Understanding string interpolation in Jenkins pipelines is essential for creating dynamic build messages, parameterized workflows, and environment-aware configurations. This guide demonstrates how Groovy handles single-quoted and double-quoted strings and walks through a Jenkinsfile showcasing various interpolation techniques.
Why String Interpolation Matters
Simplifies logging and notifications
Enables dynamic parameter and environment variable usage
Integrates arithmetic and complex Groovy expressions
In Groovy, single quotes produce literal strings, while double quotes evaluate ${} expressions.
Single vs. Double-Quoted Strings def singlyQuoted = 'Hello' def doublyQuoted = "World" def username = 'Jenkins' echo 'Hello Mr. ${username}' // Outputs: Hello Mr. ${username} echo "I said, Hello Mr. ${ username } " // Outputs: I said, Hello Mr. Jenkins
Quote Type Behavior Example Single Quotes Literal string; no eval ’Hello $‘ Double Quotes Enables interpolation ”Hello $“
Complete Jenkinsfile Example pipeline { agent any parameters { string( name : 'USER_NAME' , defaultValue : 'Hello, Jenkins from Parameter' , description : 'Name of the user' ) } environment { GREETING = 'Hello, Jenkins! from environment variable' } stages { stage( 'Print Basic String' ) { steps { echo 'Basic String Interpolation Examples:' } } stage( 'Interpolation with Variable' ) { steps { script { def name = 'Jenkins User' echo 'Hello, ${name}!' // single quotes: no interpolation echo "Hello, ${ name } !" // double quotes: interpolates } } } stage( 'Interpolation with Parameter' ) { steps { script { echo "Hello, ${ params.USER_NAME } " } } } stage( 'Interpolation with Environment Variable' ) { steps { script { echo "Environment Variable Greeting: ${ env.GREETING } " } } } stage( 'Interpolation with Expression' ) { steps { script { def x = 5 def y = 10 echo "Sum of x and y is: ${ x + y } " } } } stage( 'Complex Interpolation' ) { steps { script { def list = [ 1 , 2 , 3 ] echo "The list has ${ list.size() } items: ${ list.join(', ') } " } } } stage( 'Job Parameters' ) { steps { script { def buildNumber = currentBuild . number echo "This is build number ${ buildNumber } " } } } } }
Stage 1: Print Basic String A straightforward echo of a static message.
Basic String Interpolation Examples:
Stage 2: Interpolation with Variable Comparing single vs. double quotes around a Groovy variable.
def name = 'Jenkins User' echo 'Hello, ${name}!' // single quotes: no interpolation echo "Hello, ${ name } !" // double quotes: interpolates
Hello, ${name}! Hello, Jenkins User!
Stage 3: Interpolation with Parameter Displaying a pipeline parameter using params.
echo "Hello, ${ params.USER_NAME } "
Hello, Hello, Jenkins from Parameter
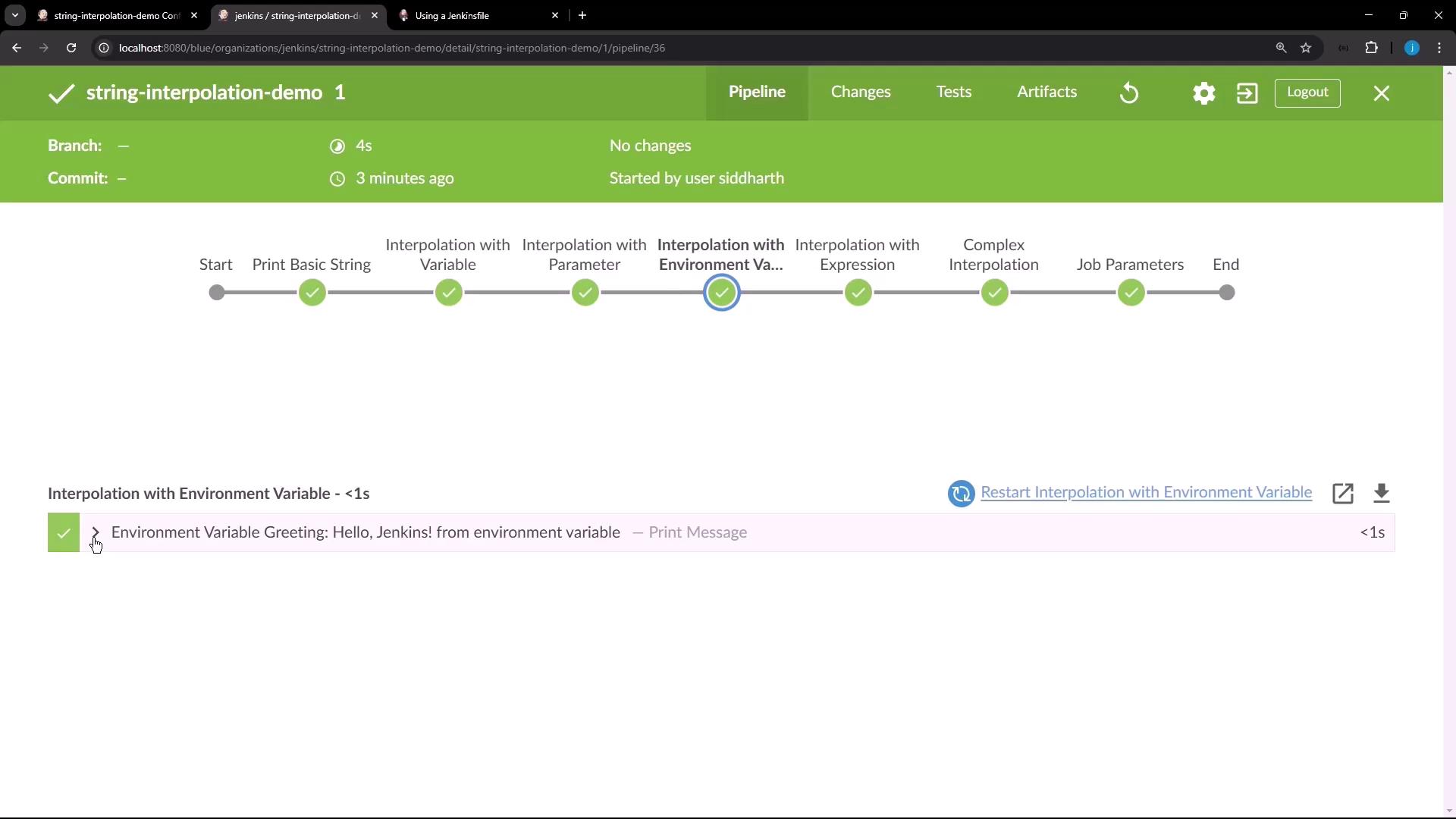
Stage 4: Interpolation with Environment Variable Pulling in an environment variable via env.
echo "Environment Variable Greeting: ${ env.GREETING } "
Environment Variable Greeting: Hello, Jenkins! from environment variable
Stage 5: Interpolation with Expression Executing arithmetic inside the interpolation.
def x = 5 def y = 10 echo "Sum of x and y is: ${ x + y } "
Stage 6: Complex Interpolation Leveraging list methods directly in the string.
def list = [ 1 , 2 , 3 ] echo "The list has ${ list.size() } items: ${ list.join(', ') } "
The list has 3 items: 1, 2, 3
Stage 7: Job Parameters Accessing the current build number for dynamic context.
def buildNumber = currentBuild . number echo "This is build number ${ buildNumber } "
Additional Resources