Prerequisites
- An existing SQS queue named
KodeKloudDemoQueue - IAM permissions to create Lambda functions and roles
- Basic familiarity with AWS Lambda and Amazon SQS
1. Navigate to the AWS Lambda Console
- Open the AWS Management Console
- In the search bar, type Lambda and select AWS Lambda
2. Create a New Function from a Blueprint
- Click Create function
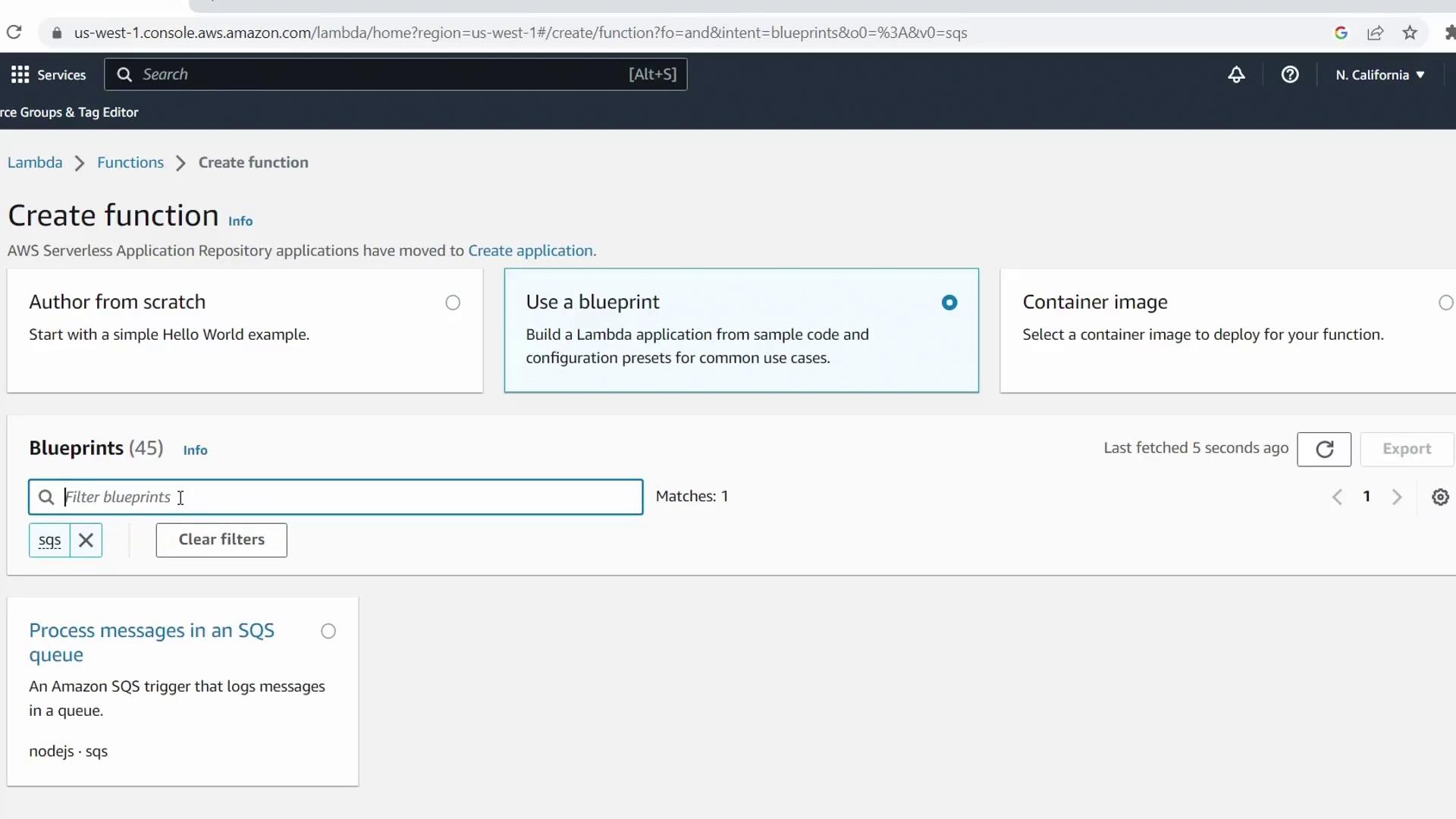
- Select the Blueprint tab
- Enter SQS in the filter box and choose the sqs-invoke-lambda blueprint
- Click Configure
Function Settings
- Function name:
KodeKloudSQSDemo - Execution role: Keep Create a new role from AWS policy templates
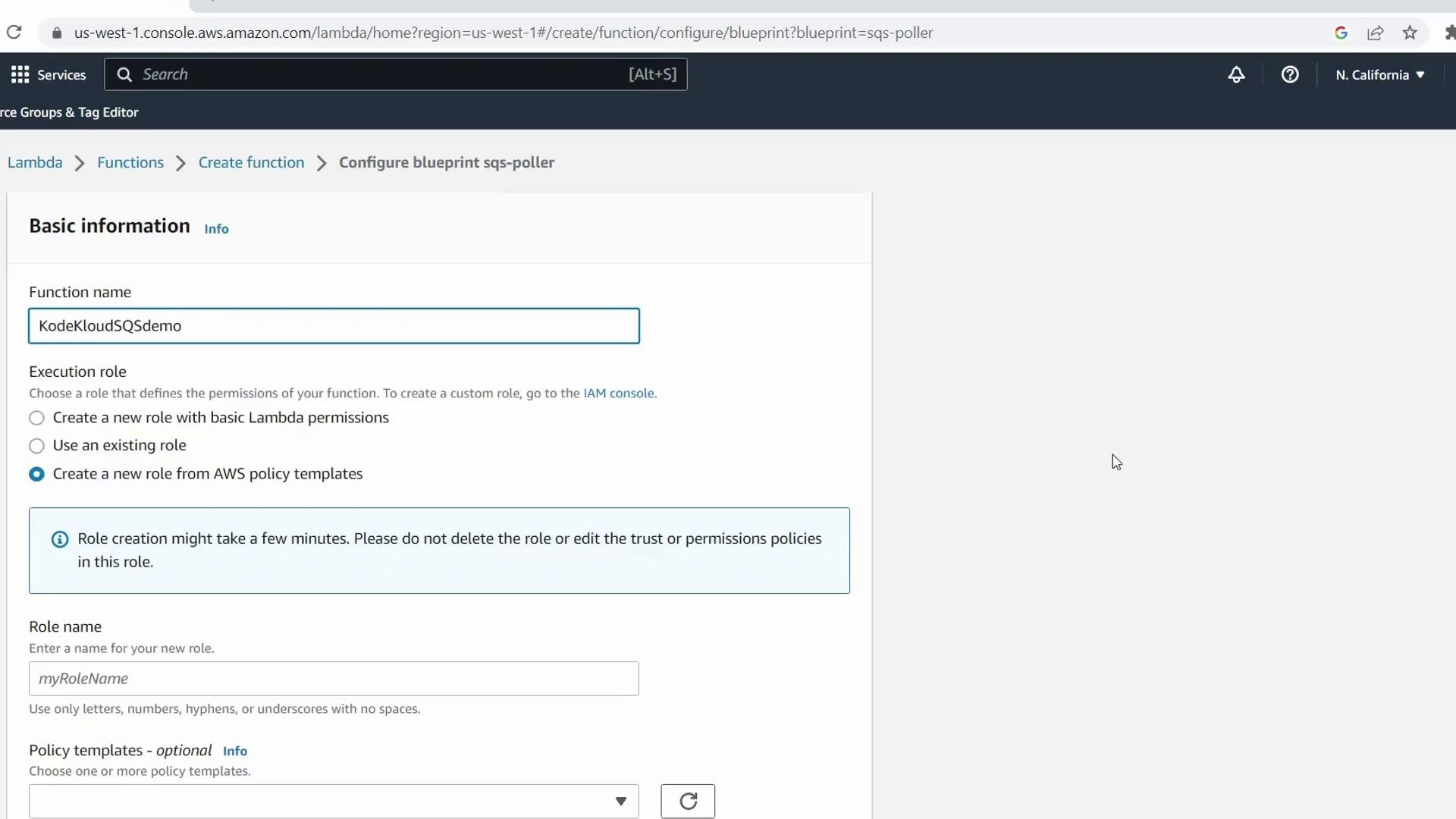
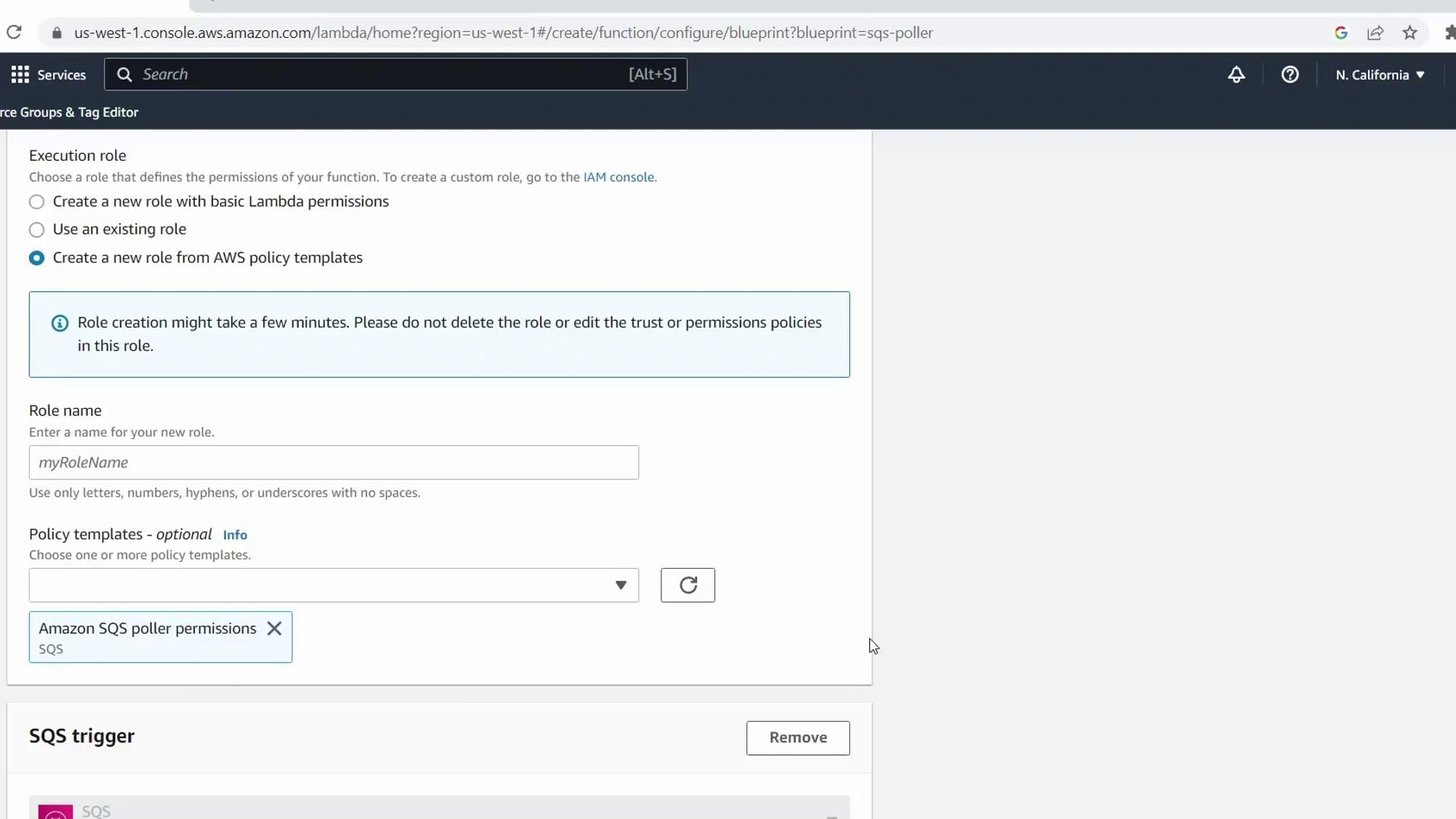
- Role name:
demo-lambda-sqs-role
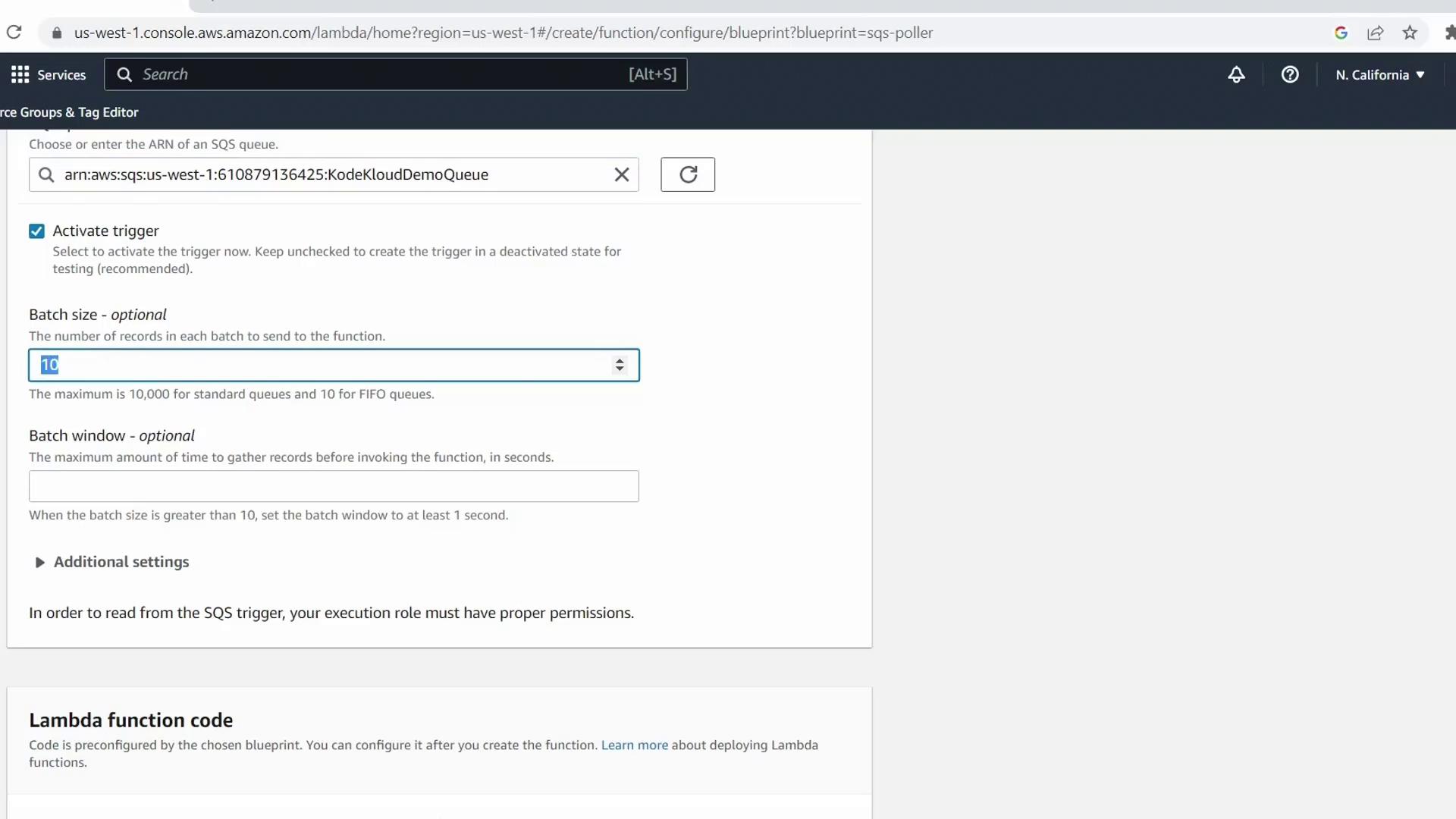
3. Configure the SQS Trigger
Under Configure triggers, pick yourKodeKloudDemoQueue queue.
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Batch size | 1 | Number of messages retrieved per Lambda invocation |
| Batch window | 1 s | Maximum wait time before invocation |
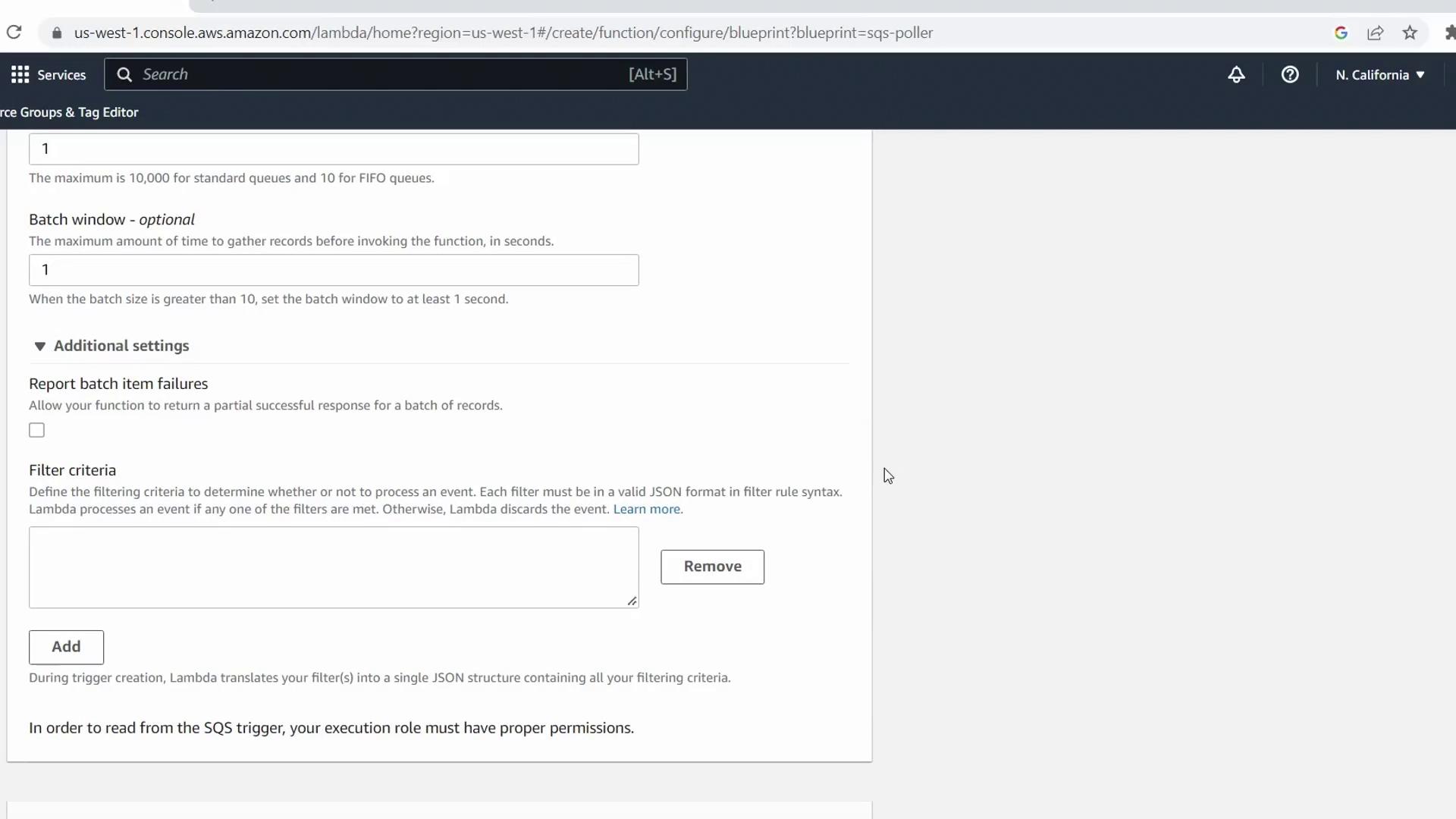
You can expand Additional settings to apply JSON filters or configure batch-item failure reporting. For this demo, we’ll skip filters.
4. Review and Deploy the Handler Code
The blueprint generates this sample Node.js handler: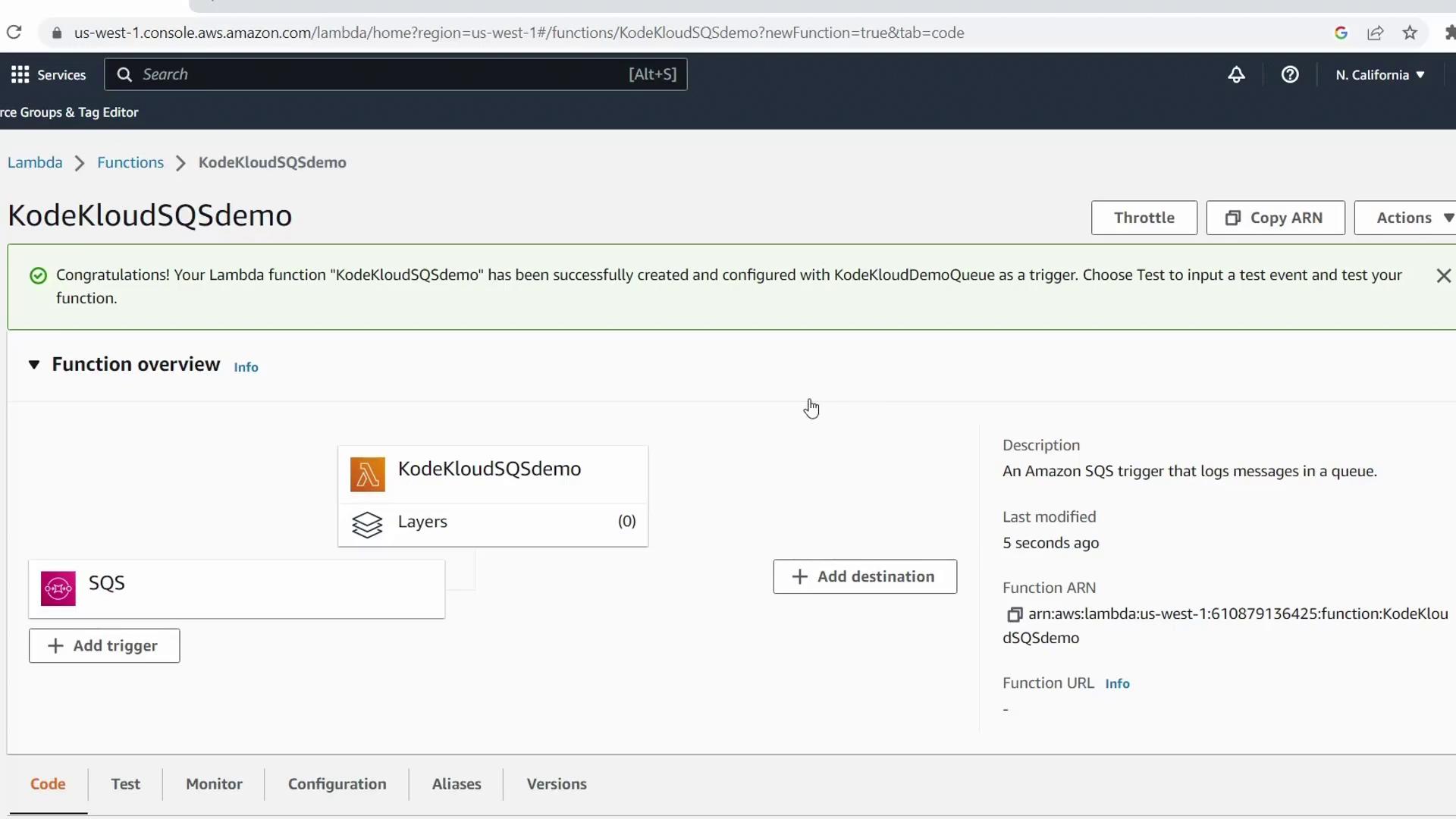
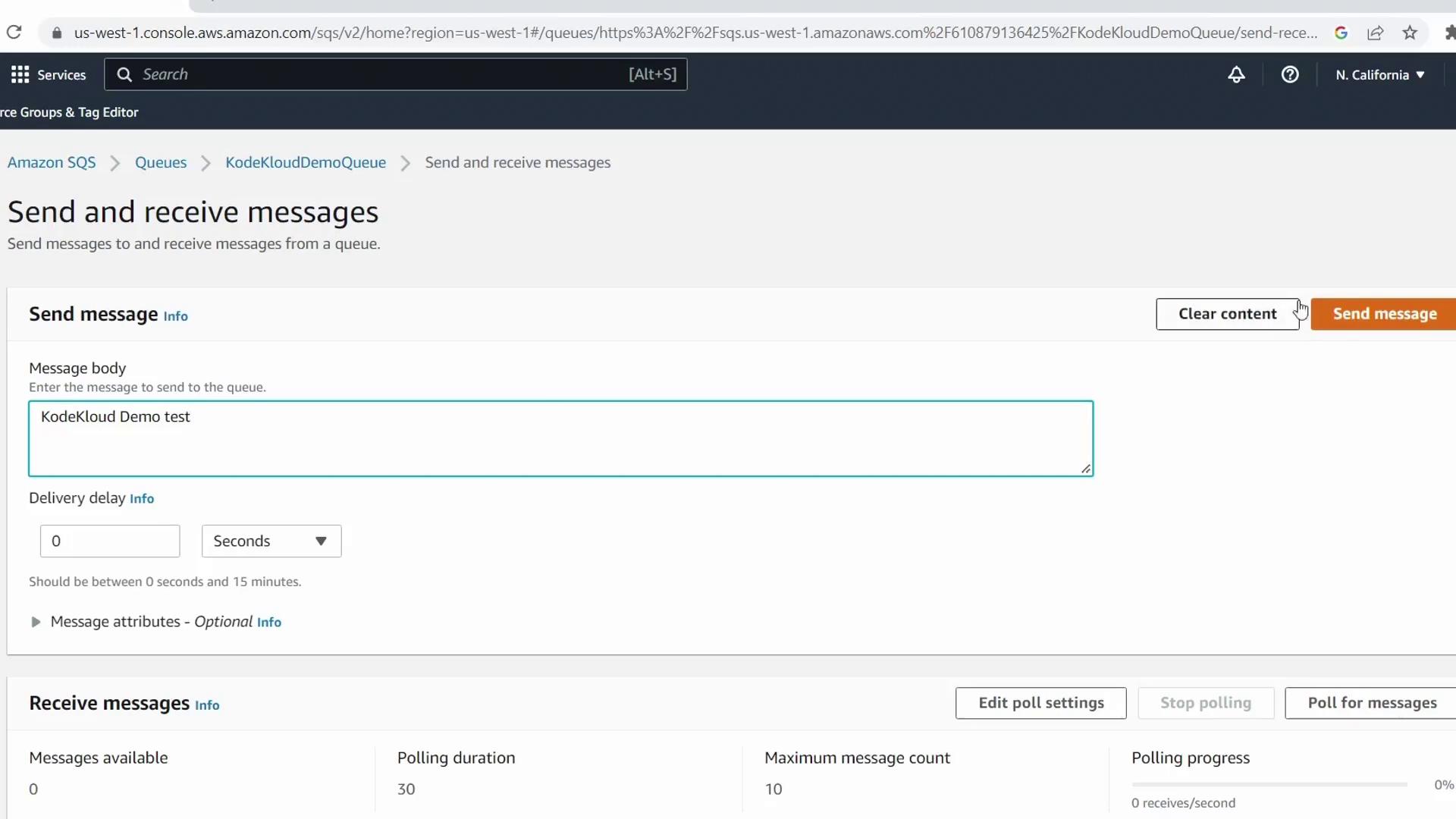
5. Send a Test Message to SQS
- In the AWS Console search bar, select Simple Queue Service
- Open KodeKloudDemoQueue
- Click Send and receive messages, enter KodeKloud Demo Test as the body, and hit Send message
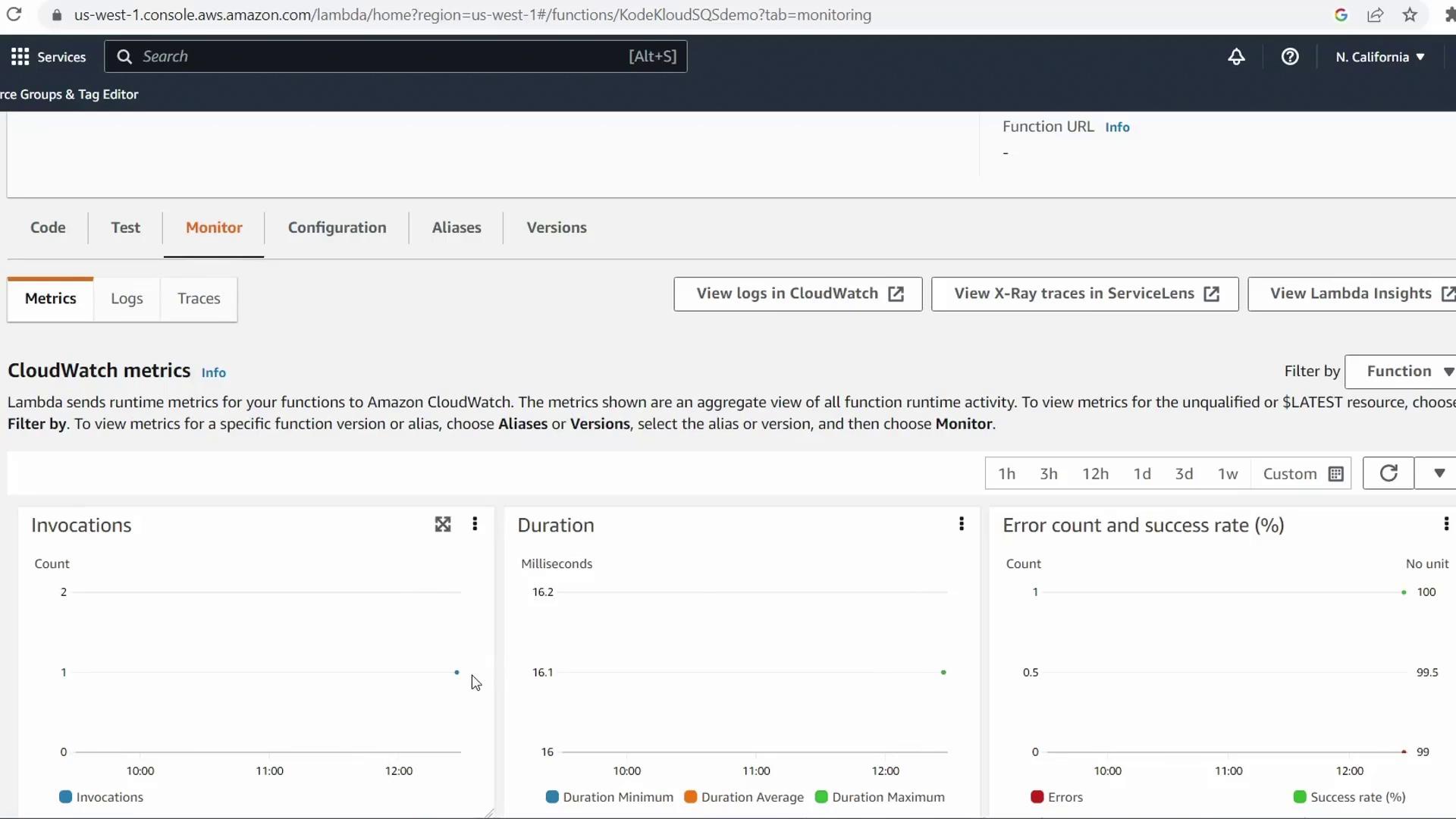
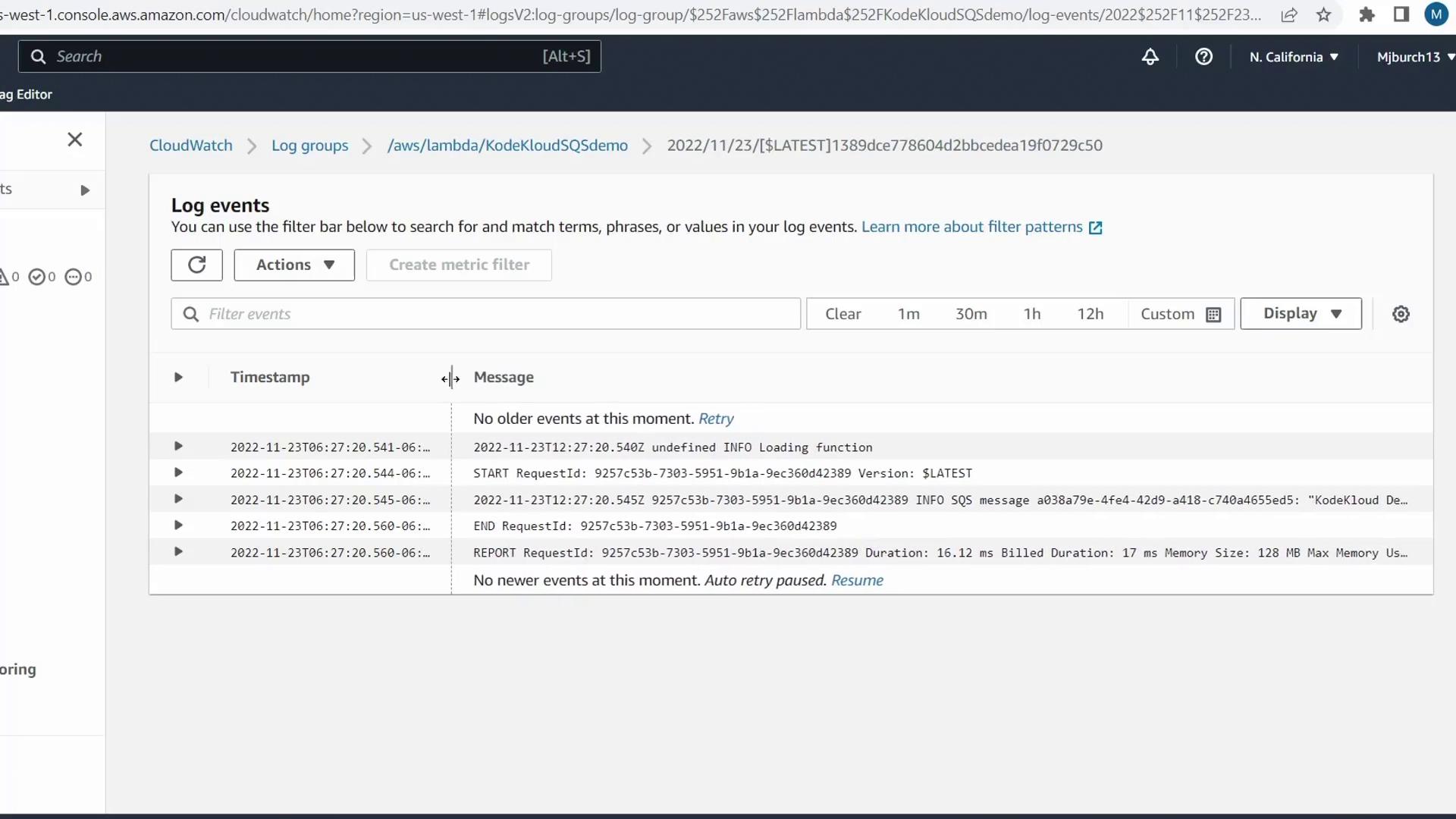
6. Verify Lambda Invocation in CloudWatch
- Return to the Lambda console for
KodeKloudSQSDemo - Select the Monitor tab
- Check Invocations and Errors in the CloudWatch metrics
Next Steps
You’ve successfully:- Created a Lambda function from the SQS blueprint
- Configured IAM roles and pull permissions
- Deployed an SQS trigger and processed a test message