1. Shared Library Code
Assume your repository has a Groovy helper undervars/notifySlack.groovy:
notifySlack() in your pipelines, configure the Shared Library in Jenkins.
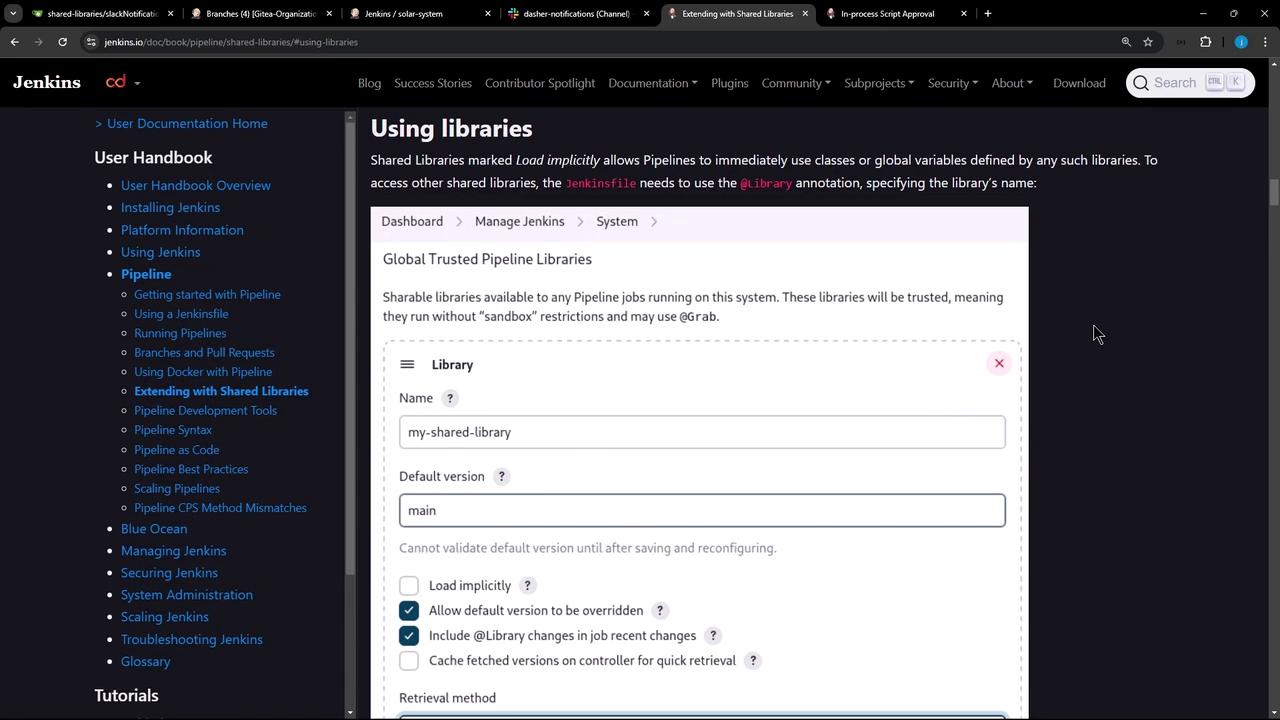
2. Configure Shared Library in the Jenkins UI
- Navigate to Jenkins Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Configure System.
- Scroll down to Global Pipeline Libraries.
- Click Add to define a new library.
Trusted vs. Untrusted Libraries
| Library Type | Sandbox | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Trusted | No restrictions | Your own libraries or organization-owned |
| Untrusted | Groovy sandbox | Community or third-party libraries; limited |
Untrusted libraries run in the Groovy sandbox. If your code calls methods not whitelisted, you’ll see errors like:Admin approval is required to whitelist new methods.
3. Adding a Trusted Shared Library
In Global Pipeline Libraries, fill out:- Name:
Dasher-Trusted-Shared-Libraries - Default version:
main - Load implicitly: unchecked
- Allow default version to be overridden: checked
- Include in job recent changes: as desired
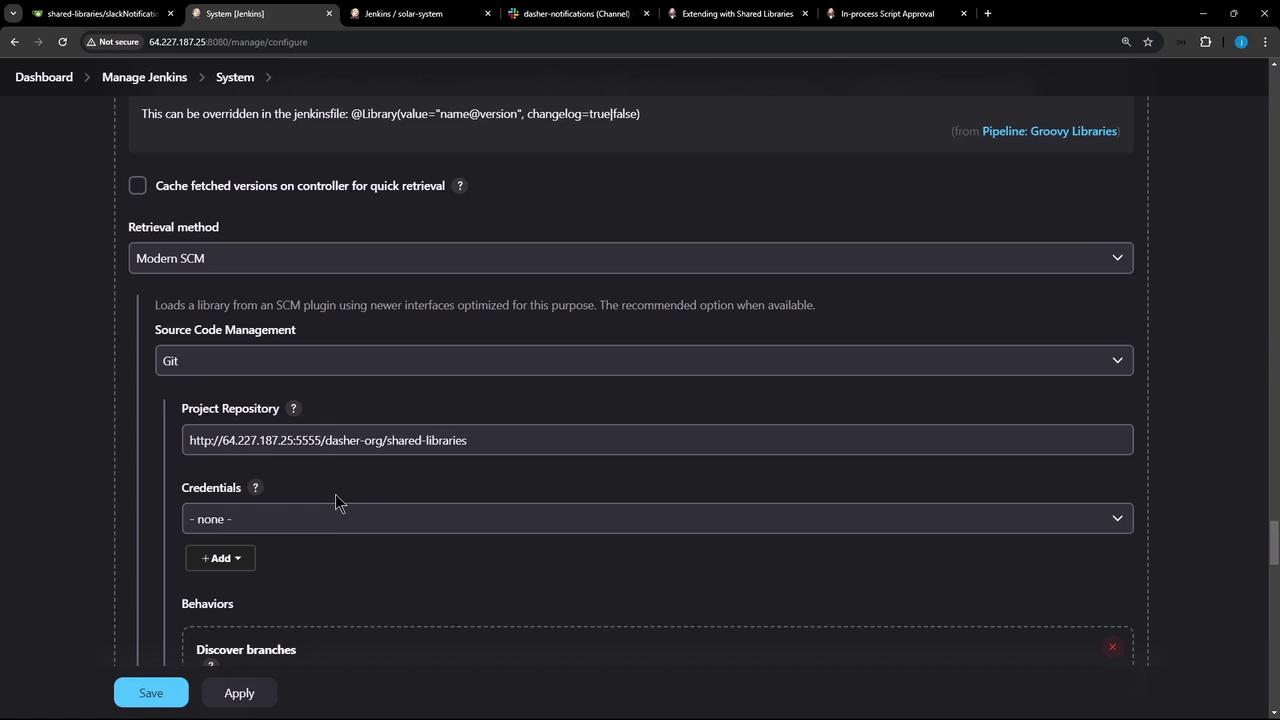
- Retrieval method: Git
- Project repository:
<your-repo-URL> - Credentials: none (public repo)
4. Pulling Dependencies with @Grab
Trusted libraries can use@Grab to fetch third-party Java dependencies from Maven Central:
@Grab works only in a trusted library (no sandbox). Attempting it in an untrusted library triggers sandbox violations and requires admin approval for each new method.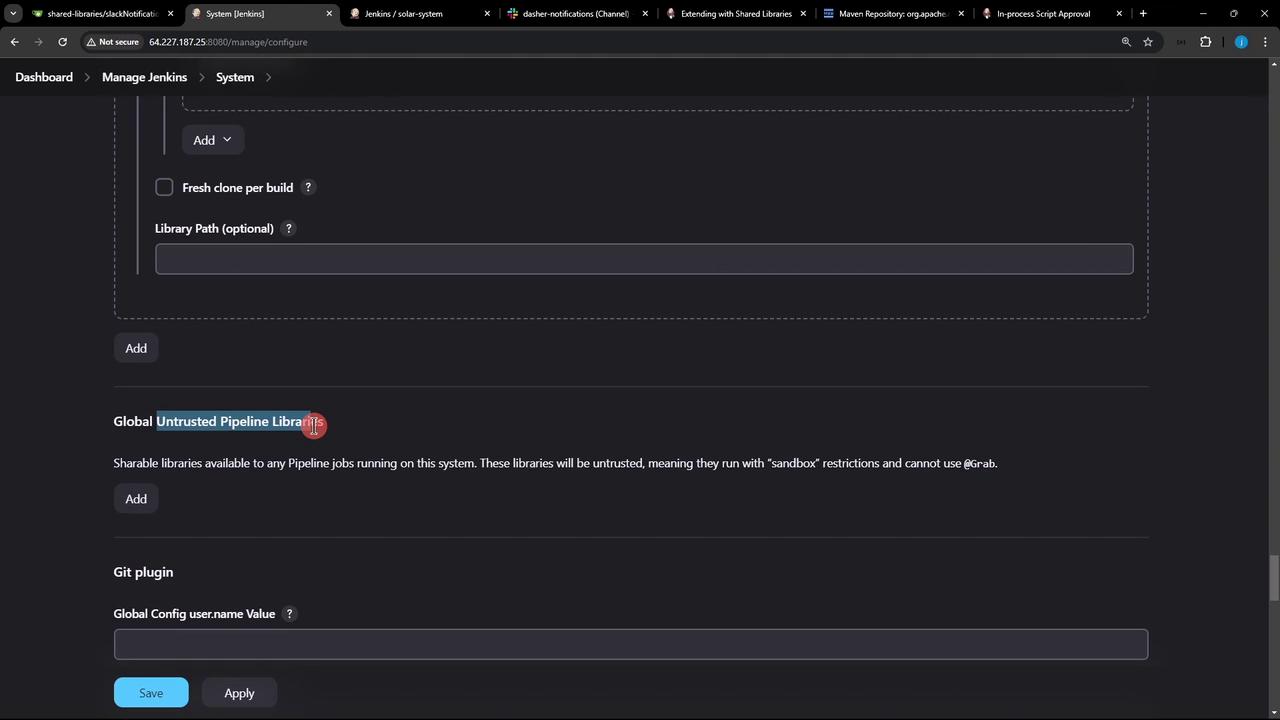
5. Next Steps
You’ve configured a trusted Shared Library. Next, we’ll load it in a Jenkinsfile using the@Library annotation and demonstrate common patterns for reusable pipeline functions.