Steps to Enable VPC Access
-
Open or create your Lambda function
In the AWS Lambda console, choose your existing function or click Create function to define a new one. -
Enable VPC configuration
Scroll to Configuration, expand Advanced settings, and toggle Enable VPC on. -
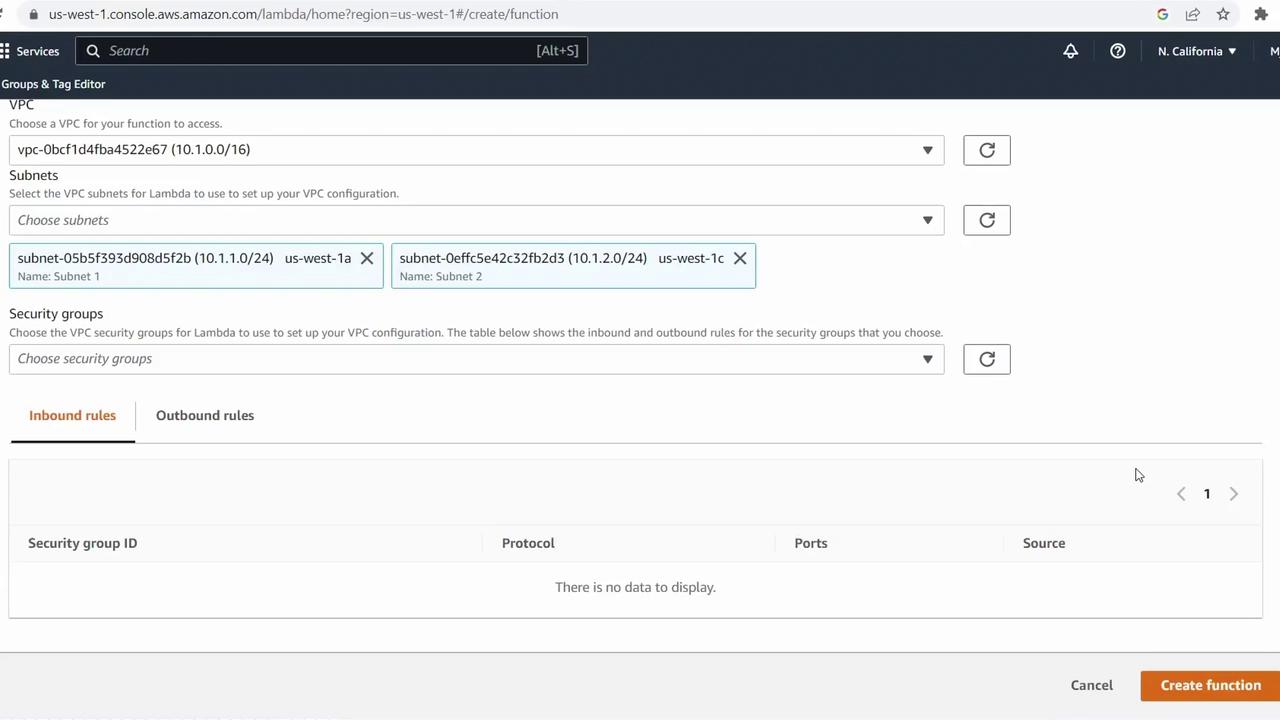
Select your VPC
From the VPC dropdown, pick the VPC you’ve already provisioned (e.g.,cold-cloud-demo-vpc). -
Choose subnets for high availability
Expand Subnets and select at least two subnets in different Availability Zones. This ensures your function remains resilient during AZ outages.- One subnet in us-west-1a
- One subnet in us-west-1c
Always select subnets from multiple Availability Zones to maintain high availability. If one AZ goes down, Lambda can still execute in the other.
- Assign security groups
Under Security groups, pick existing security groups or create new ones to control inbound and outbound traffic for your function’s Elastic Network Interface (ENI).
Attaching a Lambda function to a VPC can increase cold start times because ENIs must be initialized. Review AWS Lambda cold start considerations for mitigation strategies.