| Component | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
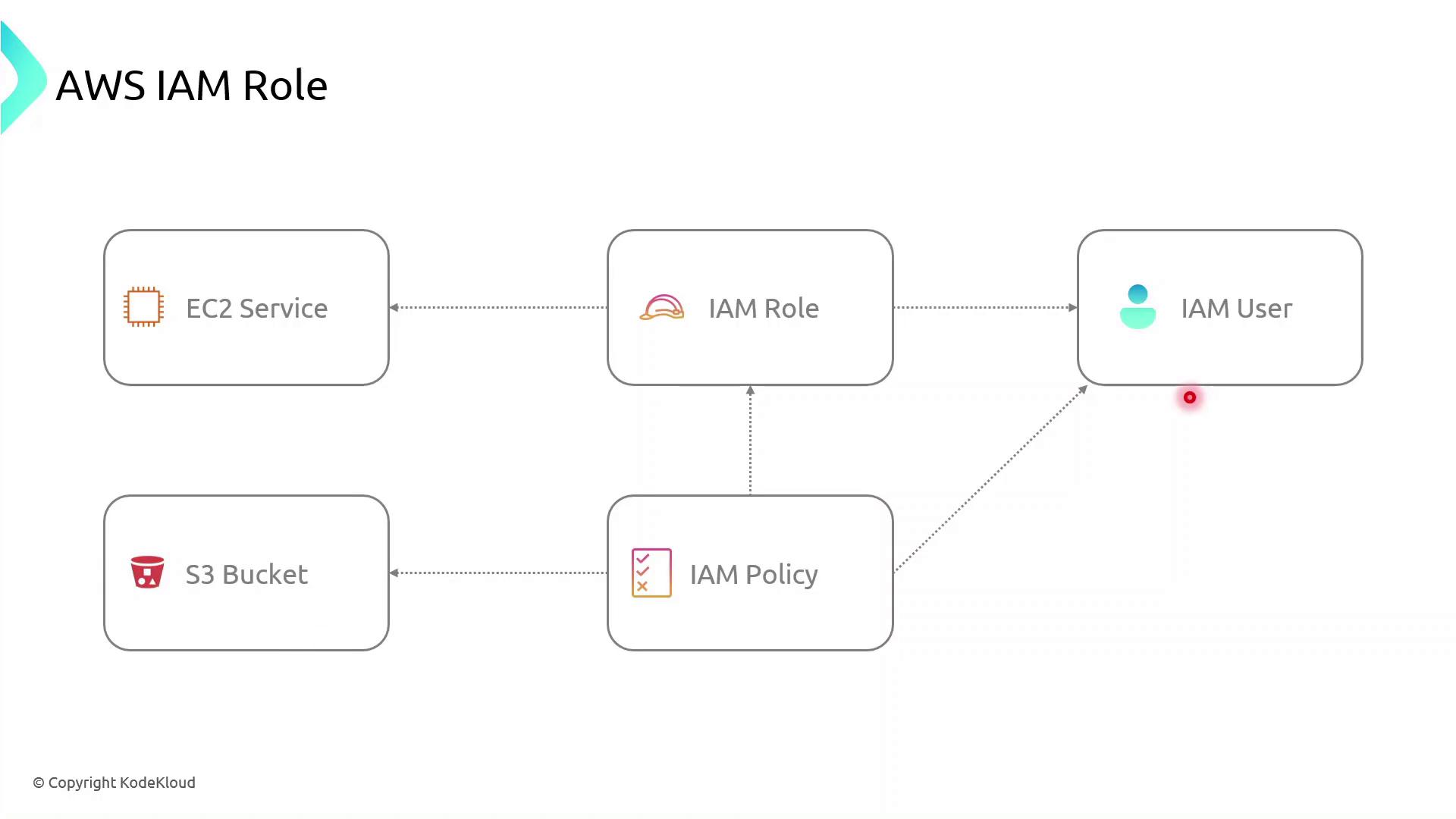
| Role | An identity with attached permissions and a trust policy | S3AccessRole |
| Permissions Policy | A JSON document specifying allowed or denied actions | AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess |
| Trust Policy | Defines which principals (services, users, or accounts) can assume the role | EC2 service: ec2.amazonaws.com |
| Temporary Tokens | Short-lived credentials issued by AWS STS | AccessKeyId, SecretAccessKey, SessionToken |
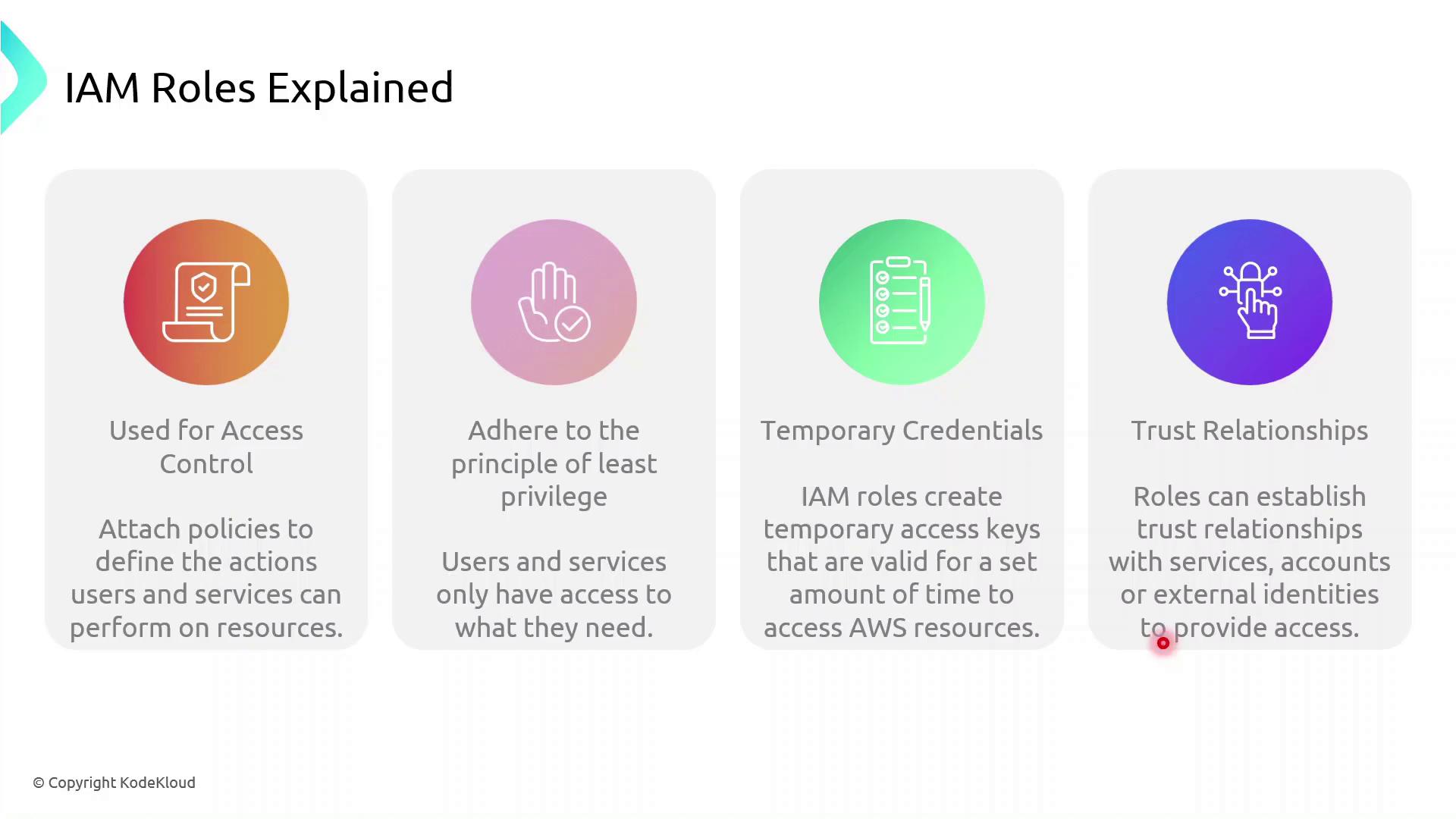
How IAM Roles Enhance Security
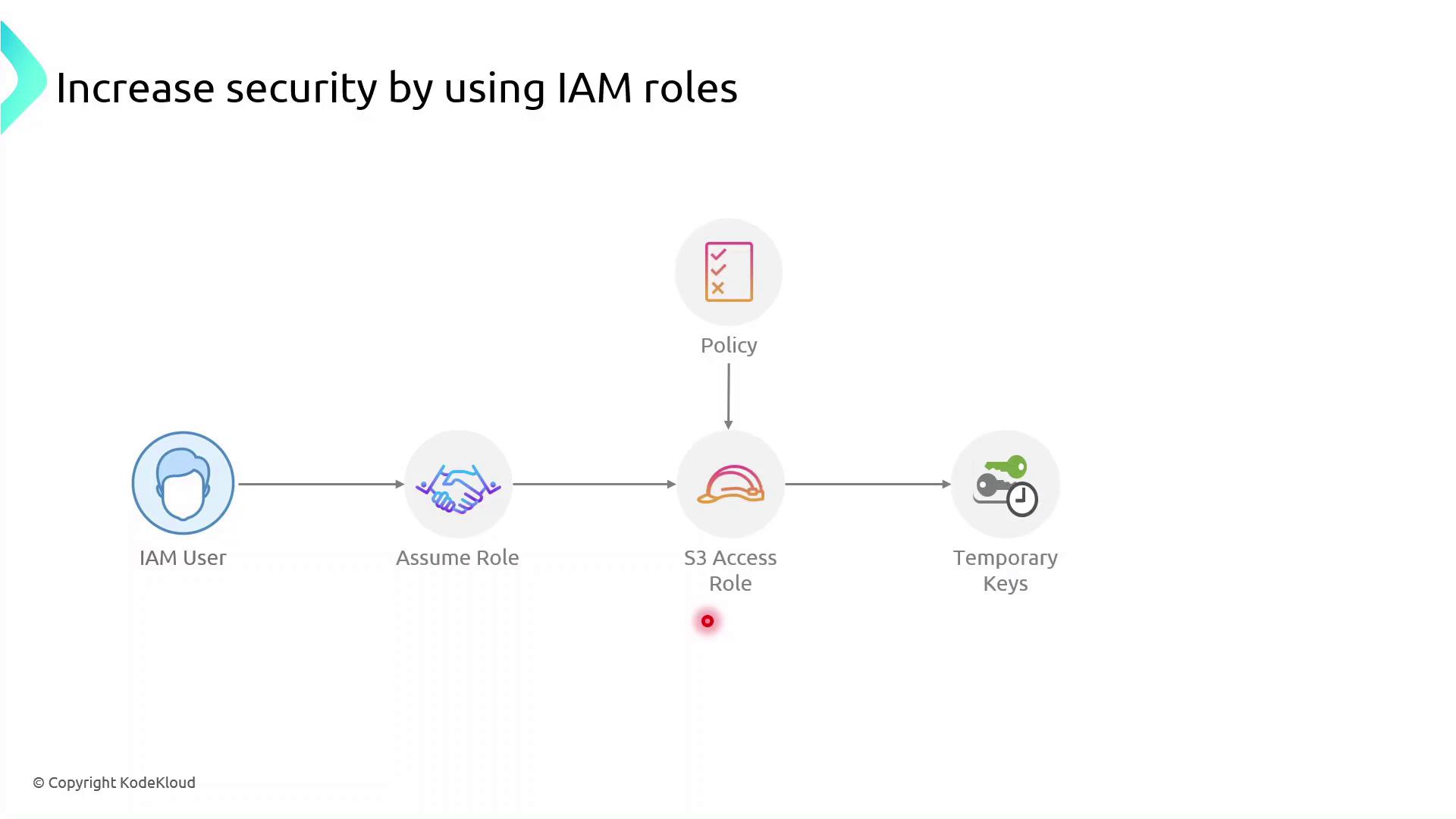
Instead of hard-coding long-term AWS keys:- A principal (user or service) calls
sts:AssumeRole. - AWS returns temporary credentials.
- The principal uses these credentials to access resources.
- Credentials expire automatically, minimizing the blast radius.
Always follow the principle of least privilege. Grant only the permissions required for the task.
Role Assumption Flow
AWS Components Interaction
Demo: Create an IAM Role for EC2 to Access S3
Follow these steps in the AWS Management Console or use the AWS CLI commands shown.Console Steps
-
Open the IAM console
https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam -
Create a new role
- In the navigation pane, choose Roles → Create role.
- Under Select trusted entity, choose AWS service, then EC2, and click Next.
-
Attach permissions
- Search for AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess (or attach your custom policy).
- Select it and click Next.
-
Name and create
- Enter Role name:
S3AccessRole - Review settings and click Create role.
- Enter Role name:
-
Attach the role to an existing EC2 instance
- Open the EC2 console, select your instance.
- Choose Actions → Security → Modify IAM role.
- Select S3AccessRole and click Save.
AWS CLI Alternative
First, create a trust policy file (trust-policy.json):