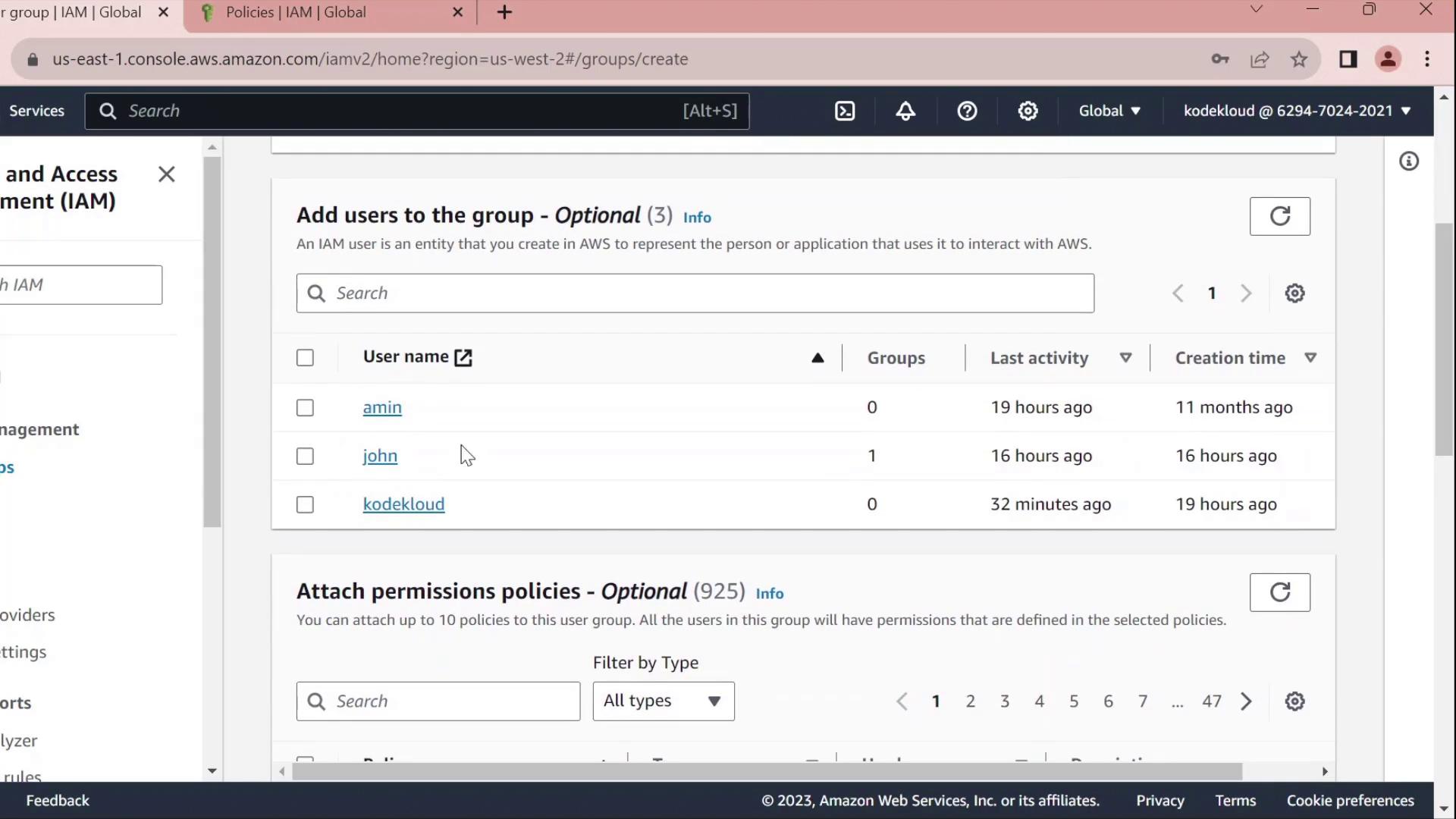
1. Create a Developers Group
- In the AWS Management Console, navigate to IAM → User groups.
- Click Create group, name it Developers, and add the user John to the group.
- Skip attaching any policies for now and finish the wizard.
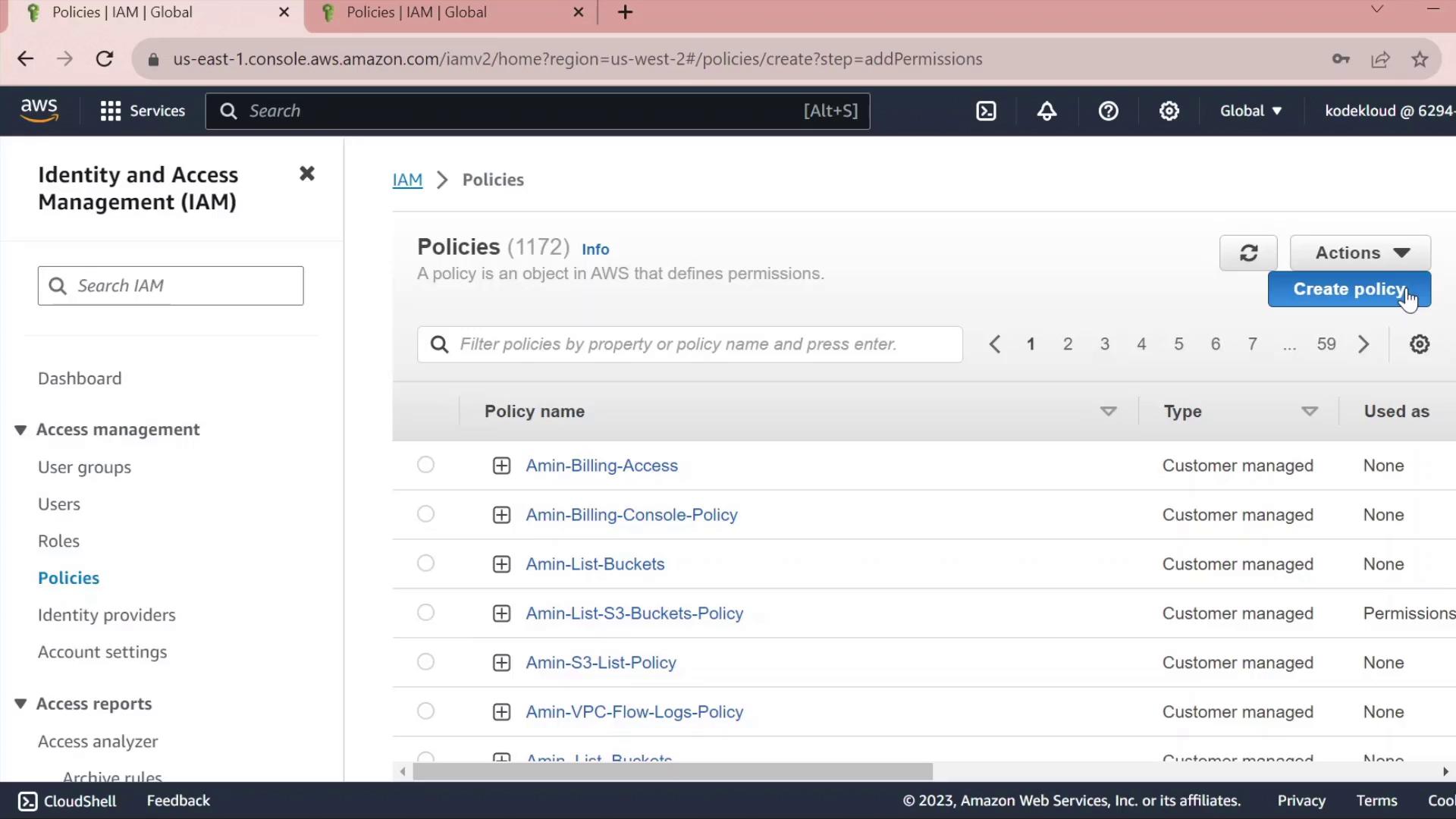
2. Create a Custom Policy
- In the IAM sidebar, select Policies.
- Click Create policy.
2.1 Grant S3 Read Access
- Under Service, choose S3.
- In Actions, expand Read and check GetObject.
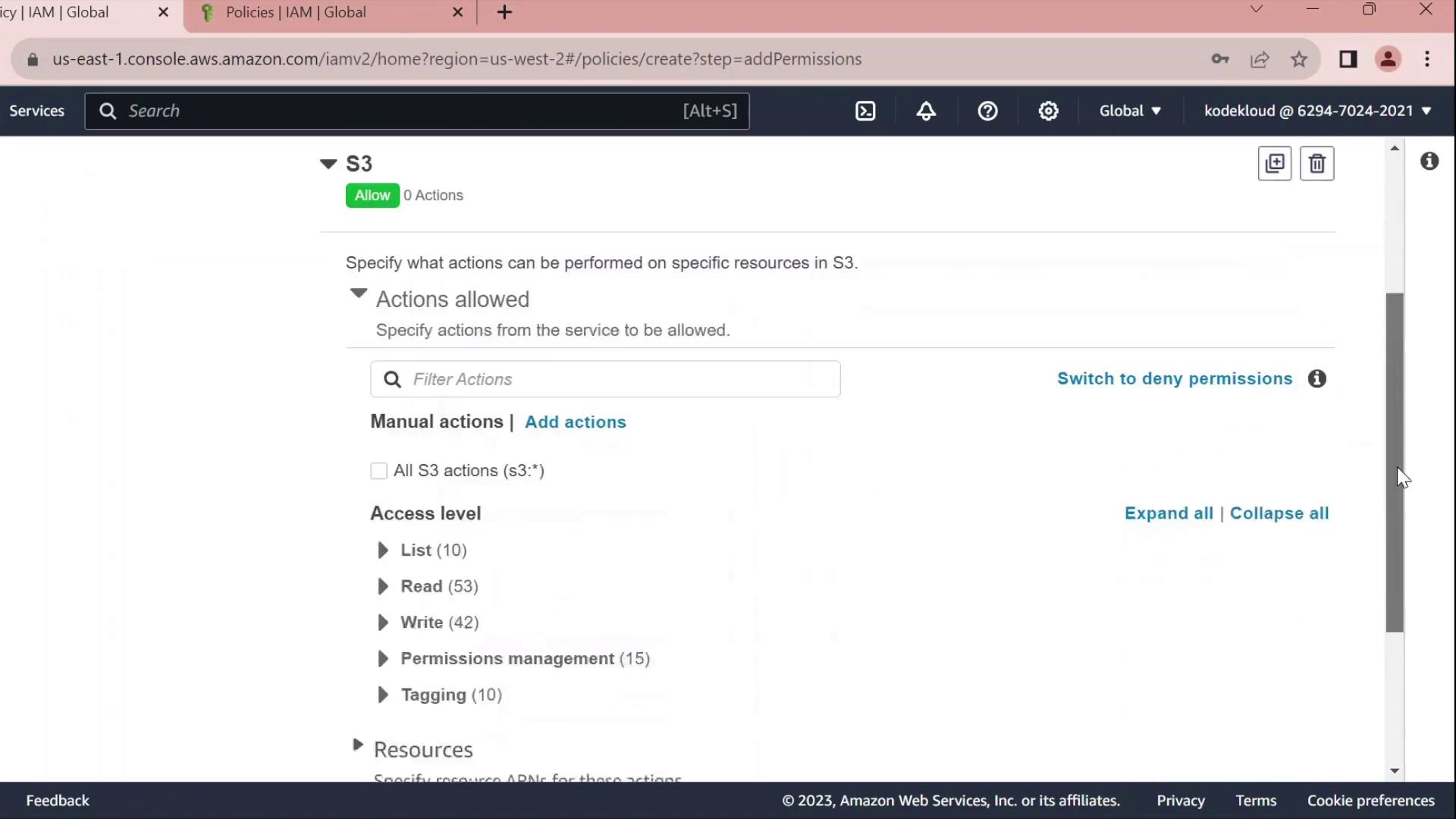
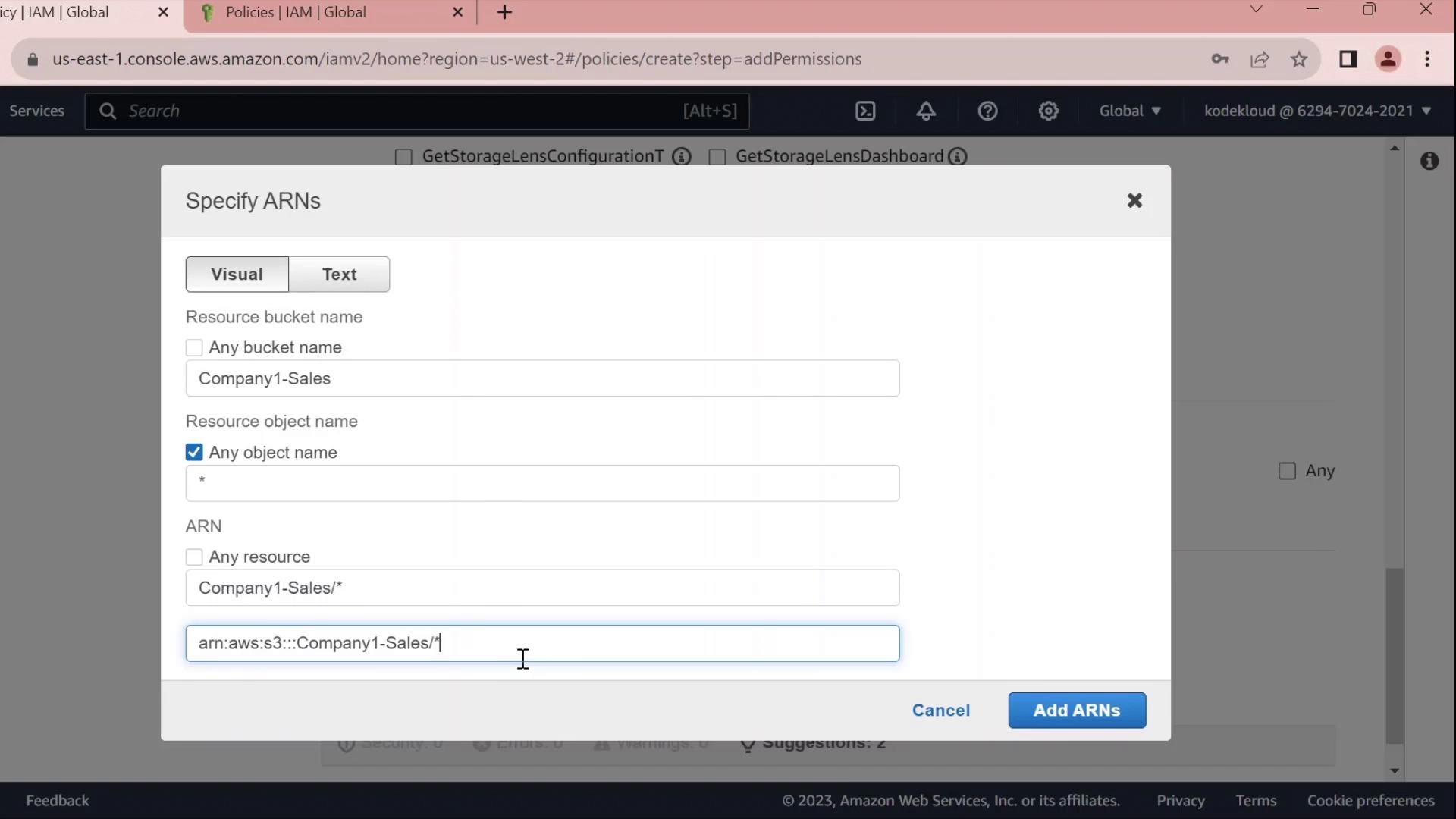
- Under Resources → Add ARN, enter:
- Bucket:
company1-sales - Object:
*
The console will build the ARN for you.
- Bucket:
2.2 Grant EC2 Full Access
- Click Add permissions → EC2.
- Select All EC2 actions under Actions.
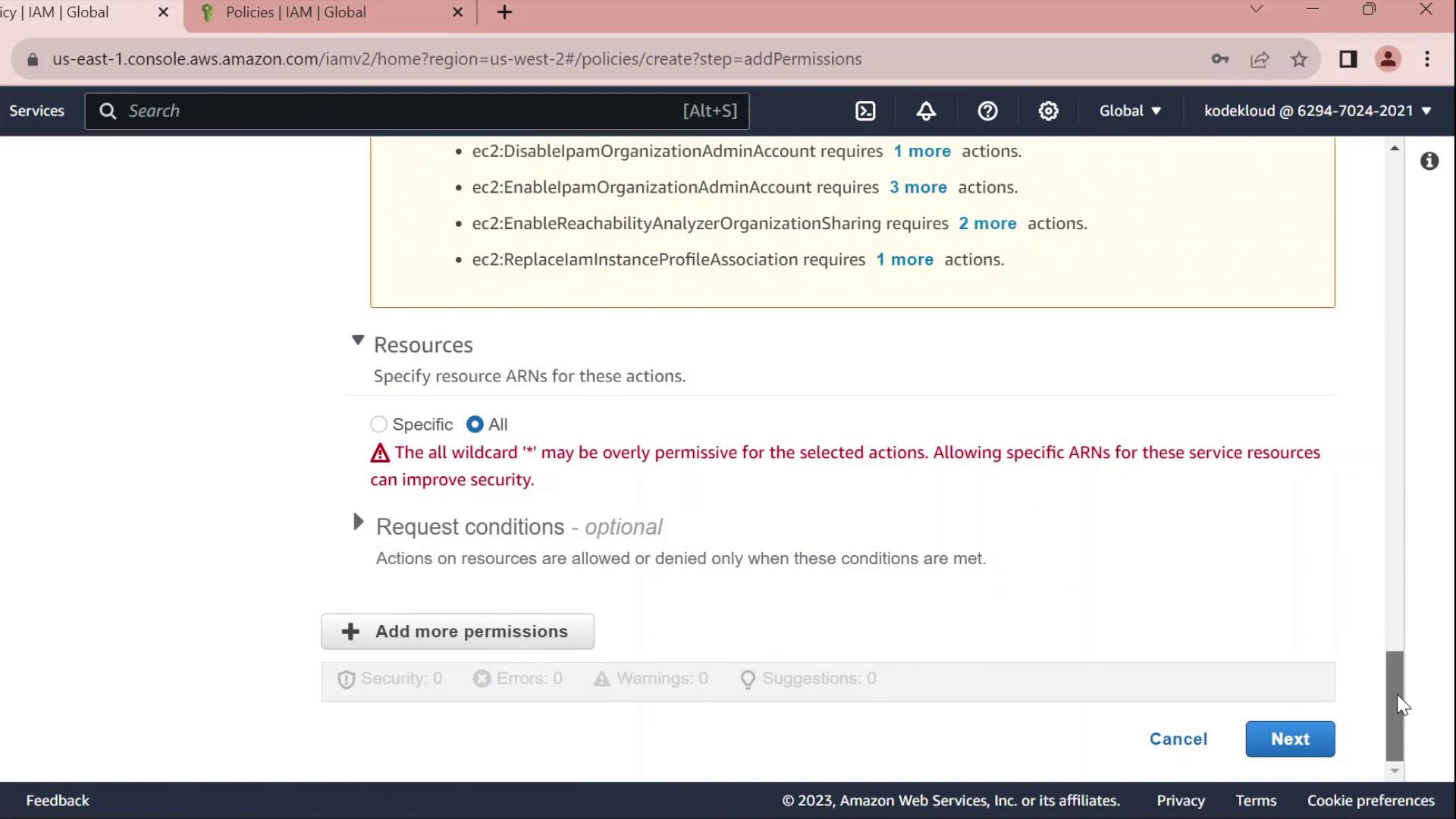
- Leave the resource set to
*for all instances.
Using
* for resources grants full access to all EC2 instances. In production, scope this down by specifying ARNs for specific instances or regions.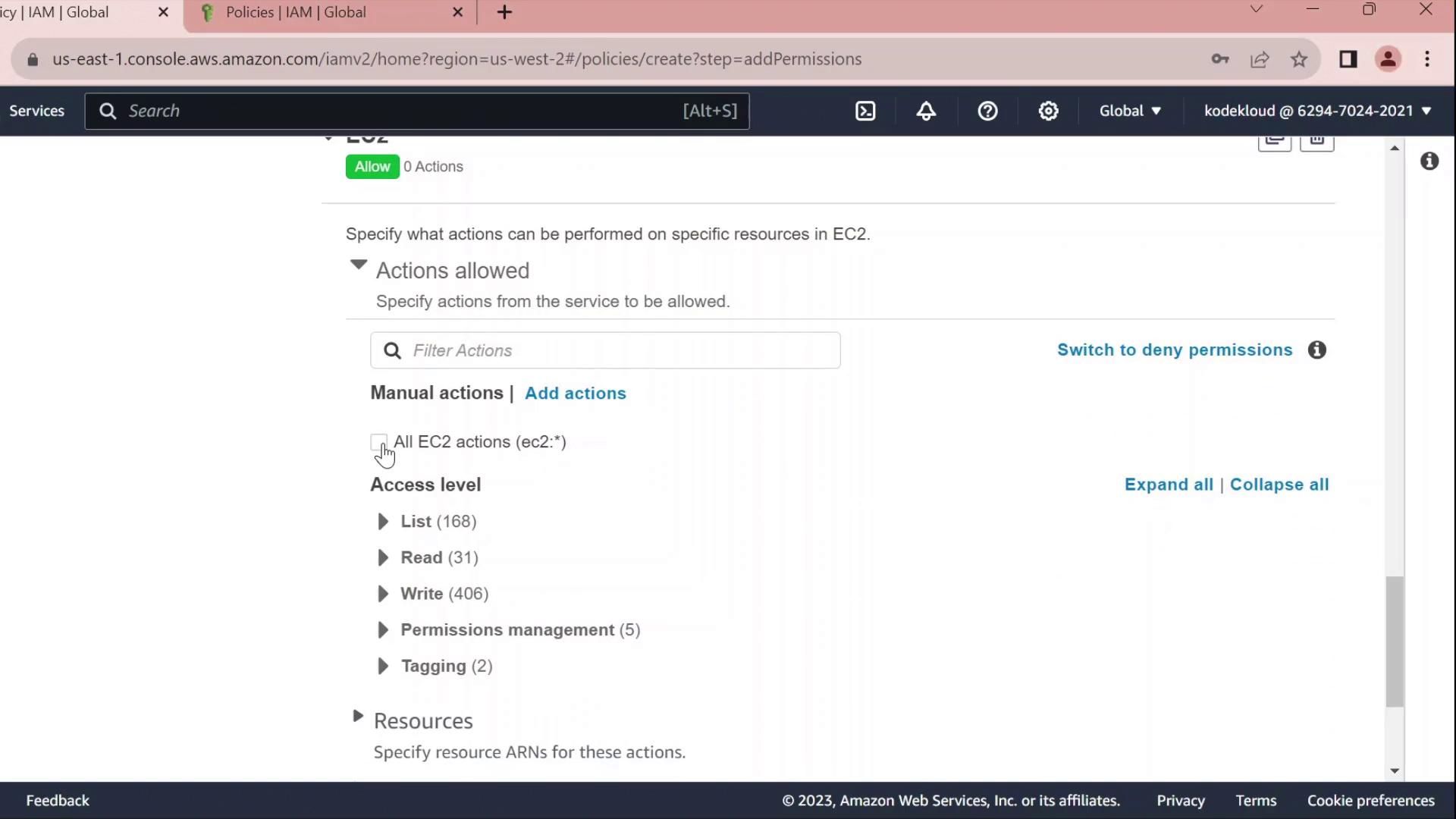
2.3 Review, Name, and Create
- Click Next until you reach Review policy.
- Set Name to
Developers_Policyand add an optional description. - Click Create policy.
3. Attach Policy to the Developers Group
- Return to IAM → User groups.
- Select Developers.
- Under the Permissions tab, click Attach policies.
- Search for and select Developers_Policy, then click Attach policy.
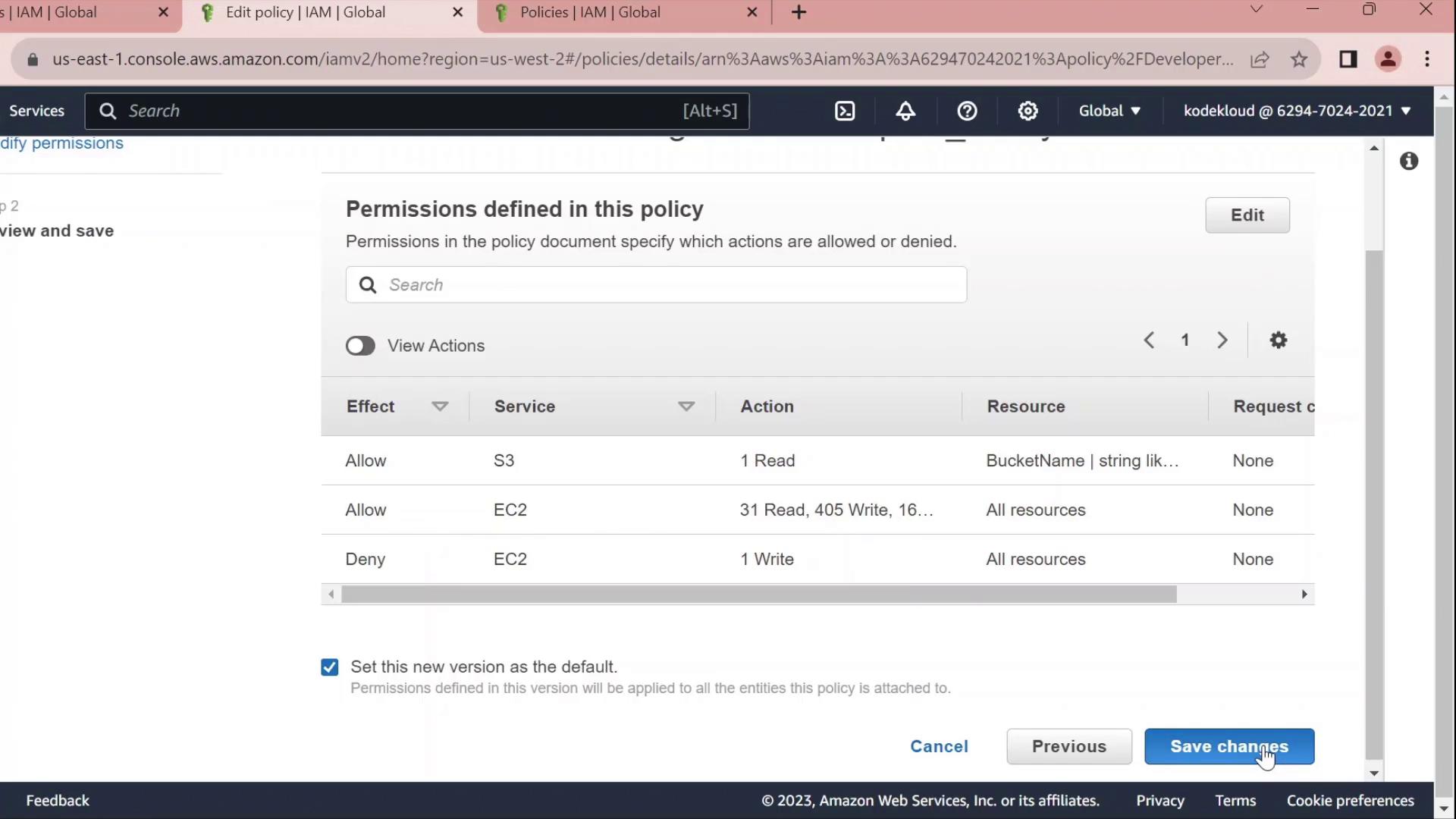
4. Edit the Policy
Click Edit policy on the Permissions tab to open the policy editor. You can switch between the Visual editor and the JSON tab.4.1 Rename Statement IDs
Replace autogeneratedSid values with clear identifiers:
4.2 Deny Stopping EC2 Instances
Add a statement to prevent developers from stopping instances:4.3 Final Policy JSON
Combine all statements into your final policy:| Sid | Effect | Action | Resource |
|---|---|---|---|
| AllowAllEC2Actions | Allow | ec2:* | * |
| AllowS3GetObject | Allow | s3:GetObject | arn:aws:s3:::company1-sales/* |
| DenyStopInstances | Deny | ec2:StopInstances | * |