Domain Names for Private IP Addresses
When you launch an EC2 instance into a public or private subnet, AWS automatically assigns it a private IPv4 address (for example, 10.0.100.10). AWS also generates a DNS hostname that embeds this IP address. Clients can connect using either the private IP or the assigned DNS name.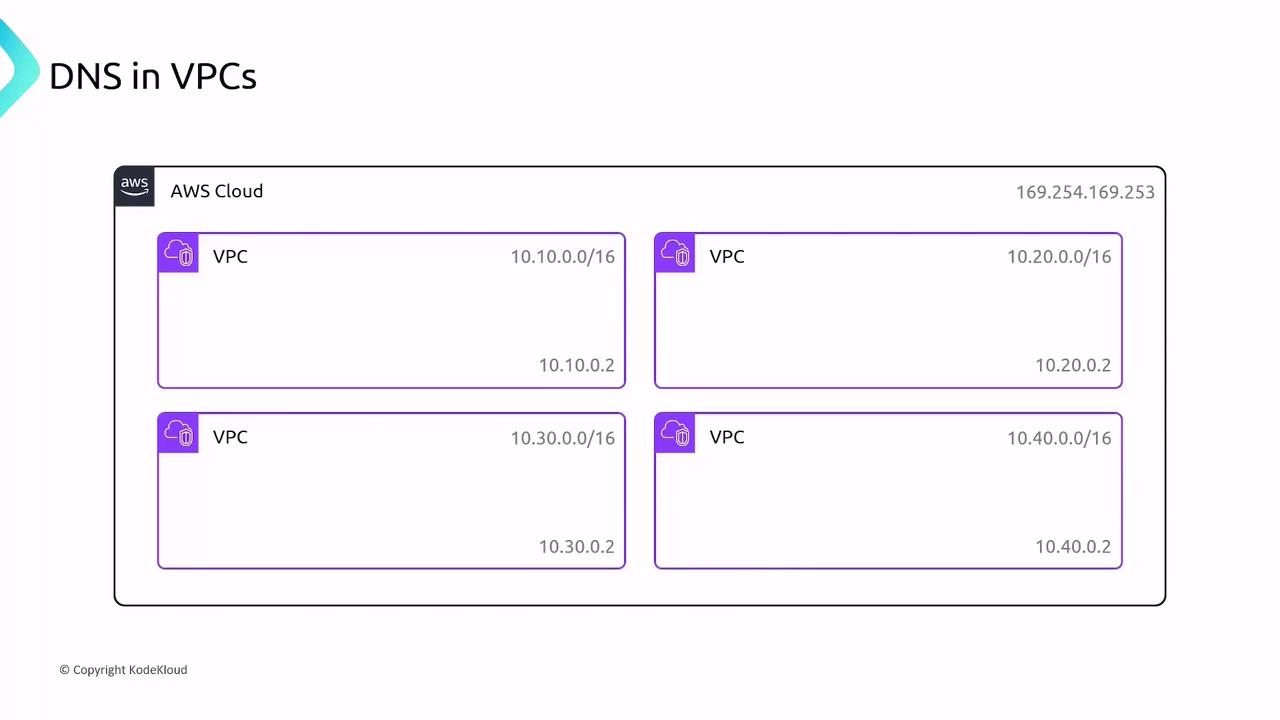
AWS-Provided DNS Servers
EC2 instances resolve these hostnames by querying the Amazon-provided DNS servers. AWS exposes two endpoints for DNS resolution within a VPC:- Link-local address: 169.254.169.253 (accessible from all instances)
- VPC CIDR second IP: e.g., 10.10.0.2 in a 10.10.0.0/16 VPC or 10.20.0.2 in a 10.20.0.0/16 VPC
In the default VPC, both DNS support and hostnames are enabled out of the box. Custom VPCs default to DNS support on and hostnames off.
VPC DNS Configuration Options
AWS provides two VPC attributes that control DNS behavior:| Option | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| enableDnsSupport | Enables DNS resolution via Amazon-provided DNS servers. | true (all VPCs) |
| enableDnsHostnames | Assigns DNS hostnames to instances with public IP addresses. | false for custom VPCs, true for default VPCs |

Disabling
enableDnsSupport prevents any DNS resolution within the VPC, which can break applications that rely on domain names.Summary
- Private IPv4 addresses are automatically mapped to DNS hostnames.
- Amazon-provided DNS endpoints are available at 169.254.169.253 and the VPC CIDR’s second IP.
- Use
enableDnsHostnamesto toggle DNS hostname assignment for instances with public IPs. - Use
enableDnsSupportto enable or disable DNS resolution within the VPC.