Challenges with VPC Peering
By default, VPCs are isolated. You must create peering connections to enable traffic flow:- VPC A ↔ VPC B
- VPC B ↔ VPC C
What Is AWS Transit Gateway?
AWS Transit Gateway acts as a regional network hub to interconnect your VPCs and on-premises environments with a single gateway.Simplified VPC Connectivity
Instead of a mesh of peerings, attach each VPC to the Transit Gateway:Subnet Attachments
When you attach a VPC to a Transit Gateway, you specify one subnet in each Availability Zone:- If your VPC spans AZ-A, AZ-B, and AZ-C, create three Transit Gateway subnets.
- TGW uses these subnets for routing and high availability.
Each Transit Gateway attachment requires at least one subnet per AZ. Plan your AZ strategy accordingly to avoid single points of failure.
Centralized On-Premises Connectivity
You can terminate all VPN and Direct Connect circuits on the Transit Gateway, reducing tunnel count and improving bandwidth utilization.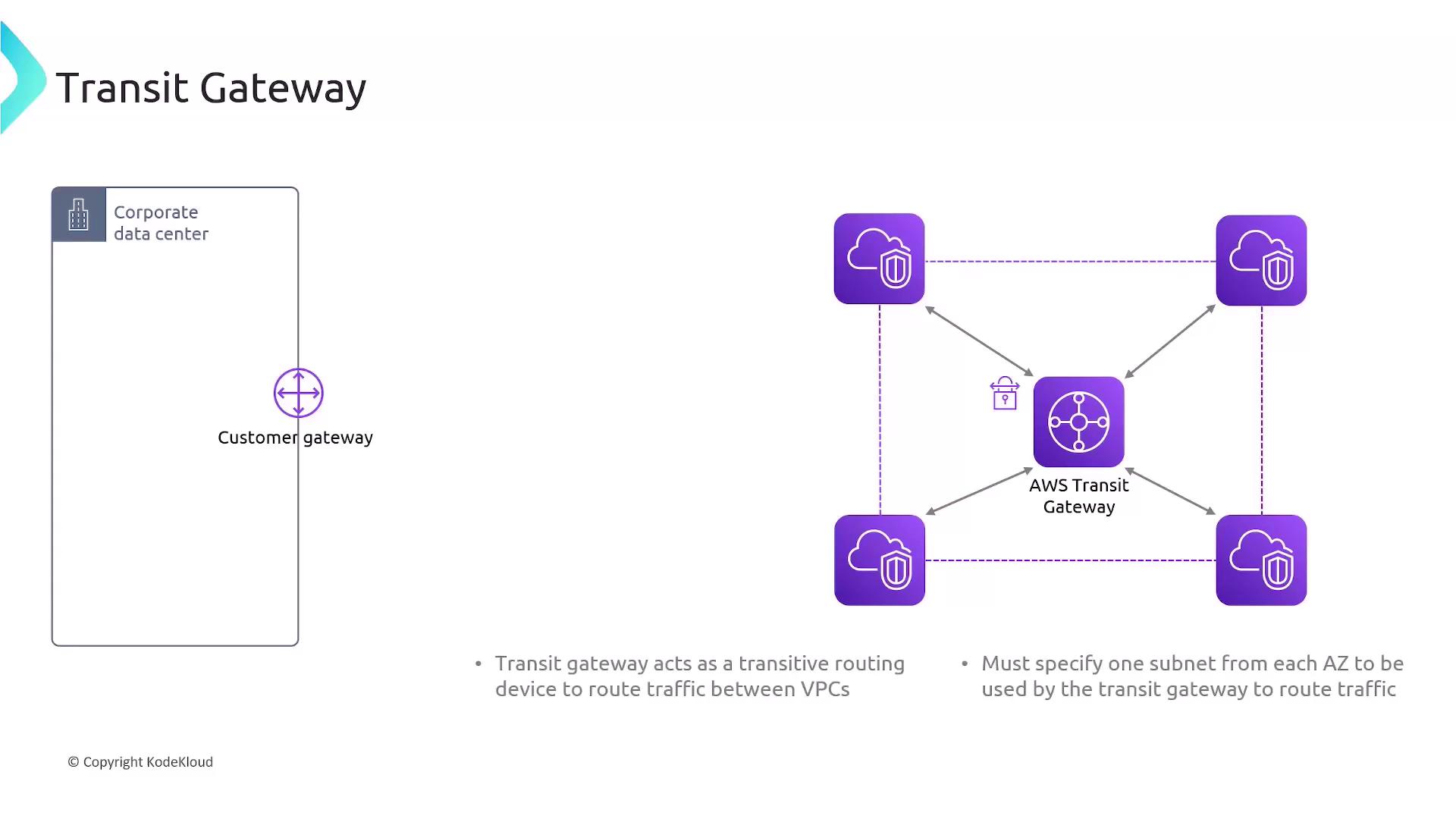
- VPN Consolidation: One VPN tunnel to TGW replaces N tunnels to N VPCs.
- Direct Connect: Attach a DX gateway to TGW for high throughput and low latency.
Transit Gateway Peering
Use Transit Gateway peering to connect hubs across regions or accounts: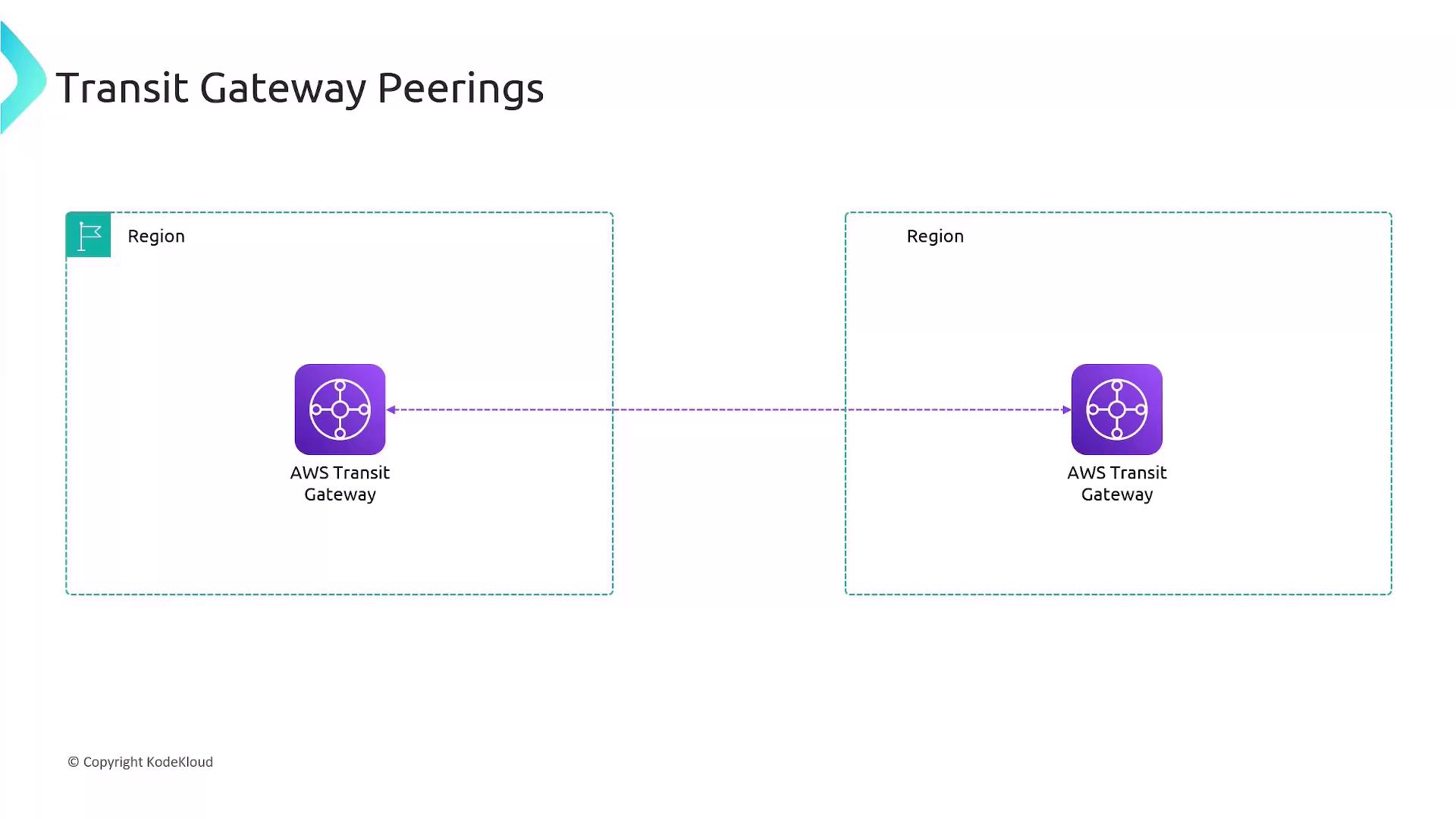
| Peering Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Inter-Region | Connect TGWs in different AWS Regions |
| Cross-Account | Share TGW attachments across AWS accounts |
Key Features and Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Simplified Topology | Single hub replaces complex VPC mesh and point-to-point links |
| Transitive Routing | Automatic routing between all attached VPCs and on-prem networks |
| Subnet Attachments | High availability with one subnet per AZ |
| Peering Capabilities | Global reach via cross-region and cross-account connections |
Ensure your AWS account limits and route table entries align with the number of Transit Gateway attachments to avoid resource exhaustion.
By adopting AWS Transit Gateway, you streamline your network architecture, enable scalable transitive routing, and centralize connectivity for both cloud and on-premises environments.