Certified Jenkins Engineer
Pipeline Enhancement and Caching
Demo Sequential stages
Sequential stages in a Jenkins pipeline let you break down work inside each parallel branch into ordered steps. Introduced in late 2018, this feature boosts pipeline visibility by displaying each sub-stage separately—no need to drill into logs to monitor progress.
Note
You’ll need Jenkins 2.x with Pipeline plugin 2.5 or later to use nested stages in a declarative pipeline.
Original Jenkinsfile
Below is a simplified excerpt showing the original declarative pipeline that defined only one stage per branch. This setup runs Node.js commands and tests all at once.
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('NodeJS 20') {
agent {
docker {
image 'node:20-alpine'
}
}
options { retry(2) }
steps {
sh 'node -v'
sh 'npm test'
}
}
stage('Code Coverage') {
// Coverage steps...
}
}
}
Adding Sequential Stages
To split the NodeJS 20 branch into two sequential steps—installing dependencies first, then testing—nest a stages block inside the existing stage:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('NodeJS 20') {
agent {
docker {
image 'node:20-alpine'
}
}
stages {
stage('Install Dependencies') {
options { retry(2) }
steps {
sh 'node -v'
sh 'npm install --no-audit --cache .'
}
}
stage('Testing') {
options { retry(2) }
steps {
sh 'node -v'
sh 'npm test'
}
}
}
}
stage('Code Coverage') {
// Coverage steps...
}
}
}
This configuration ensures Install Dependencies completes before Testing begins, all within the same parallel branch.
Committing and Triggering the Pipeline
Save your changes, then commit and push to trigger a new build:
git commit -m "Add sequential stages for NodeJS pipeline"
git push
After pushing, Jenkins will queue a new build (for example, pipeline #14). In the Blue Ocean or classic view you’ll now see separate steps for installing dependencies and running tests.
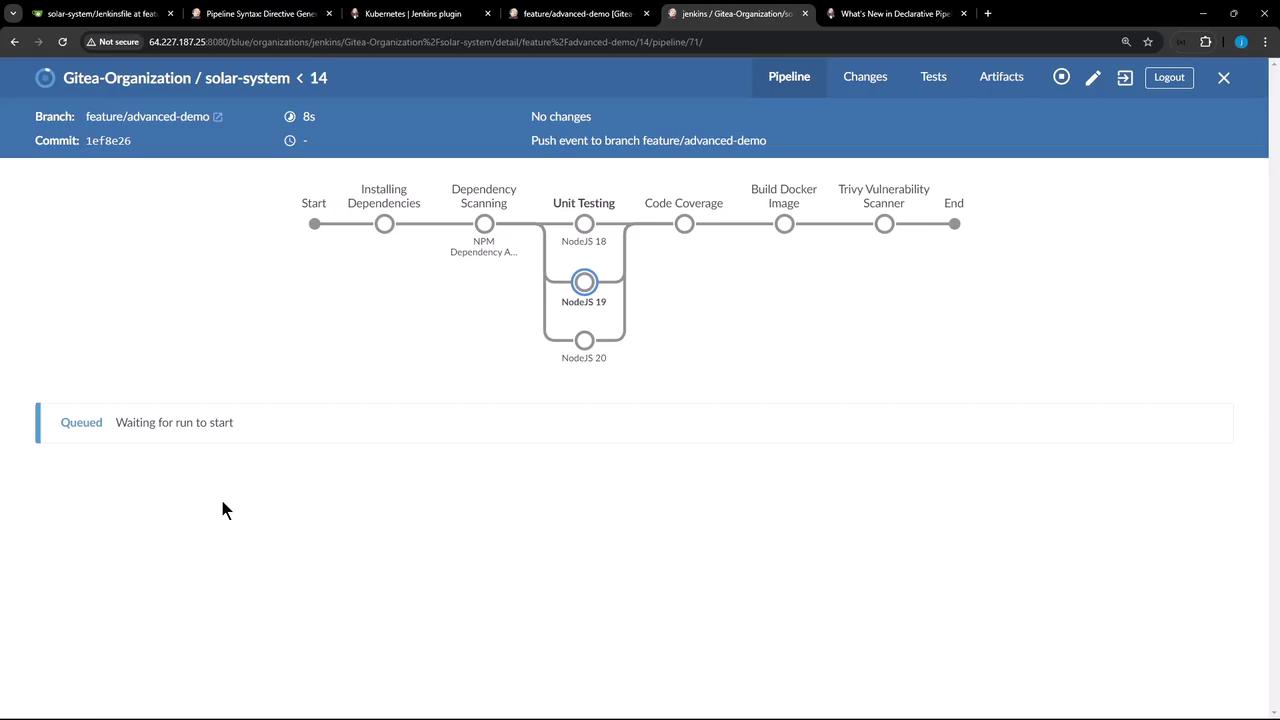
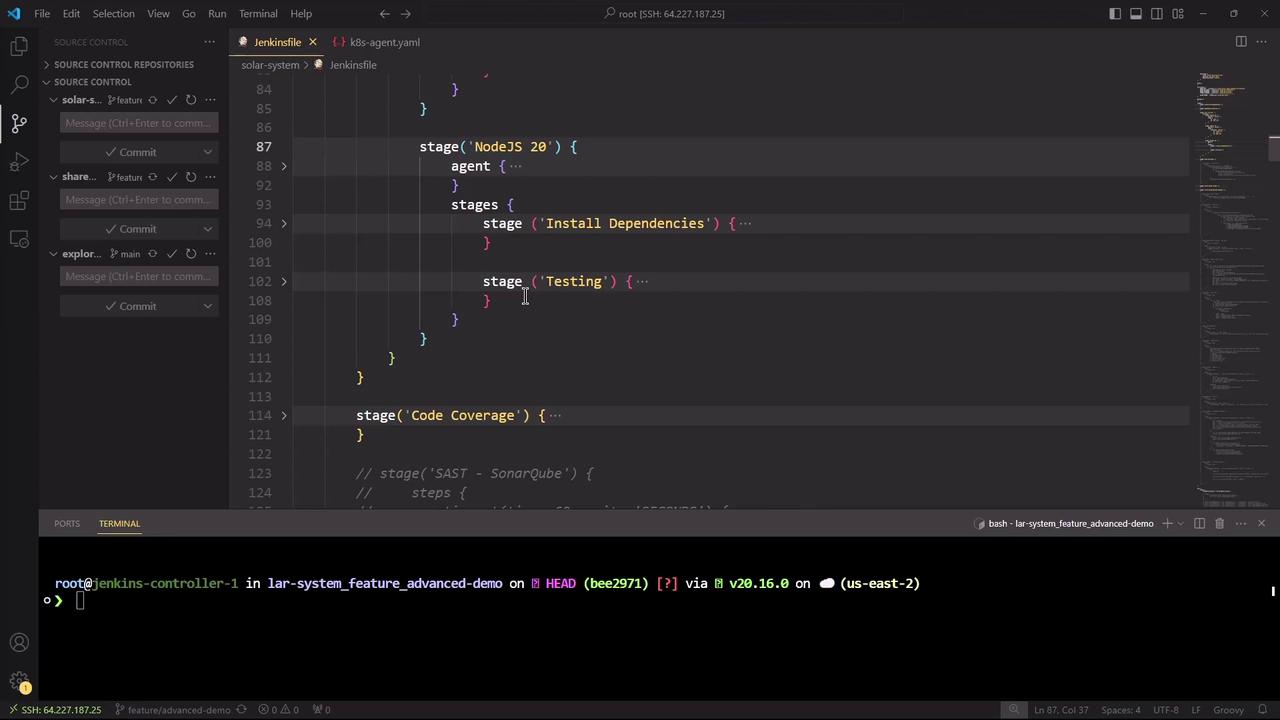
Viewing the Jenkinsfile in VS Code
Open the Jenkinsfile in your IDE to review the nested stages syntax. In this example, Visual Studio Code displays both the pipeline structure and an SSH session to the Jenkins controller.
Handling a Node.js Cache Error
In one run, the Install Dependencies stage failed due to a Node.js cache error:
npm install --no-audit --cache .
npm ERR! code ENOTEMPTY
npm ERR! syscall rename
npm ERR! path '/var/lib/jenkins/workspace/lar-system_feature_advanced-demo/node_modules/chai'
npm ERR! dest '/var/lib/jenkins/workspace/lar-system_feature_advanced-demo/node_modules/.chai-51vnicl6v'
npm ERR! errno -39
npm ERR! ENOTEMPTY: directory not empty, rename '.../node_modules/chai' -> '.../.chai-51vnicl6v'
Warning
This error originates from Node.js/npm and is not caused by Jenkins. Because Install Dependencies failed, the Testing stage was skipped—demonstrating how nested stages enforce correct execution order.
Summary
- Sequential stages improve clarity when you need ordered steps inside a parallel branch.
- Nested
stagesblocks are fully compatible with Docker agents,options, andpostactions. - You can share workspaces (e.g., installed
node_modules) between sequential stages automatically.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content