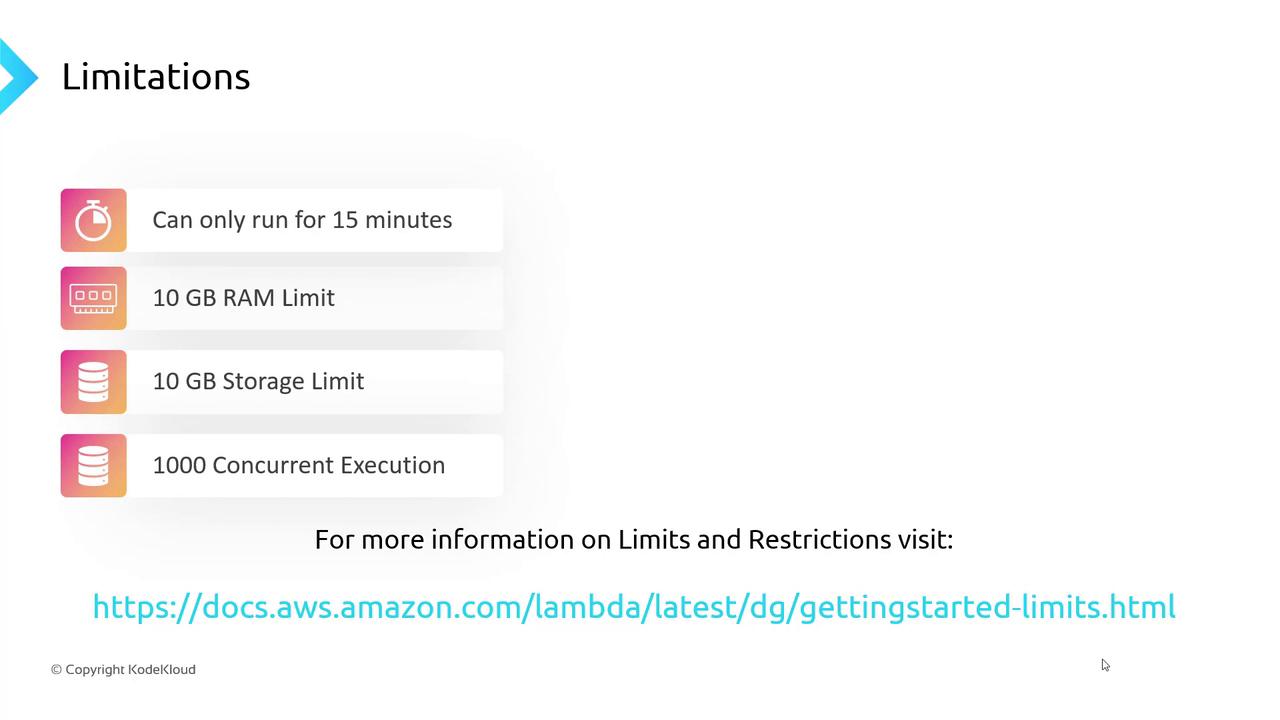
Key Service Limits
| Limit | Maximum | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Execution timeout | 15 minutes | Ideal for short-lived tasks. Long-running batch jobs may require alternative services. |
| Memory allocation | 128 MB – 10 GB | Configurable per function. Affects CPU power proportionally. |
Ephemeral storage (/tmp) | Up to 10 GB | Temporary read/write space that persists only during the invocation. |
| Concurrent executions | 1,000 (soft limit) | Burst up to 3,000 in some Regions. Request a quota increase via the AWS Service Quotas console. |
Memory allocation scales CPU and network throughput. Allocating more memory can improve performance for CPU-intensive workloads.
Ephemeral storage is not persistent. Data in
/tmp is lost after the function completes.To raise your concurrency limit permanently, open a quota increase request in the AWS Service Quotas console. Approval depends on your use case.
With Lambda’s primary limits on execution time, memory, storage, and concurrency covered, the next step is to implement robust monitoring and observability.