Advanced Bash Scripting
Globs
Globs Question Mark
In this lesson, we dive into how the ? wildcard works in glob patterns. In Bash and most shells, ? matches exactly one character, so the filenames must align in length with your pattern. This enables precise control over file selection by combining fixed text and single-character placeholders.
? Wildcard Basics
?replaces exactly one character.- Does not match zero characters.
- Treats the dot (
.) as an actual character (unlessdotglobis enabled).
Note
The ? wildcard differs from *, which matches zero or more characters. Use ? when you need strict length matching.
Example 1: Single Character Prefix Before “ail”
Assume the directory contains:
rail, Document.doc, fail, hail, bar, sail, foo, mail, 4ail, foobar.
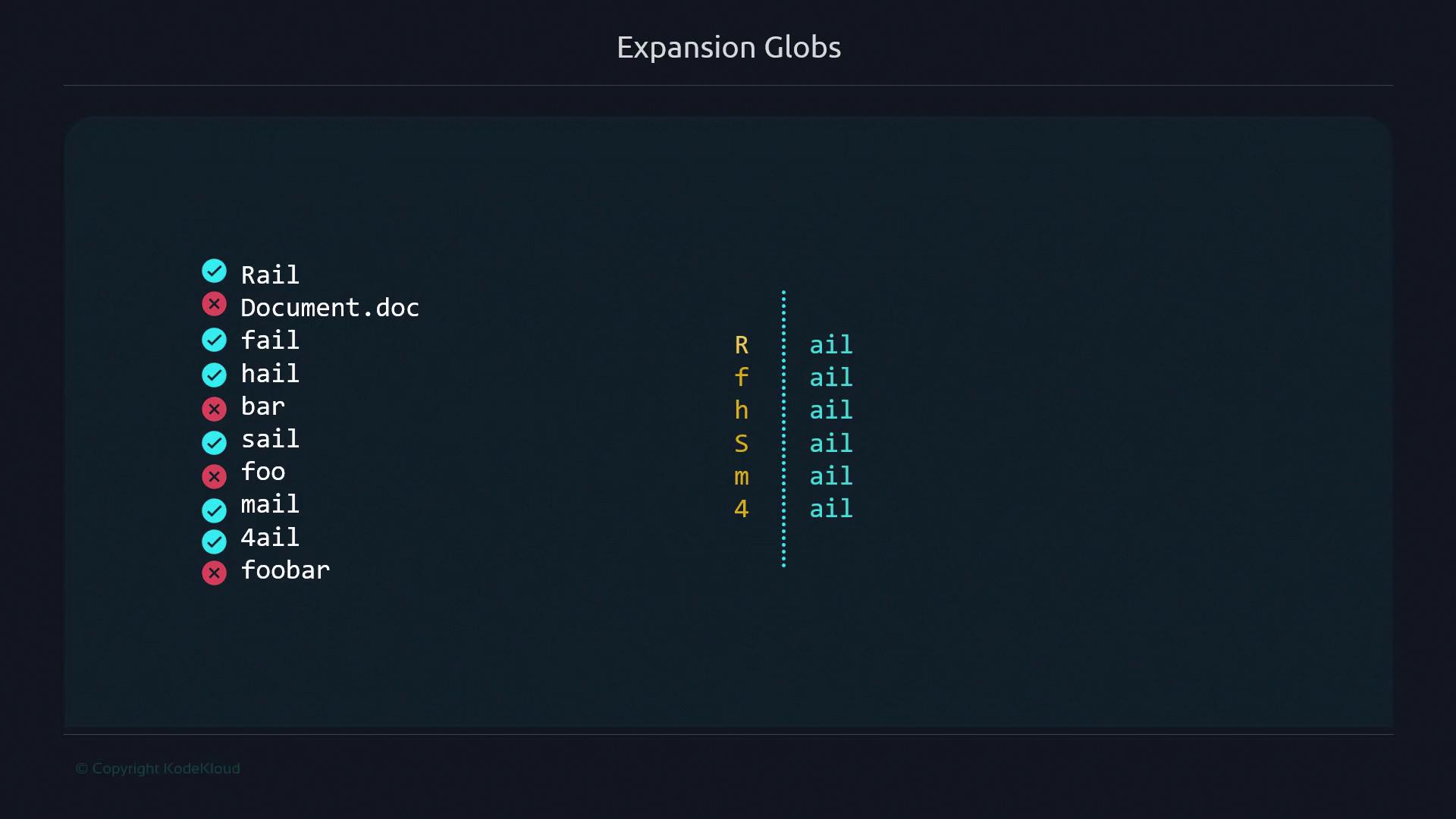
Use ?ail to match any single-character prefix followed by ail:
$ ls
rail Document.doc fail hail bar sail foo mail 4ail foobar
$ ls ?ail
rail fail hail sail mail 4ail
?matches one character (r,f,h,s,m,4).ailanchors the suffix.
Example 2: “tes” + Two Characters + “.txt”
Directory listing:
test.sh, file.txt, tes1t.txt, test2.txt, file1.txt.

With the pattern tes??.txt:
$ ls
test.sh file.txt tes1t.txt test2.txt file1.txt
$ ls tes??.txt
tes1t.txt test2.txt
tesfixes the first three letters.??matches exactly two characters (1t,2.)..txtmatches the file extension.
Example 3: “test” + One Character + “.txt”
Consider these files:
test1-2.txt, tes1t.txt, test2.txt, test3.sh, test1.txt, file1.txt.

Use test?.txt to find files with a single character after test and before .txt:
$ ls
test1-2.txt tes1t.txt test2.txt test3.sh test1.txt file1.txt
$ ls test?.txt
test1.txt test2.txt
testanchors the prefix.?matches one character (1,2)..txtensures the extension.
Example 4: One Character + “est.” + Three Characters
Matching pattern ?est.??? to include any one-character prefix, est., and exactly three characters as the extension:
$ ls
test.txt vest.txt test.jpg file.sh rest.txt west.doc
$ ls ?est.???
test.txt vest.txt test.jpg rest.txt west.doc
?estallows any single first character.- The
.afterestis literal. ???requires exactly three-character extension.
Example 5: Exactly Four-Character Filenames
Directory content:
1234, abcd, kei5, some_file.txt, x0f4p, 90c1, dir, keio5, touch, x0fp.
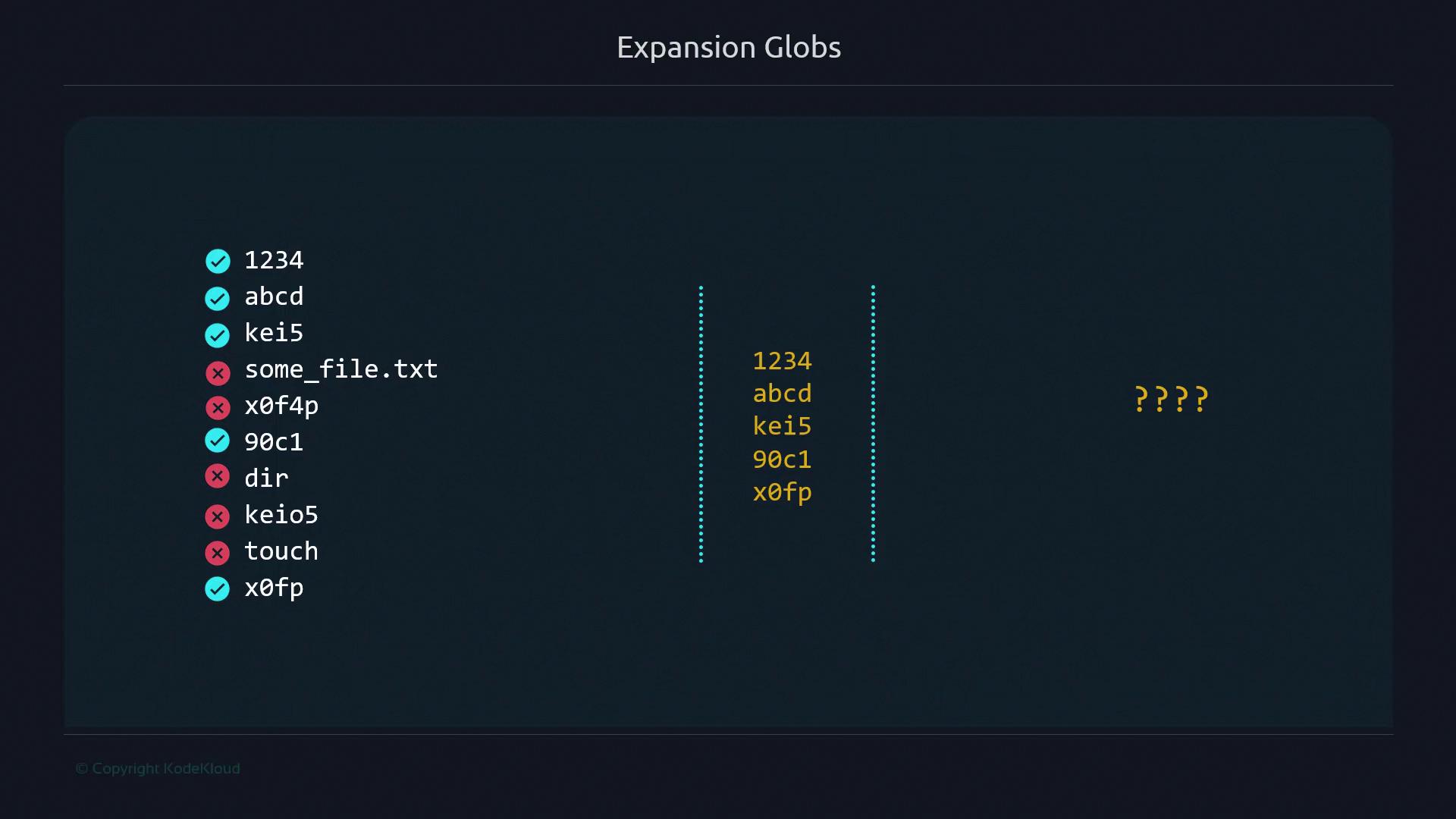
Pattern ???? finds names exactly four characters long:
$ ls
1234 abcd kei5 some_file.txt x0f4p 90c1 dir keio5 touch x0fp
$ ls ????
1234 abcd kei5 90c1 x0fp
- Four
?must each match one character. - Filters out any name not exactly four characters.
Conclusion
Using the ? wildcard in your glob patterns helps you precisely filter filenames by length and content. Combine fixed text with ? placeholders to tailor your matches exactly.
Links and References
Ensure you enable dotglob if you want to include hidden files in matches:
shopt -s dotglob
Watch Video
Watch video content