Cursor AI
Understanding and Customizing Cursor
Demo Choosing Models
In this lesson, we’ll show you how to run Flask tests and configure different AI models inside Cursor for autocompletion, code explanation, or multi-step tasks. By the end, you’ll know how to select, customize, and manage models to fit your development workflow.
1. Running Flask Application Tests
Start by defining fixtures and writing basic tests for your Flask app:
import os
import pytest
from app import app, init_db
@pytest.fixture
def client():
# Initialize test client and database
with app.test_client() as client:
with app.app_context():
init_db()
yield client
# Clean up temp database files
os.close(db_fd)
os.unlink(app.config['DATABASE'])
def test_index_redirect(client):
"""Ensure the index page redirects to login."""
response = client.get('/')
assert response.status_code == 302
assert '/login' in response.headers['Location']
def test_register(client):
"""Verify user registration flow."""
response = client.post(
'/register',
data={'username': 'testuser', 'password': 'testpass'},
follow_redirects=True
)
assert response.status_code == 200
assert b'Account created successfully!' in response.data
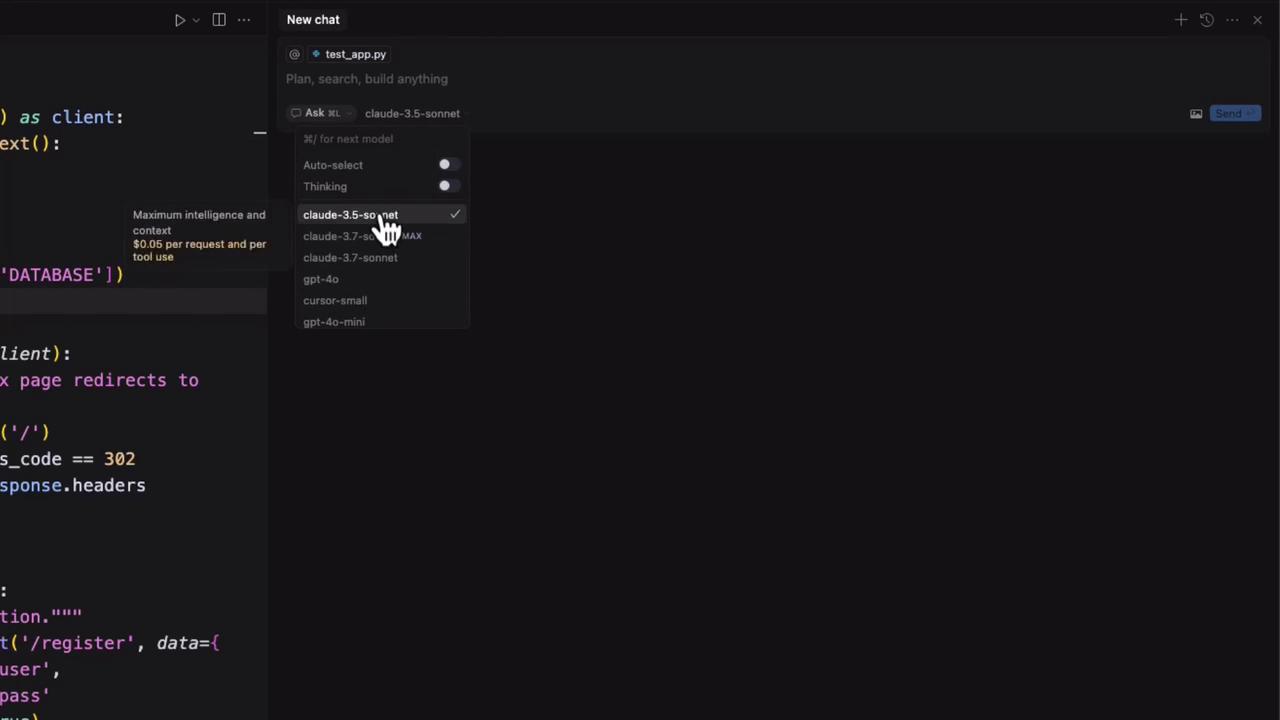
2. Browsing Model Options in Cursor
Open the chat interface to explore AI model settings:
- Left sidebar: Toggle autocompletion modes (Ask, Agentic, Edit).
- Right pane: Choose a specific model or leave on Auto-select.
Note
Auto-select lets Cursor pick the best model based on your preferences and credits.
3. AI Model Categories
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Traditional LLM | Direct response (e.g., ChatGPT, Claude). |
| Thinking LLM | Returns answer + step-by-step reasoning. |
| Agentic LLM | Automates complex, multi-step workflows (Agentic mode). |
Example: 2 + 2
Traditional LLM
Prompt: "What is 2 plus 2?"
Response: "4"
Thinking LLM
To find 2 plus 2, I add the numbers together: 2 + 2 = 4. Therefore, the answer is 4.
4. Popular Models in Cursor
| Model | Key Strength | Pricing Example |
|---|---|---|
| Claude 3.5 Sonnet | Reliable baseline | — |
| Claude 3.7 | Advanced reasoning | $0.05 per request/tool |
| GPT-4 | High speed & accuracy | — |
| GPT-4 Mini | Cost-effective | — |
Warning
Costs can add up quickly—monitor your credits and usage in Cursor Pro or via public API billing.
5. Ask Mode for Detailed Explanations
Switch to Ask Mode to request human-friendly explanations:
“Explain what
def test_index_redirectmeans.”
def test_index_redirect(client):
"""Test that the index page redirects to login."""
response = client.get('/')
assert response.status_code == 302
assert '/login' in response.headers['Location']
With GPT-4 in Ask Mode, you might see:
“This function uses Flask’s test client to ensure a request to
/returns a 302 redirect to/login.”
Experiment by selecting a thinking model and adding prompts like “explain it like I’m five” for varied results.
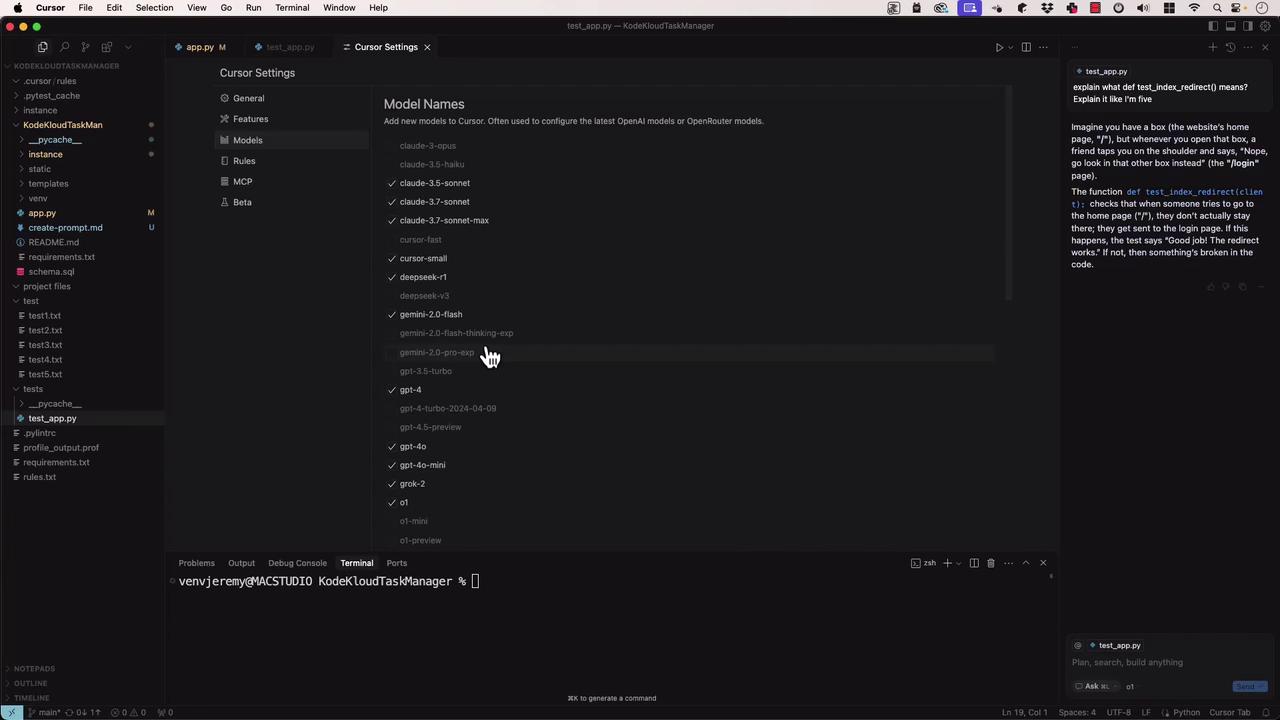
6. Customizing Models in Settings
Under Cursor Settings → Models, you can:
- Toggle models on/off
- Enter API keys for OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Cloud, Azure
- Manage billing preferences (Cursor Pro vs. public API)
Enable or disable the models you need, then close the panel to apply changes.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content