Protocol Support
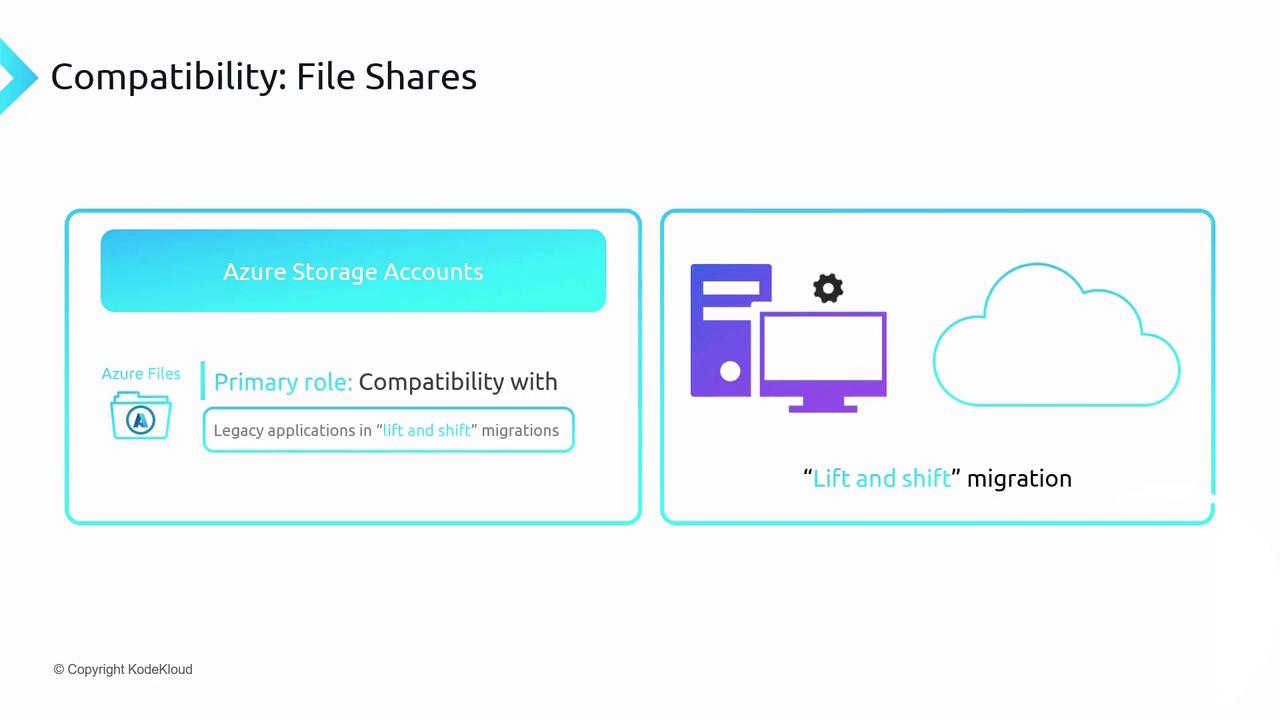
Azure Files provides two primary network file protocols:-
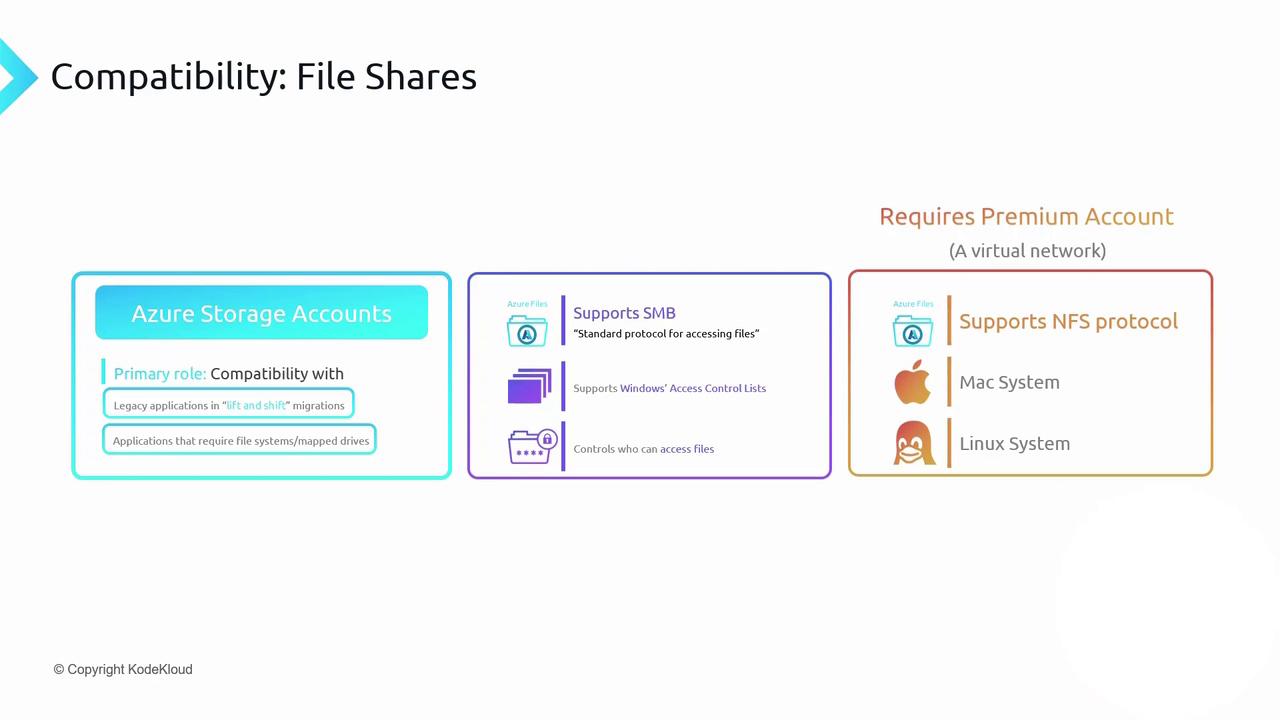
SMB (Server Message Block)
Fully compatible with Windows clients and supports Windows ACLs just as on-premises. -
NFS (Network File System 4.1)
Ideal for Linux and macOS workloads. Available only in Premium storage accounts within a virtual network.
NFS support requires a Premium storage account and VNet deployment.
SMB is available in both Standard and Premium tiers.
SMB is available in both Standard and Premium tiers.
Capacity, Scale, and Quotas
| Feature | Limit |
|---|---|
| Maximum share size | 100 TiB |
| Maximum individual file size | 1 TiB |
| Maximum concurrent connections | 2,000/share |
Uploading and Managing Files
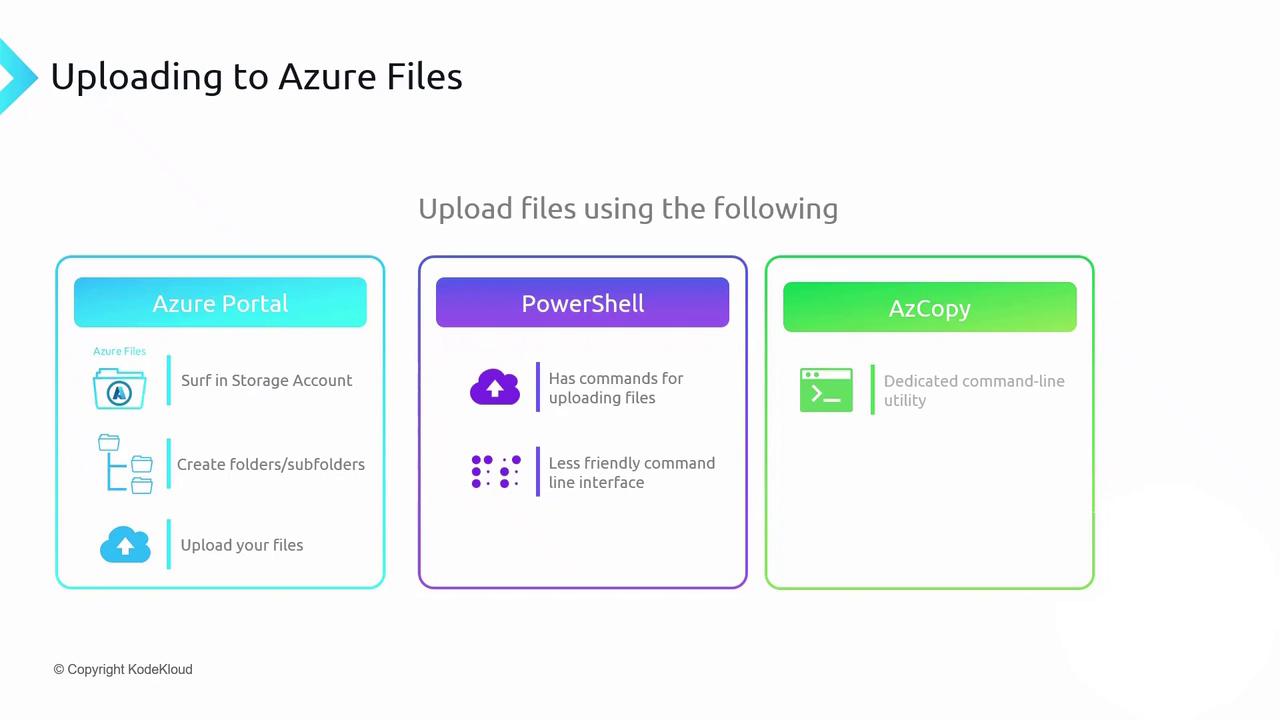
You can add, retrieve, and organize files in an Azure Files share using:| Method | Use Case | Sample Command / Action |
|---|---|---|
| Azure Portal | Quick GUI-based creation and upload | Click Upload within the Azure Storage UI |
| PowerShell | Script and automation | New-AzStorageShare; Get-AzStorageFileContent |
| AzCopy | High-performance, large-scale moves | azcopy copy ... --recursive |
Example: Upload with AzCopy
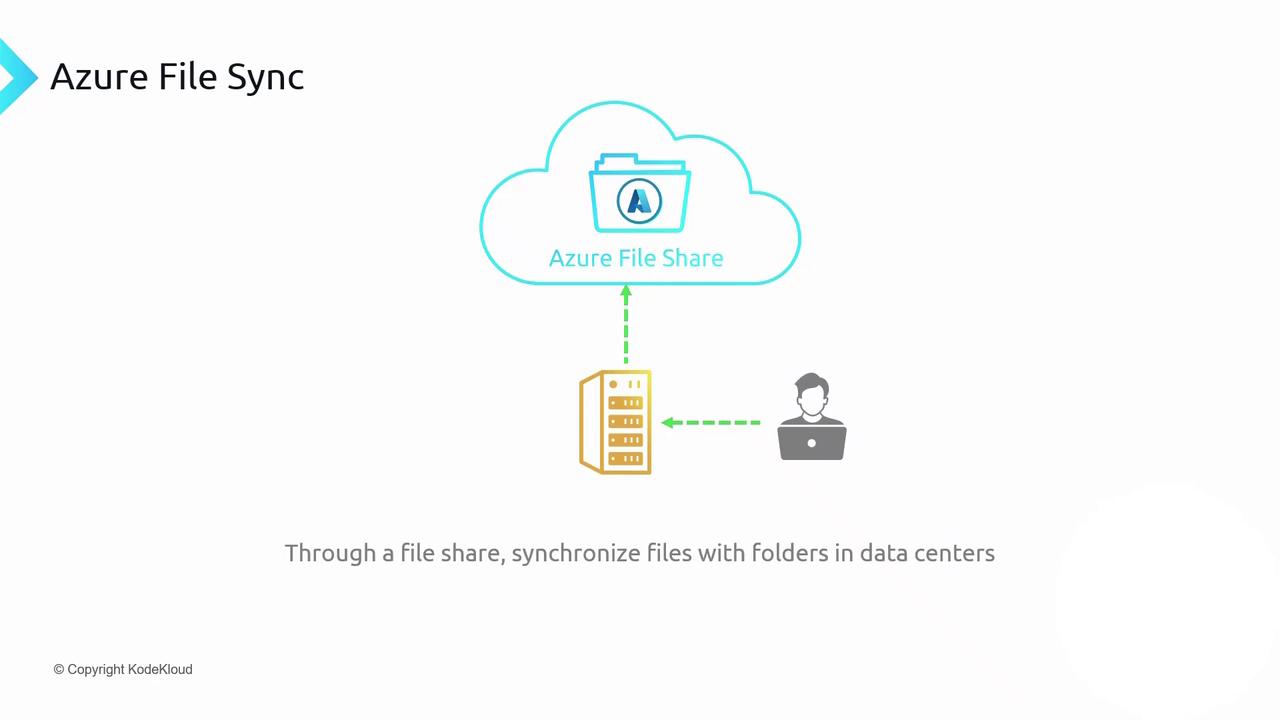
Azure File Sync
Azure File Sync extends your on-premises Windows file servers into Azure Files. Deploy the Azure File Sync agent, register your server with a Storage Sync Service, and create a sync group to connect local folders to an Azure file share. File changes replicate bidirectionally:- On-prem → Azure: New or modified files upload automatically.
- Azure → On-prem: Updates propagate to all registered servers.
Large-scale synchronization can incur data transfer charges and may impact network performance. Plan your cache settings and sync schedules to optimize costs and user experience.