Core Concepts
1. Data Stream
A data stream is a continuous flow of information, such as temperature readings from IoT sensors, log data, or financial transactions. This continuous collection is vital for capturing trends over time, which can be used for monitoring, analysis, or predictive analytics.2. Event Processing
Event processing deals with discrete occurrences. Think of a car passing through a tollgate: as the vehicle passes, details like license plate number, VIN, timestamp, and other relevant data are immediately captured, processed, and stored. This rapid processing is essential for real-time decision-making.The End-to-End Process
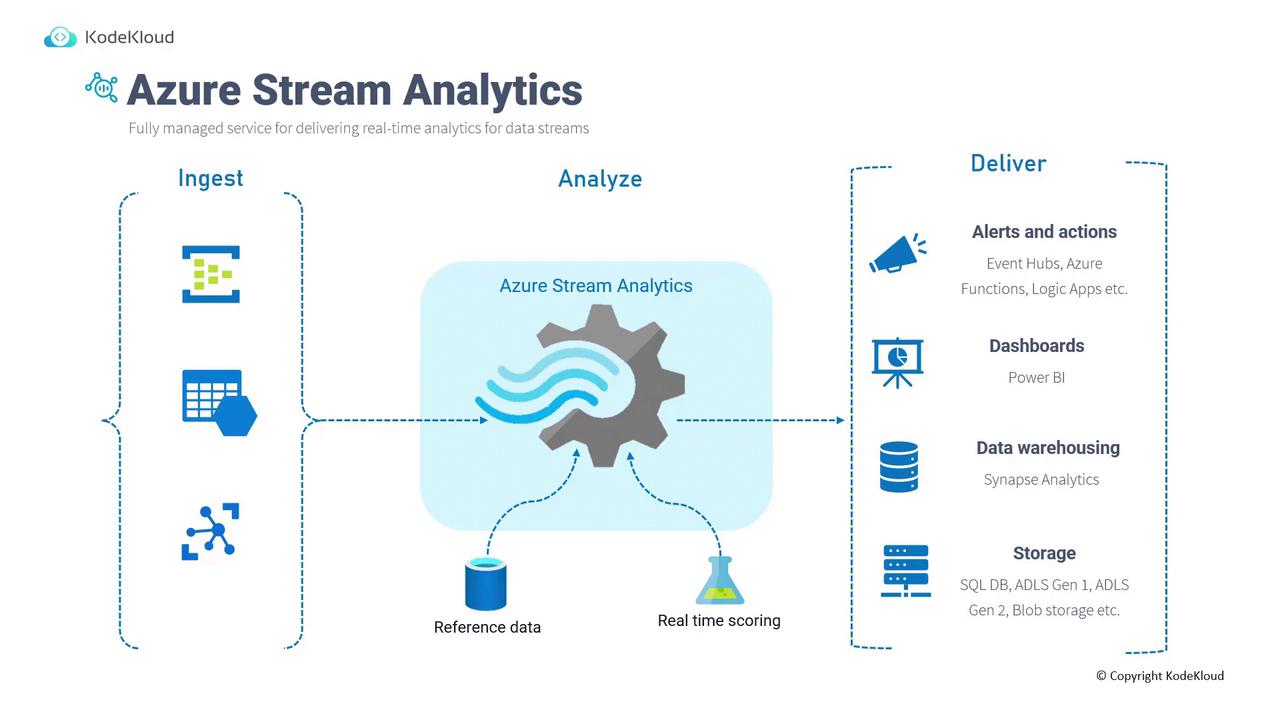
Azure Stream Analytics follows a three-stage process: ingestion, analysis, and delivery.Data Ingestion
Data ingestion is the first step where data from diverse sources is collected. Common sources include:- IoT devices
- Log files
- Financial transactions
- Weather data
- Business applications
Data Analysis
Once the data is ingested, Azure Stream Analytics utilizes its robust analytics engine for real-time processing. For example, an IoT sensor sending temperature readings every minute to an IoT Hub can have its streaming data evaluated against historical reference data (e.g., temperature readings from the past week) to perform real-time scoring and predictive analytics, such as forecasting upcoming temperature trends.Data Delivery
After analysis, the processed data is delivered for several downstream applications, including:- Triggering alerts and automated actions
- Updating interactive dashboards
- Consolidating data in Synapse Analytics for data warehousing
- Storing results in SQL databases, ADLS, or Blob Storage
Benefits of Azure Stream Analytics
Azure Stream Analytics is fully managed by Microsoft, which means you avoid the overhead of setting up and maintaining infrastructure. The service is cost-effective, easy to deploy, high-performing, and equipped with robust security features.Azure Stream Analytics’s fully managed approach significantly reduces administrative overhead, allowing you to focus on extracting insights from your data.

When to Use Azure Stream Analytics
Azure Stream Analytics is ideal for many real-time data processing scenarios. Here are five key use cases:- IoT Data Streams: Analyze real-time data from IoT sensors.
- Clickstream Analysis: Process web log data to enhance customer engagement, such as suggesting new products based on browsing habits.
- Geospatial Analytics: Monitor streaming data from satellite images, mobile devices, or sensors to track weather changes or geospatial metrics.
- Remote Monitoring: Collect data from industrial machinery to predict maintenance requirements and prevent downtime.
- POS Data Analysis: Analyze point-of-sale data to detect anomalies and potential fraudulent credit card transactions.

Designing an Effective Data Flow Strategy
In the next section, we will explore strategies for designing an effective data flow using Azure Stream Analytics. This involves carefully planning the methods for ingesting, processing, and delivering data to ensure that business requirements are met efficiently.Understanding the interplay between data ingestion, analysis, and delivery is essential for building robust real-time data solutions with Azure Stream Analytics.