Kubernetes Controllers and the Cloud Controller
Originally, Kubernetes ran all controllers—including the cloud controller—inside the API Server and Controller Manager. Modern setups (like EKS) run the cloud controller separately: it watches Service resources and calls your cloud provider’s API to create load balancers and other infrastructure.
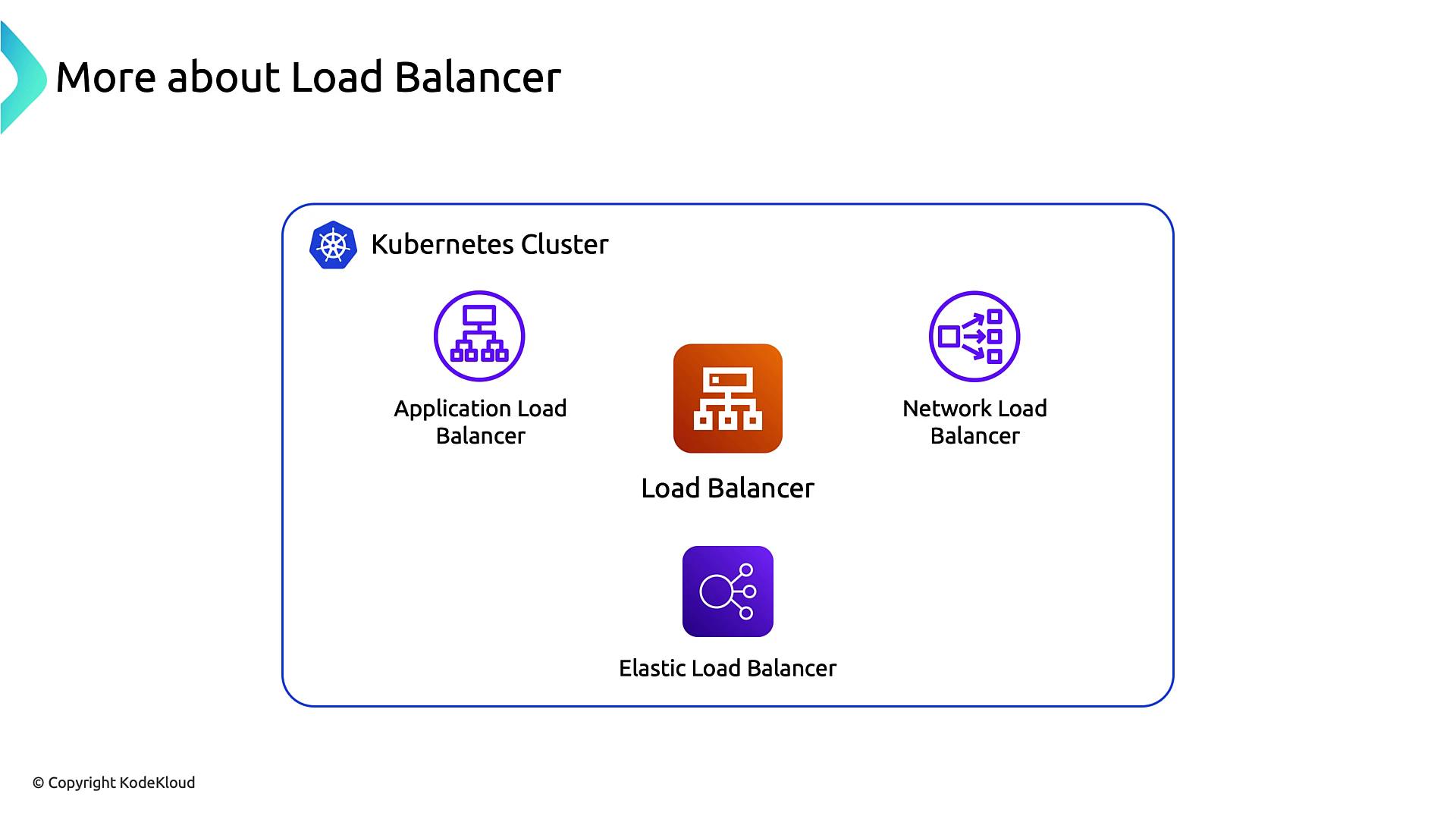
AWS Load Balancer Options
AWS supports three main load balancer types for Kubernetes Services:| Load Balancer | Use Case | Annotation |
|---|---|---|
| Application Load Balancer (ALB) | HTTP/HTTPS routing, host/path-based rules | service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: alb |
| Network Load Balancer (NLB) | TCP/UDP, ultra-low latency | service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: nlb |
| Classic ELB | Legacy, limited feature set | (default when no annotation is set) |
How Traffic Flows: Nodes, Pods, and Services
A Kubernetes node runs Pods that serve your application. To expose a Pod externally, you define a Service. Kubernetes maps a port on each node (NodePort) to your Pod’s port behind the scenes.
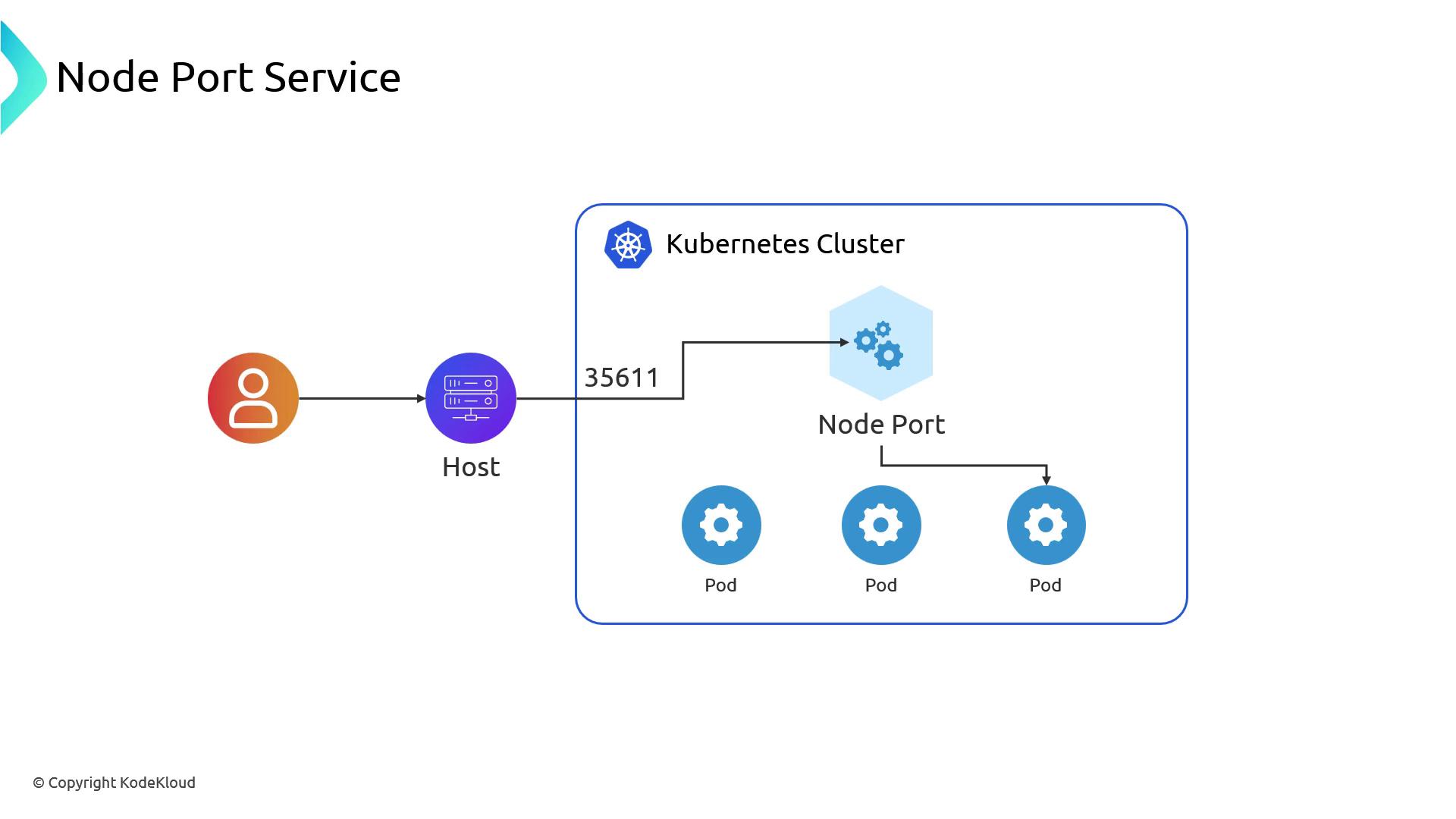
NodePort Service
A Service of typeNodePort opens the same high port on every node. You can then reach your application at:
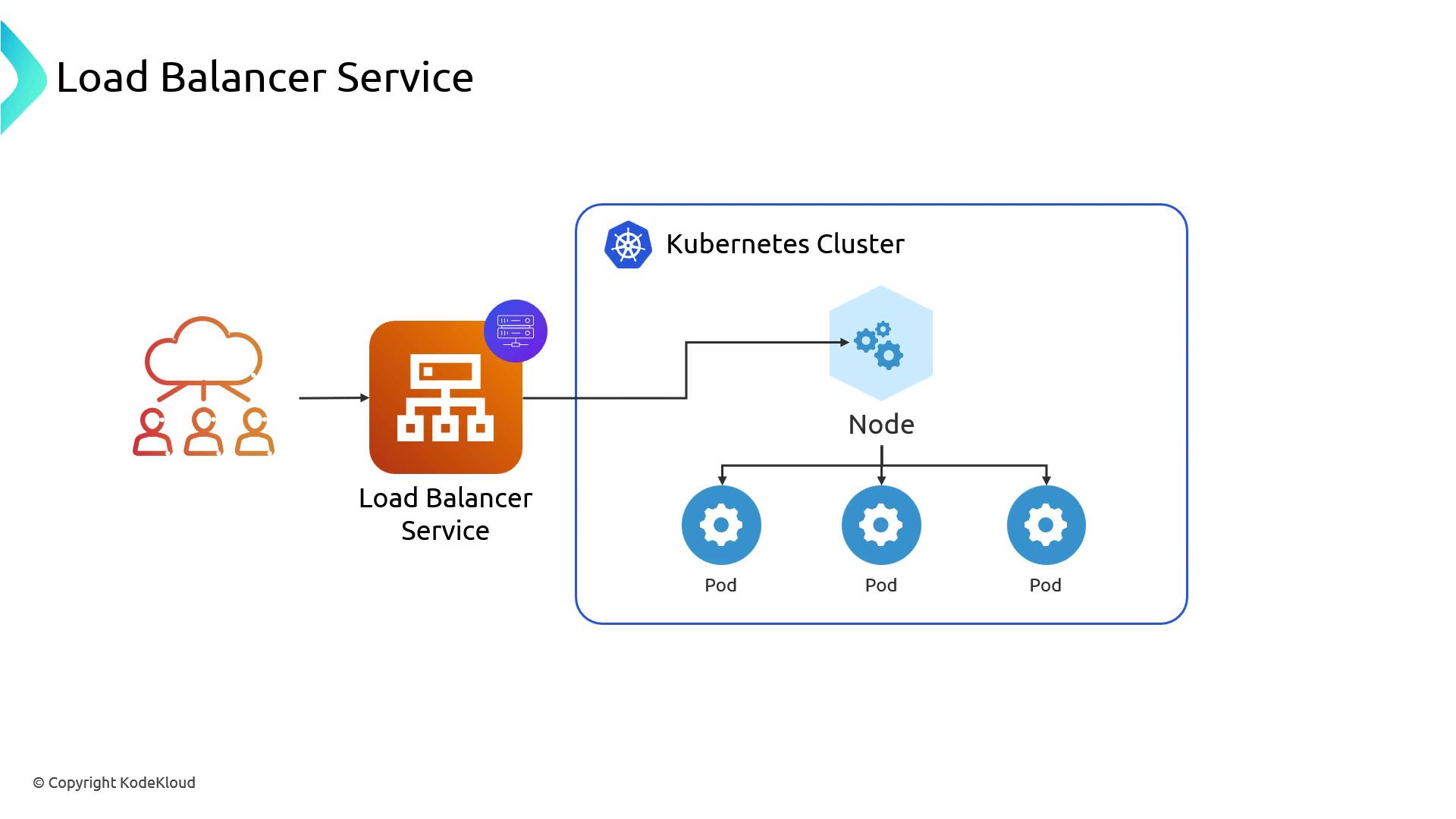
LoadBalancer Service
Settingtype: LoadBalancer still opens the NodePort, but also provisions an external load balancer that fronts all nodes and handles health checks, distributing traffic automatically:
Health Checks and kube-proxy
By default, the cloud load balancer health-checks every node, even those without Pods for this Service. When traffic lands on an empty node,kube-proxy reroutes it to a healthy node, possibly incurring cross-AZ hops.
Set
externalTrafficPolicy: Local on your Service to ensure only nodes with active Pods are in the load balancer’s target group. This reduces extra hops and cross-zone charges.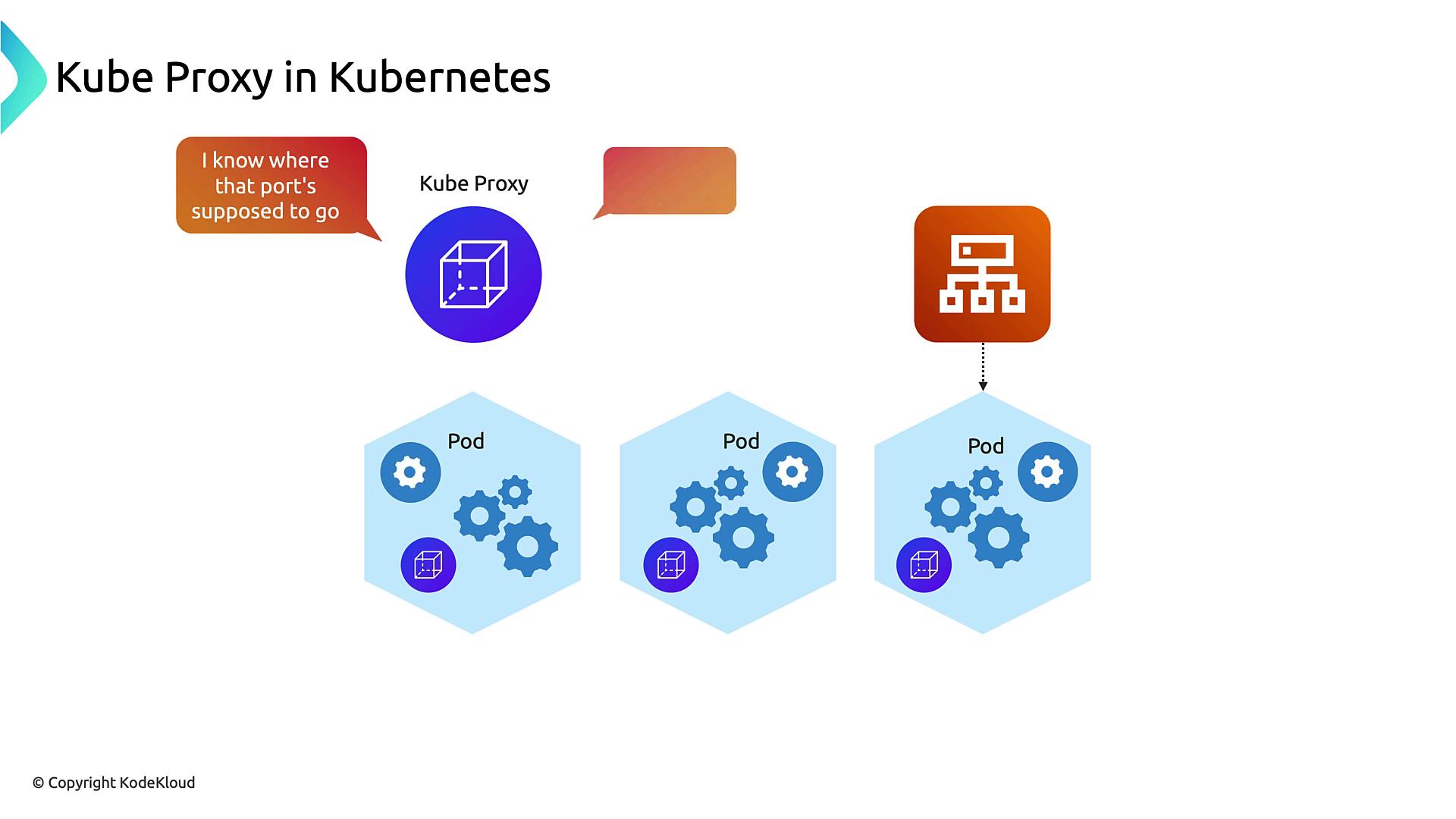
AWS Load Balancer Controller
The AWS Load Balancer Controller observes Services (and Ingresses) annotated for a load balancer. It then:- Provisions ALBs, NLBs, or Classic ELBs
- Configures security groups, listener rules, and target groups
- Keeps resources in sync with Kubernetes objects
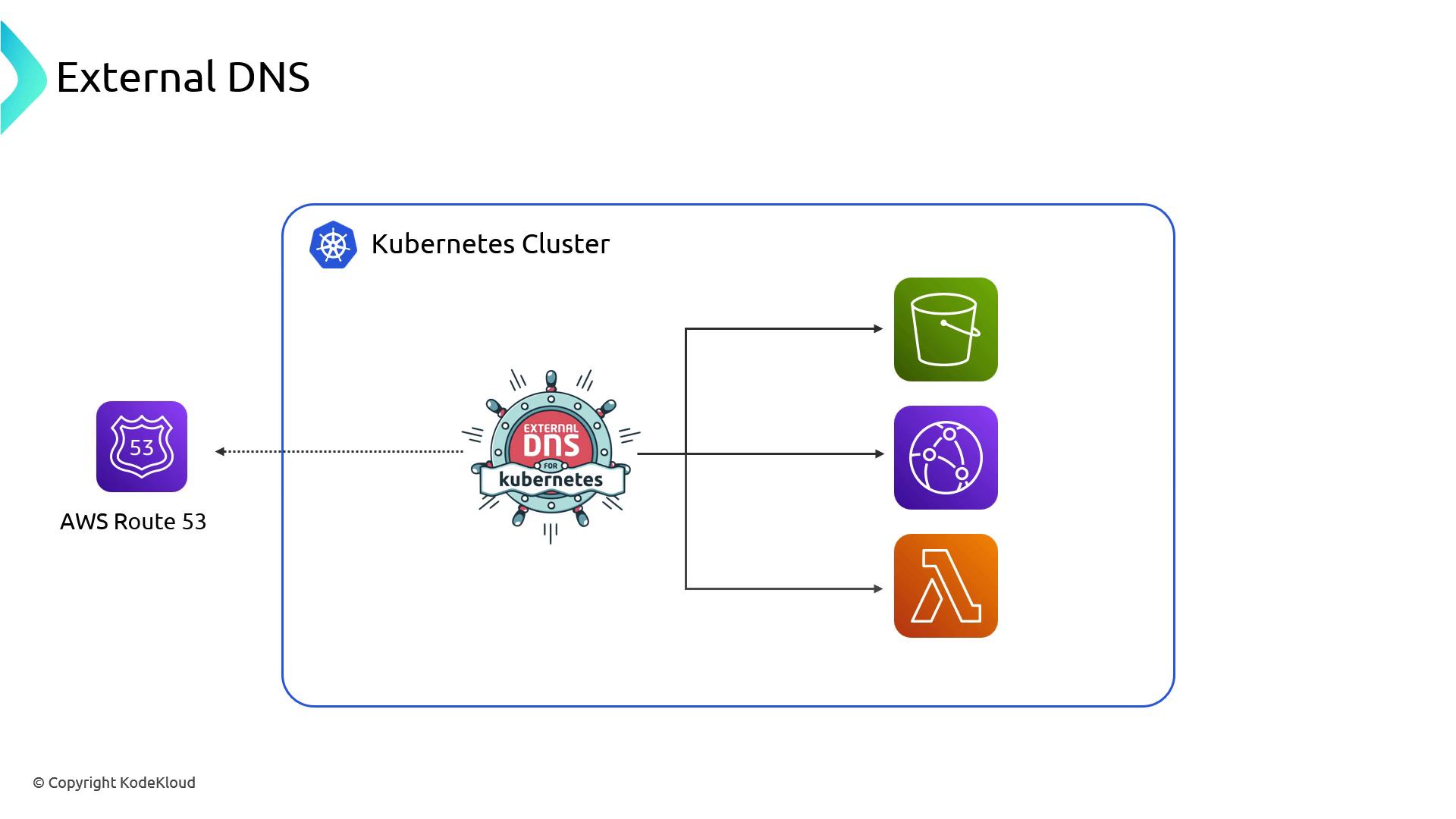
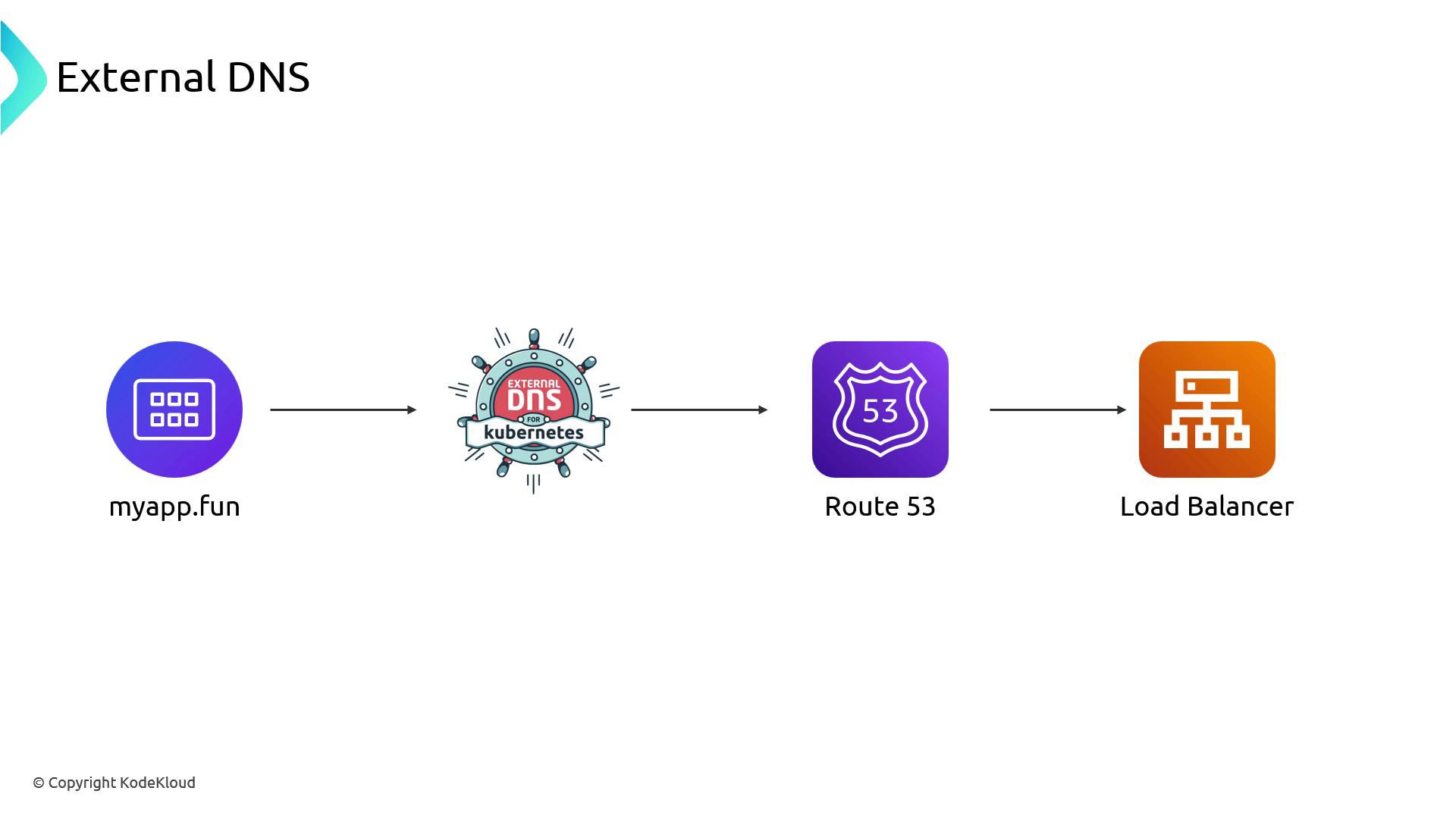
Integrating External DNS
To automate DNS entries in Route 53 (or other providers), run External DNS alongside the Load Balancer Controller. External DNS watches Services and Ingresses and creates DNS records pointing to your ALB/NLB. For example, a Service namedmyapp.fun can automatically generate a myapp.fun A record in Route 53 that resolves to your load balancer.
Global Load Balancer
AWS offers a Global Load Balancer for routing traffic across regions. You point a Route 53 alias to it and distribute traffic to regional ALBs/NLBs with failover or weighted policies. Currently, the AWS Load Balancer Controller manages only regional resources, but global support may arrive in future releases.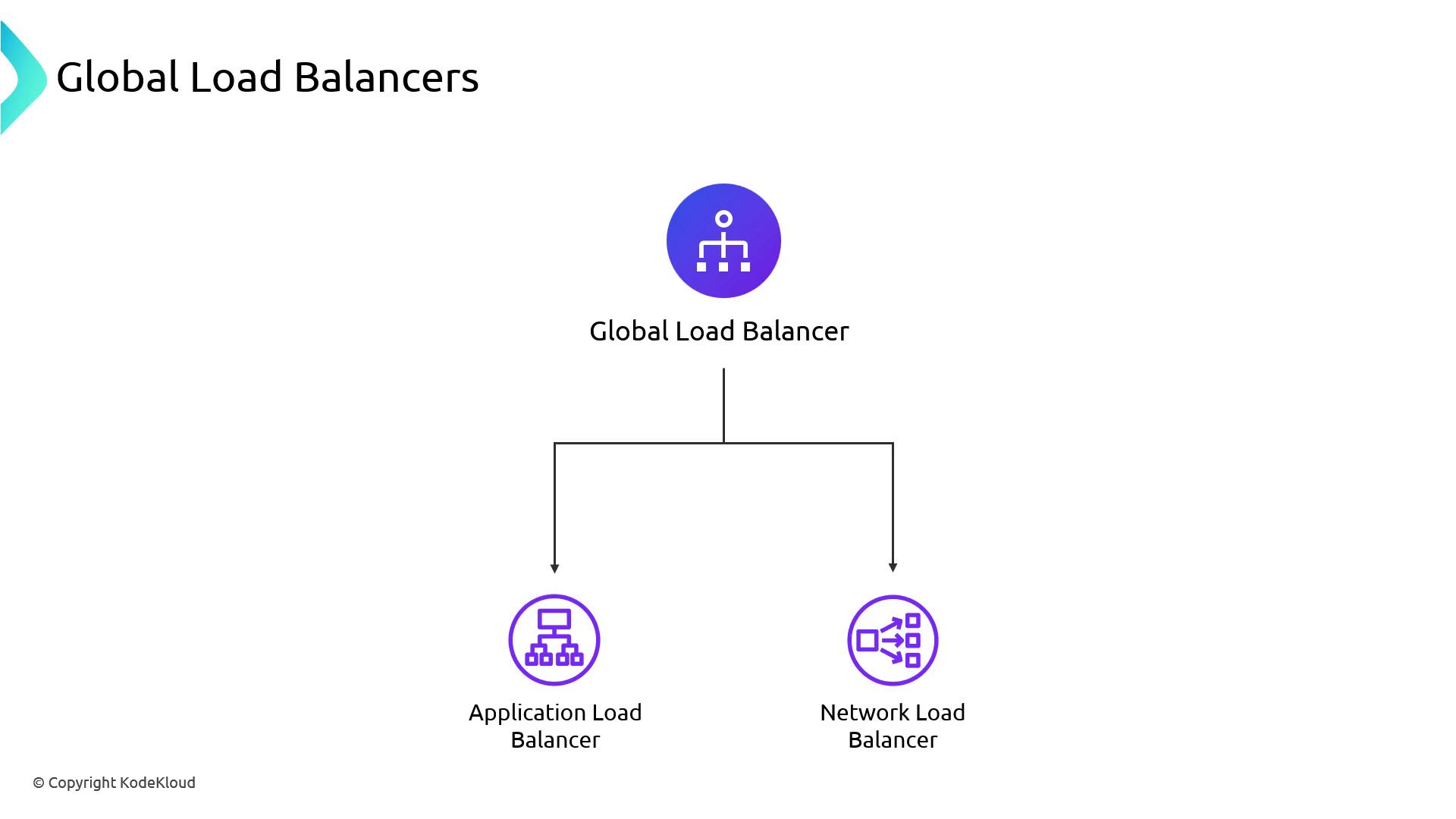
Summary
- Kubernetes Services (
NodePortandLoadBalancer) expose Pods to external traffic kube-proxyhandles traffic forwarding when nodes are healthy- AWS Load Balancer Controller automates ALB, NLB, and ELB provisioning
- External DNS with Route 53 automates DNS record management
- AWS Global Load Balancer enables multi-region routing and failover