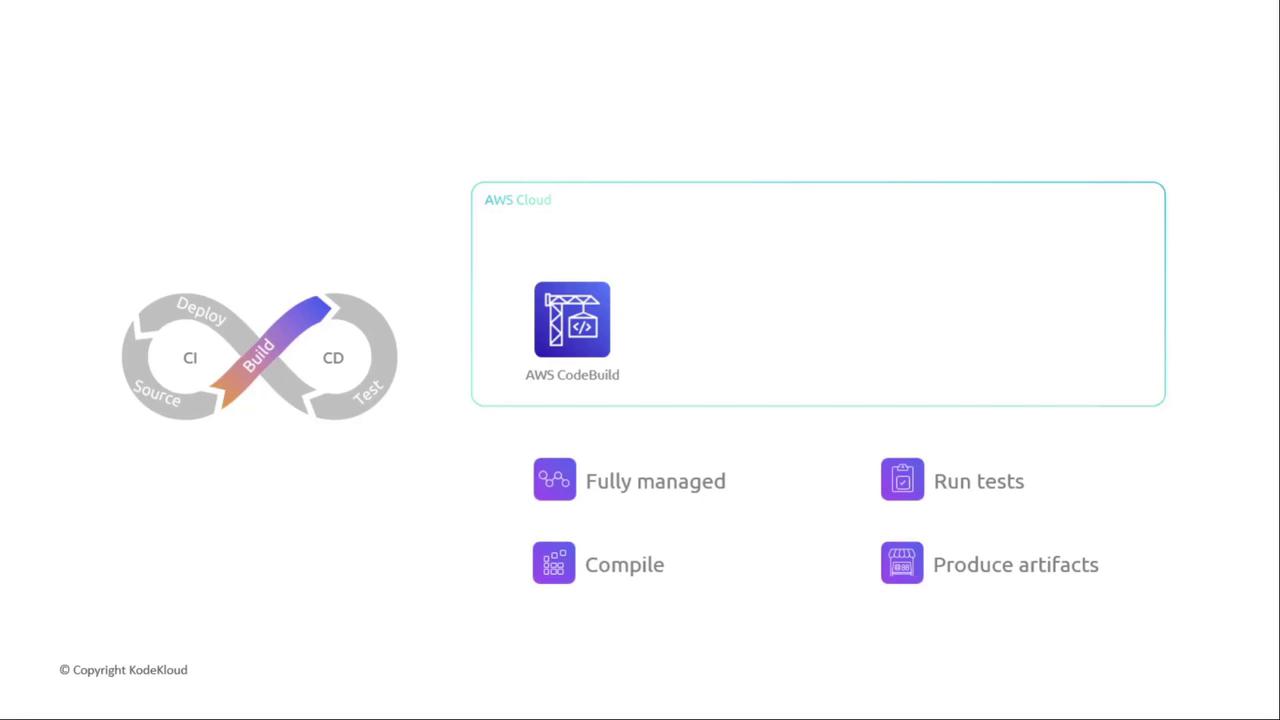
Ensure your CodeBuild service role has permissions to pull source and write artifacts to S3 or Amazon ECR.
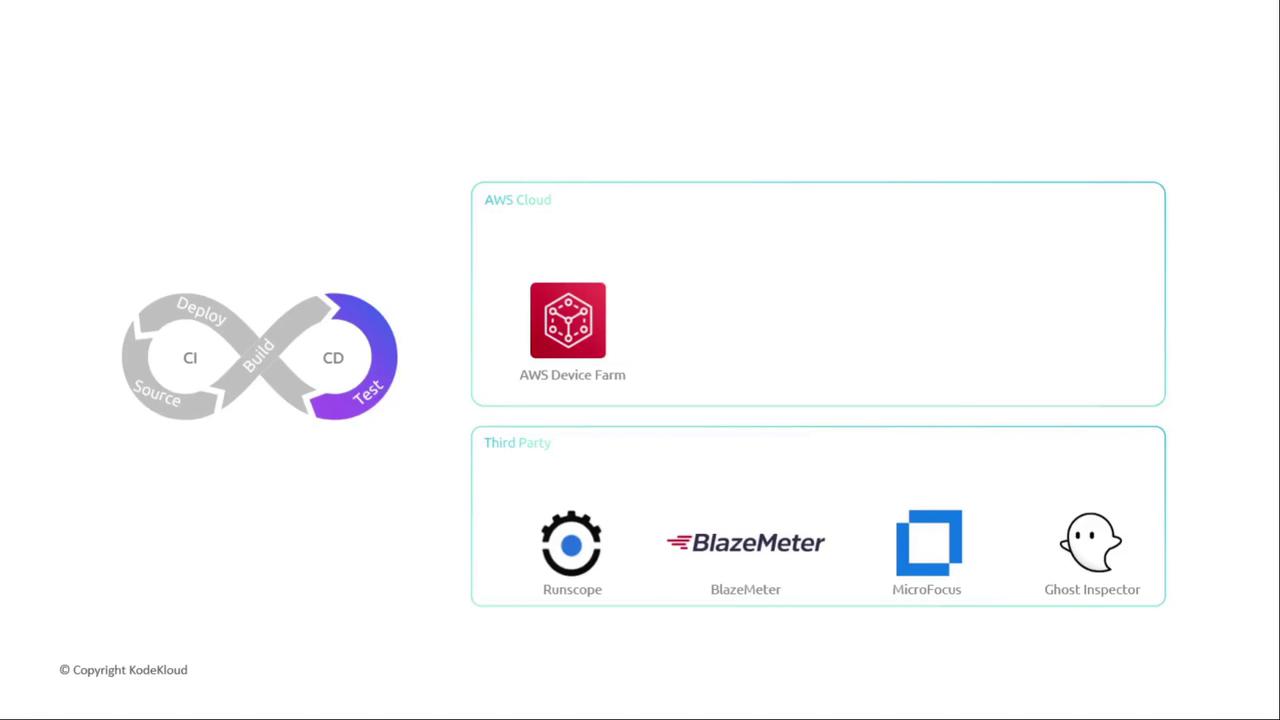
3. Test Stage Integrations
Depending on your workflow, combine testing with build or use dedicated test platforms. Combined Build/TestRun unit and integration tests within CodeBuild, Jenkins, TeamCity, or CloudBees. Dedicated Test Tools
- AWS Device Farm for mobile and web app testing
- Third-party services: BlazeMeter, RunScope, Micro Focus, Ghost Inspector
4. Deploy Stage Integrations
Target servers, serverless environments, containers, or static sites with flexible deployment actions.| Target Type | AWS Service | Third-Party Example |
|---|---|---|
| Static Websites | Amazon S3 + CloudFront | – |
| EC2 & On-Premise | AWS CodeDeploy | XebiaLabs |
| Containers | Amazon ECS / EKS | – |
| Serverless | AWS Lambda + API Gateway | – |
| Full Stack | Elastic Beanstalk, OpsWorks | – |
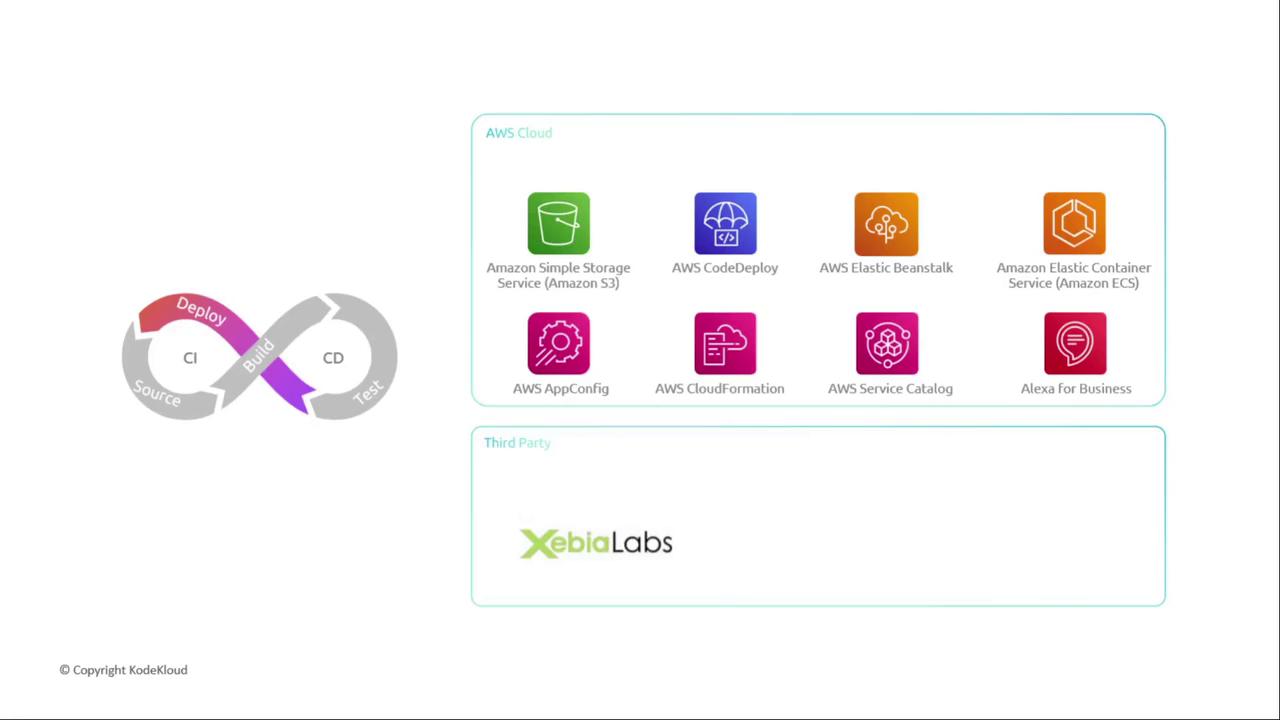
Key AWS Deployment Services
- Amazon S3: Host static sites and assets
- AWS CodeDeploy: Blue/green and in-place deployments
- Elastic Beanstalk: Automated provisioning & scaling
- AWS OpsWorks: Chef-based server configurations
- CloudFormation, Service Catalog, AppConfig, Alexa Skills
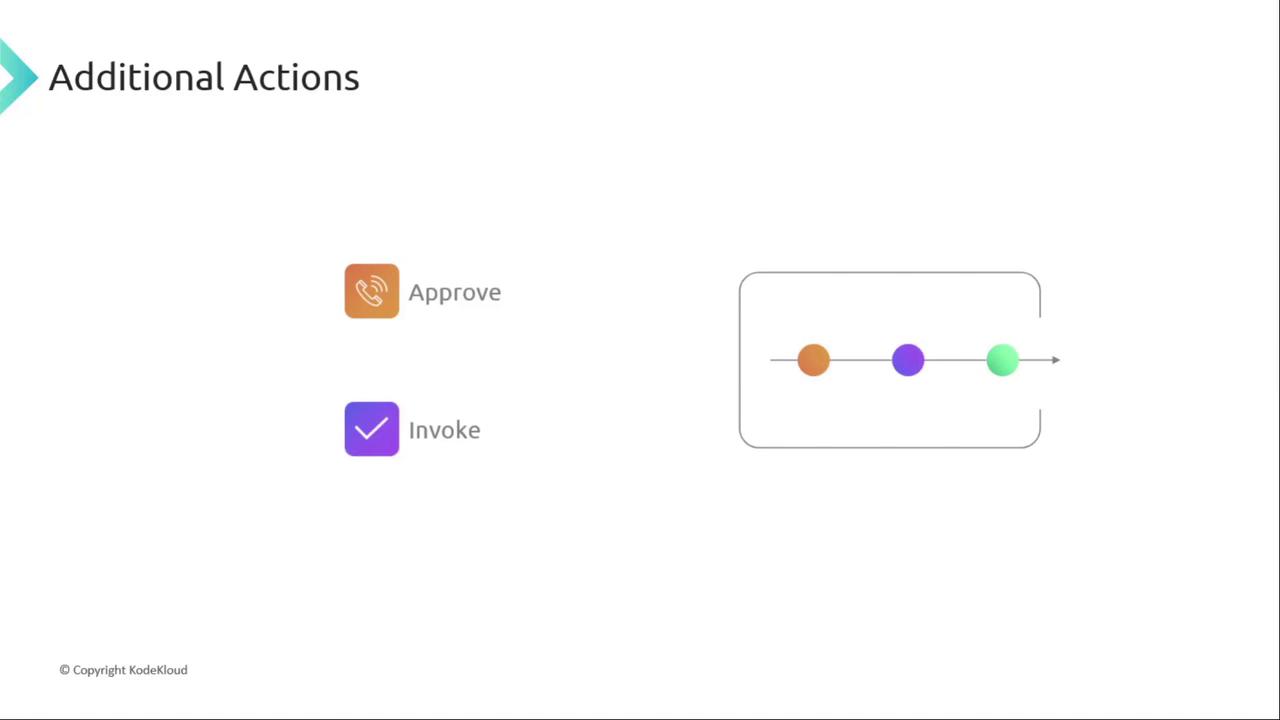
5. Additional Actions: Approvals & Invocations
Beyond core stages, incorporate approvals or invoke custom logic as needed.Manual Approvals
Use Amazon SNS or AWS Chatbot to notify stakeholders. Approvers click an action in the AWS Console or via email/SMS to proceed.
Configure your SNS topics and endpoints carefully to avoid spamming recipients.
Automated Invocations
Trigger AWS Lambda functions or Step Functions to run custom validations, security scans (e.g., Snyk), or complex orchestrations.
By mixing and matching AWS services and third-party tools, you can tailor CodePipeline to fit any CI/CD workflow—from simple static sites to complex microservices architectures.