Default Lambda Service VPC
When you create a Lambda function, AWS places it into a managed Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) called the Lambda service VPC. This isolated environment lets Lambda scale automatically without requiring your own VPC infrastructure.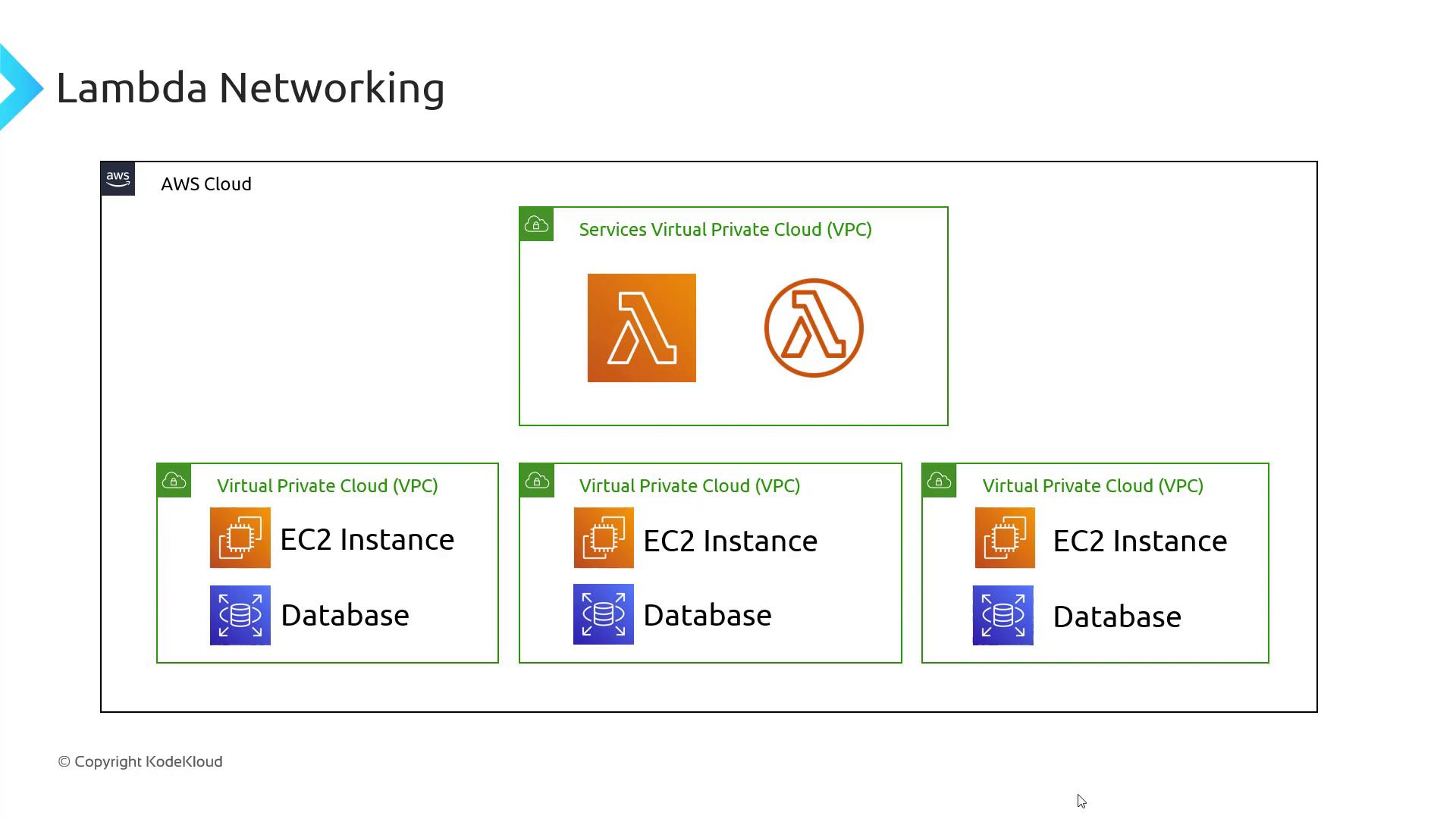
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Outbound Internet Access | Enabled by default for calling public endpoints. |
| AWS Service Connectivity | Direct access to AWS APIs, governed by IAM permissions. |
The default Lambda service VPC cannot communicate with resources in your private VPCs. Use one of the options below to reach EC2 instances, private databases, or to lock down internet access.
Connecting to Private VPC Resources
To access private VPC resources or remove default internet access, choose one of these methods:- Deploy Lambda inside your VPC.
- Use an interface VPC endpoint to bridge the AWS-managed VPC and your private VPC.

Option 1: Run Lambda in Your Private VPC
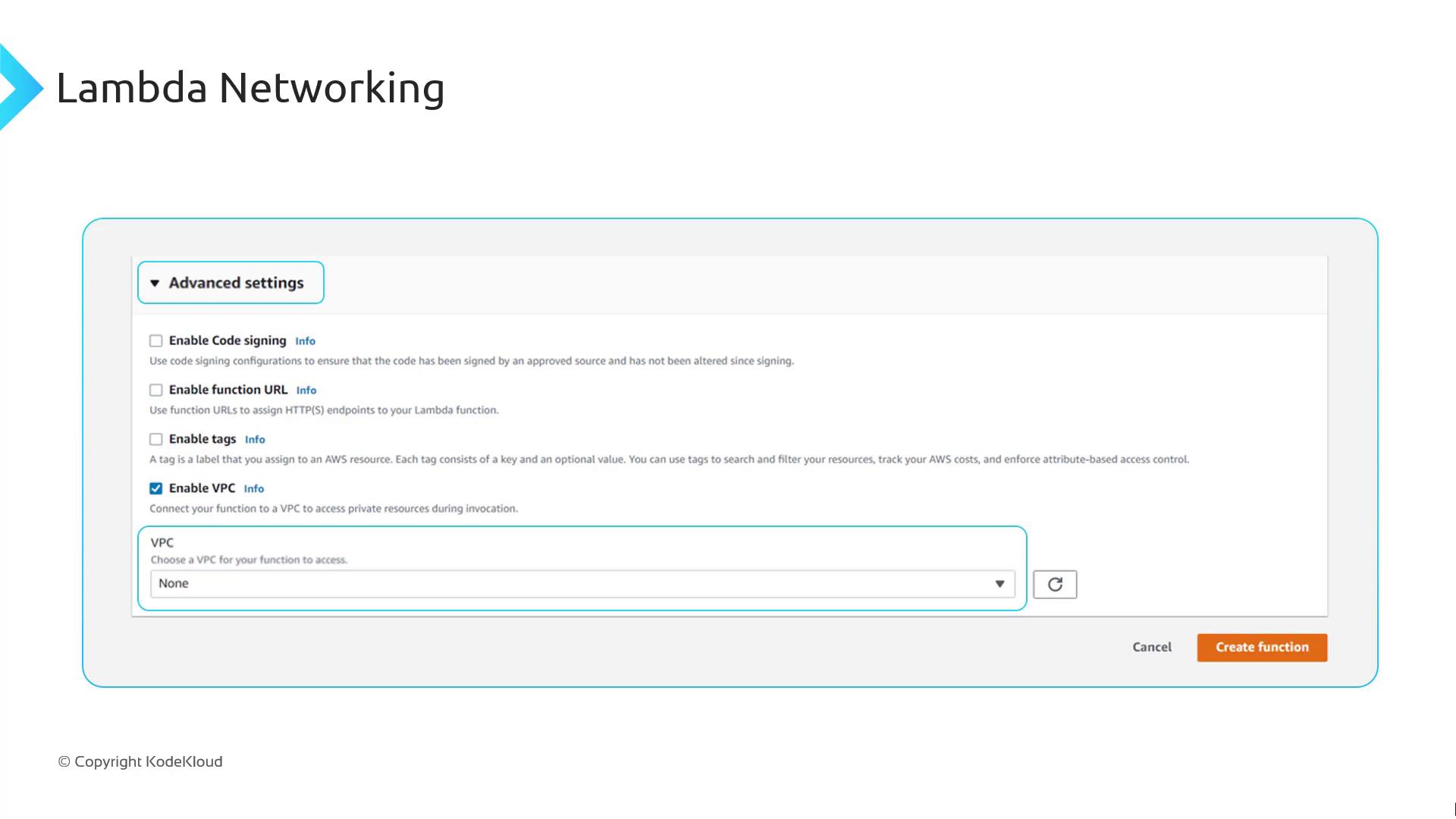
Attach your function to a custom VPC via the Lambda console:- Open your function and scroll to Advanced settings.
- Choose your VPC, select subnets across Availability Zones, and assign security groups.
- Save to deploy the function inside your VPC.
| Consideration | Details |
|---|---|
| High Availability | Use subnets in multiple AZs. A failure in one AZ affects only functions in that AZ. |
| Internet Connectivity | Private VPC functions lose default internet access. Deploy NAT gateways per AZ to restore outbound traffic. |
| AWS Service Access | VPC-deployed functions cannot reach AWS services without VPC endpoints. |
| Additional Costs | Expect charges for NAT gateways, interface endpoints, and Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs). |
| ENI Limits | Each concurrent execution creates an ENI. Reaching the ENI quota in your VPC or region caps Lambda concurrency. |
Be mindful of ENI limits: exceeding the Elastic Network Interface quota in your VPC will throttle new concurrent executions. Request a limit increase if necessary.
Option 2: Use an Interface VPC Endpoint
Keep Lambda in the AWS-managed VPC and create an AWS Lambda interface endpoint in your private VPC. This approach offers:- Secure, private connectivity to your VPC resources
- Continued internet and AWS service access managed by AWS
- No ENI-based concurrency constraints in your VPC
- A minimal hourly cost for the interface endpoint
- Open the VPC console.
- Select Endpoints > Create Endpoint.
- Choose AWS services and pick com.amazonaws.<region>.lambda.
- Associate with your private subnets and security groups.
- Create the endpoint.