1. Access the File Shares Blade
First, go to the storage account you created earlier (e.g., PHVIS2). In the left-hand menu under Data Storage, select File Shares to view and manage your shares.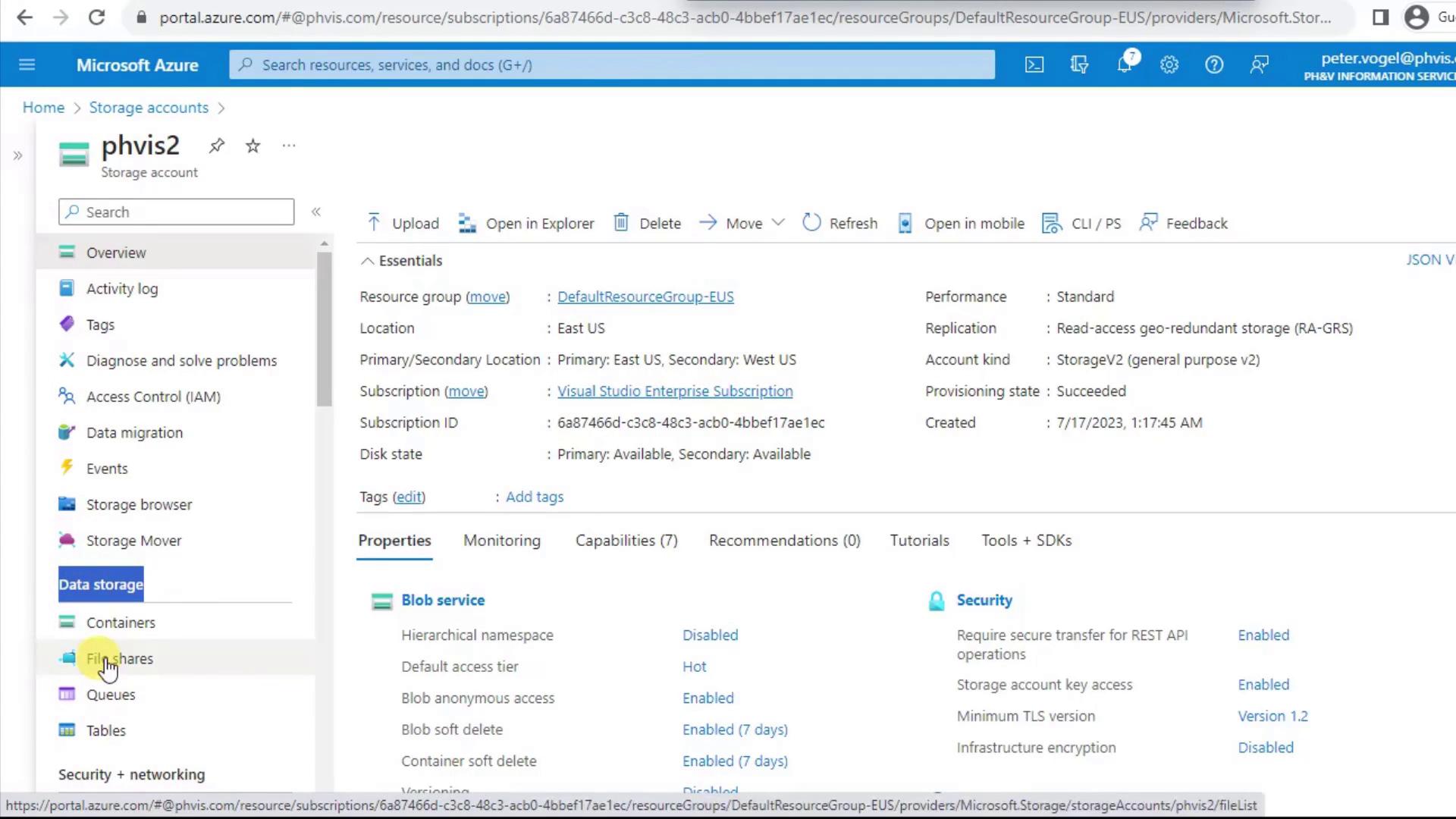
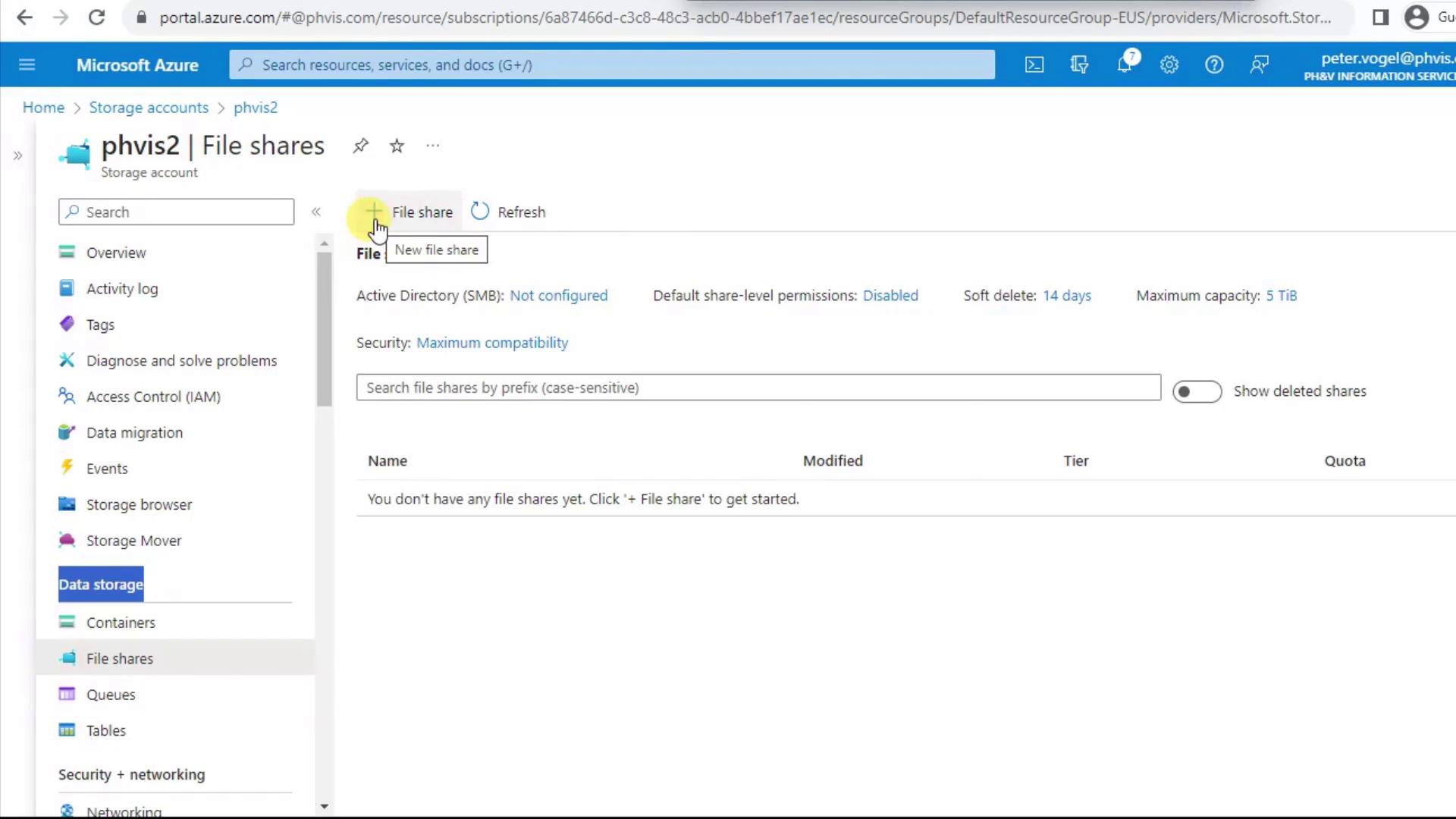
2. Create a New File Share
Click + File Share to open the creation pane. Since you’re scoped to the storage account, your subscription and resource group are already selected.- Enter a lowercase, space-free Name (e.g.,
phvfiles). - Review the default Performance (Transaction Optimized, 1,000 IOPS) and Max size (5 TiB).
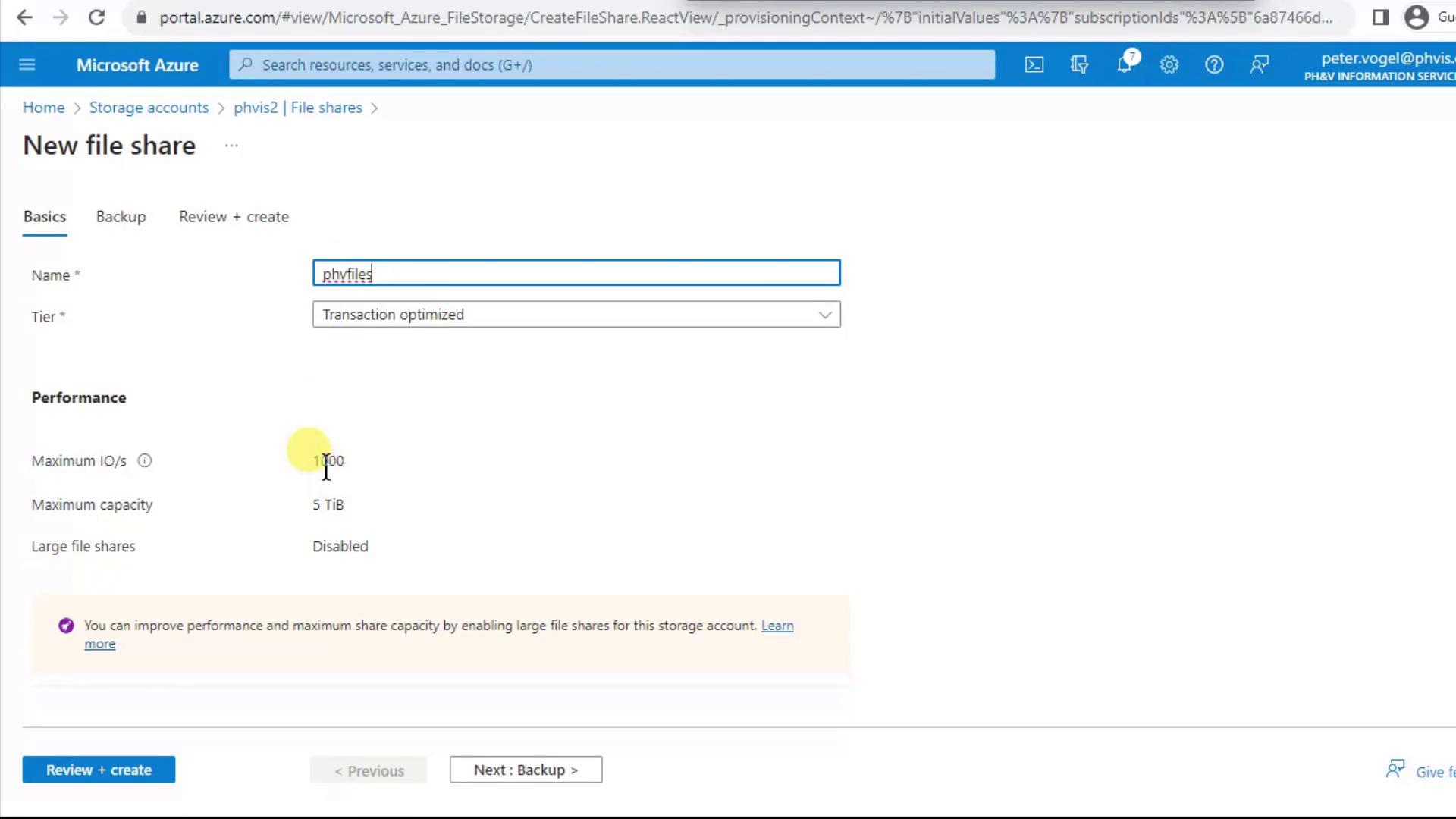
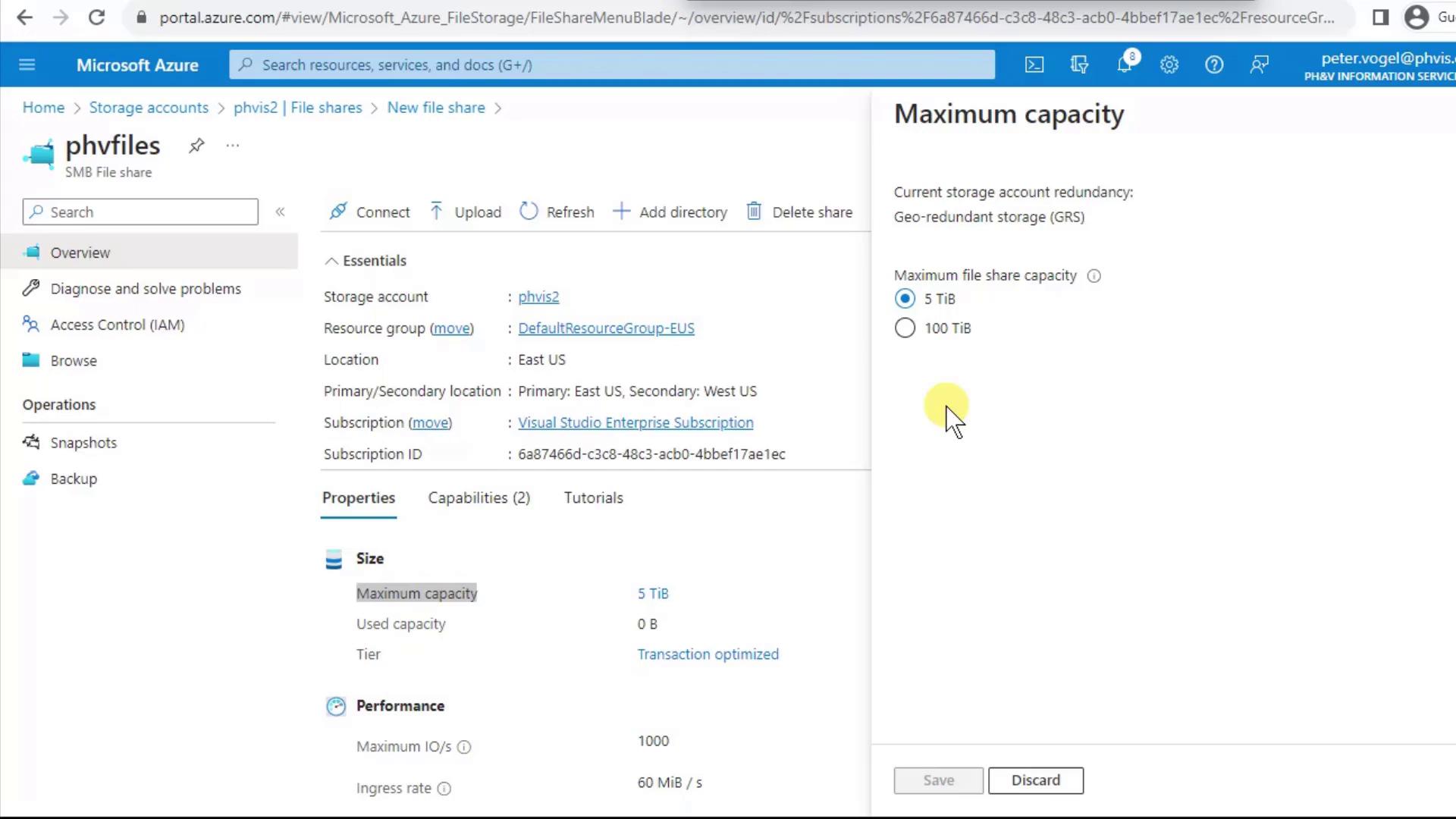
If you expect to exceed 5 TiB, you can enable large file shares (up to 100 TiB) either at the storage account level or per share after creation.
3. Adjust Tier and Quota
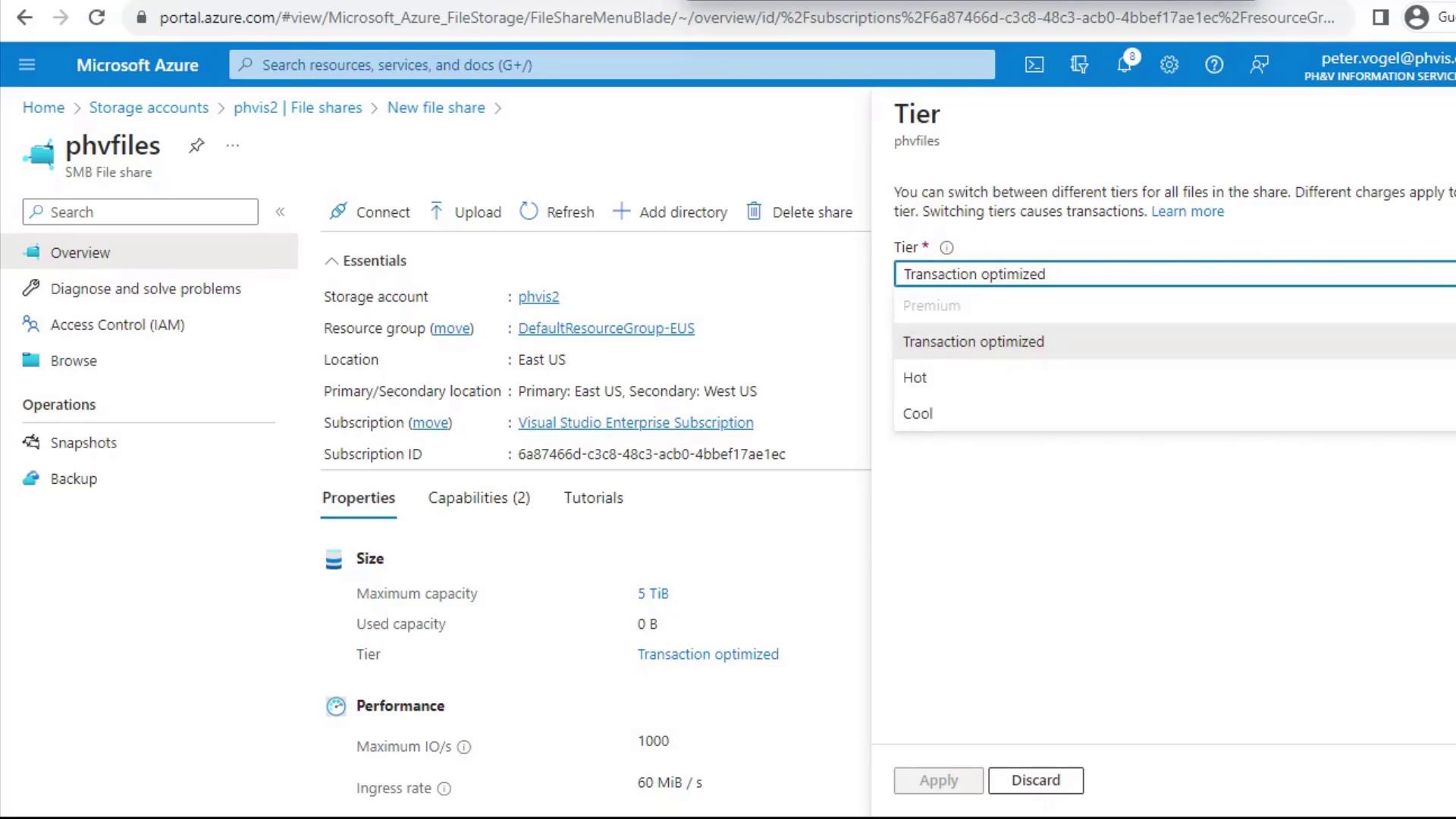
After creation, you can fine-tune performance, capacity, and retention: Change TierClick Change tier to pick the right performance level for your workload:
| Tier Name | Best For | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Optimized | Balanced read/write workloads | ~1,000 IOPS, moderate cost |
| Hot | Frequent file sharing & Azure File Sync | Higher throughput, higher cost |
| Cool | Infrequently accessed files | Lower storage cost, lower performance |
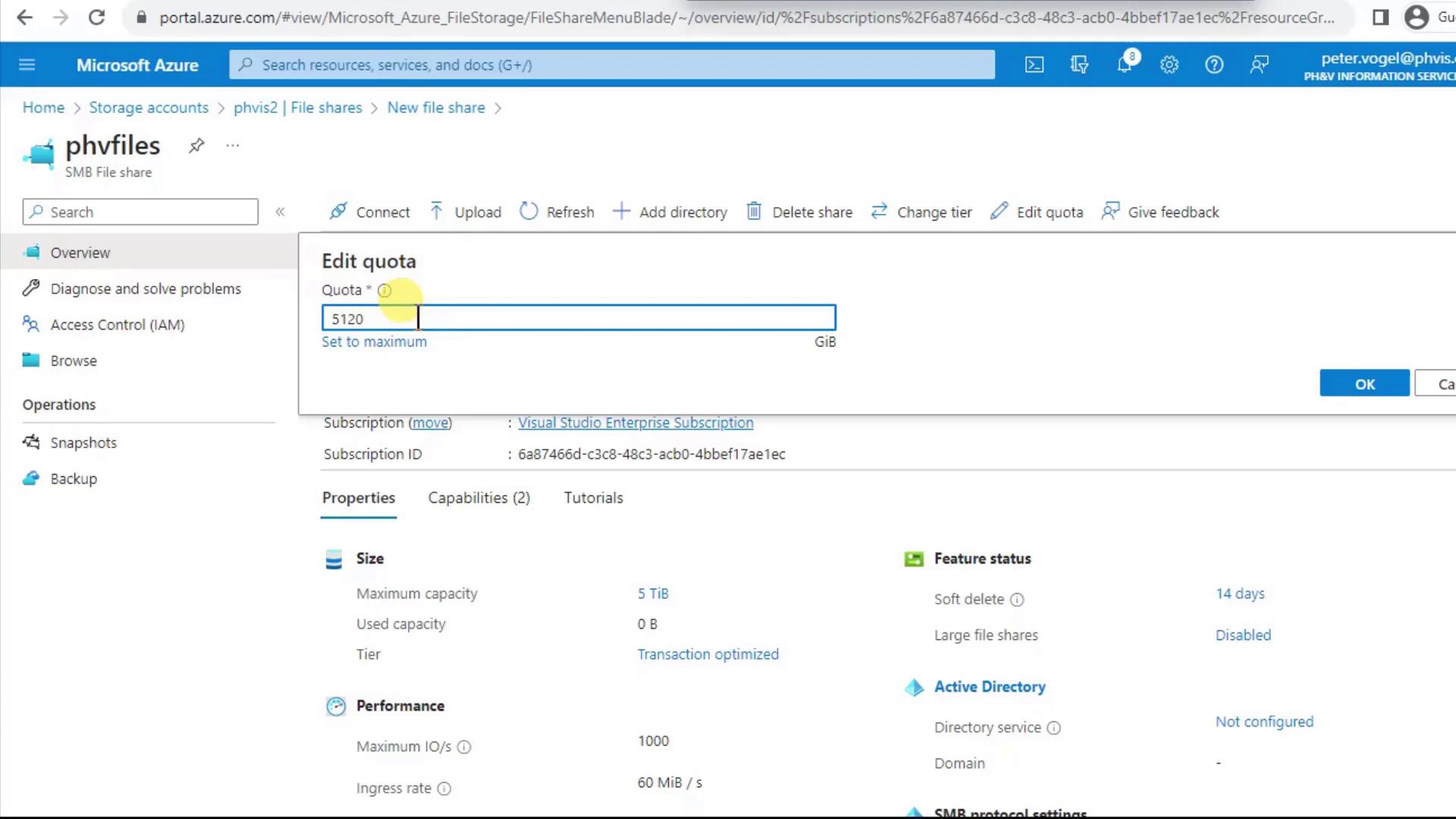
Open Properties (or click the share name) to view size, usage, and quota settings. By default, it’s 5,120 GiB (5 TiB).
Soft Delete is enabled by default (14 days). Deleted files are recoverable within that period but still incur storage costs.
Large file shares (100 TiB) do not support geo-redundancy. Plan accordingly if you need cross-region replication.
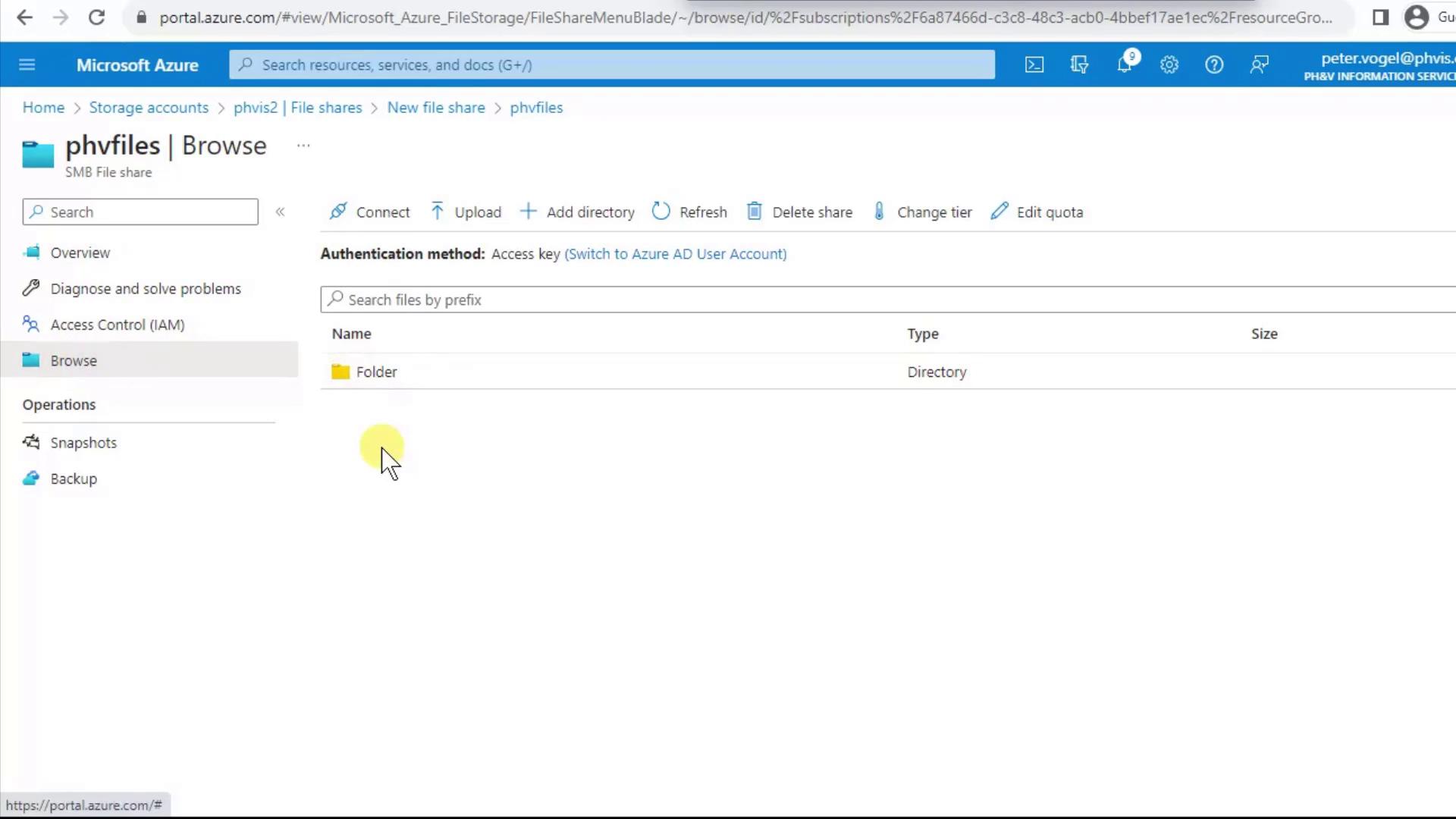
4. Organize Data with Directories
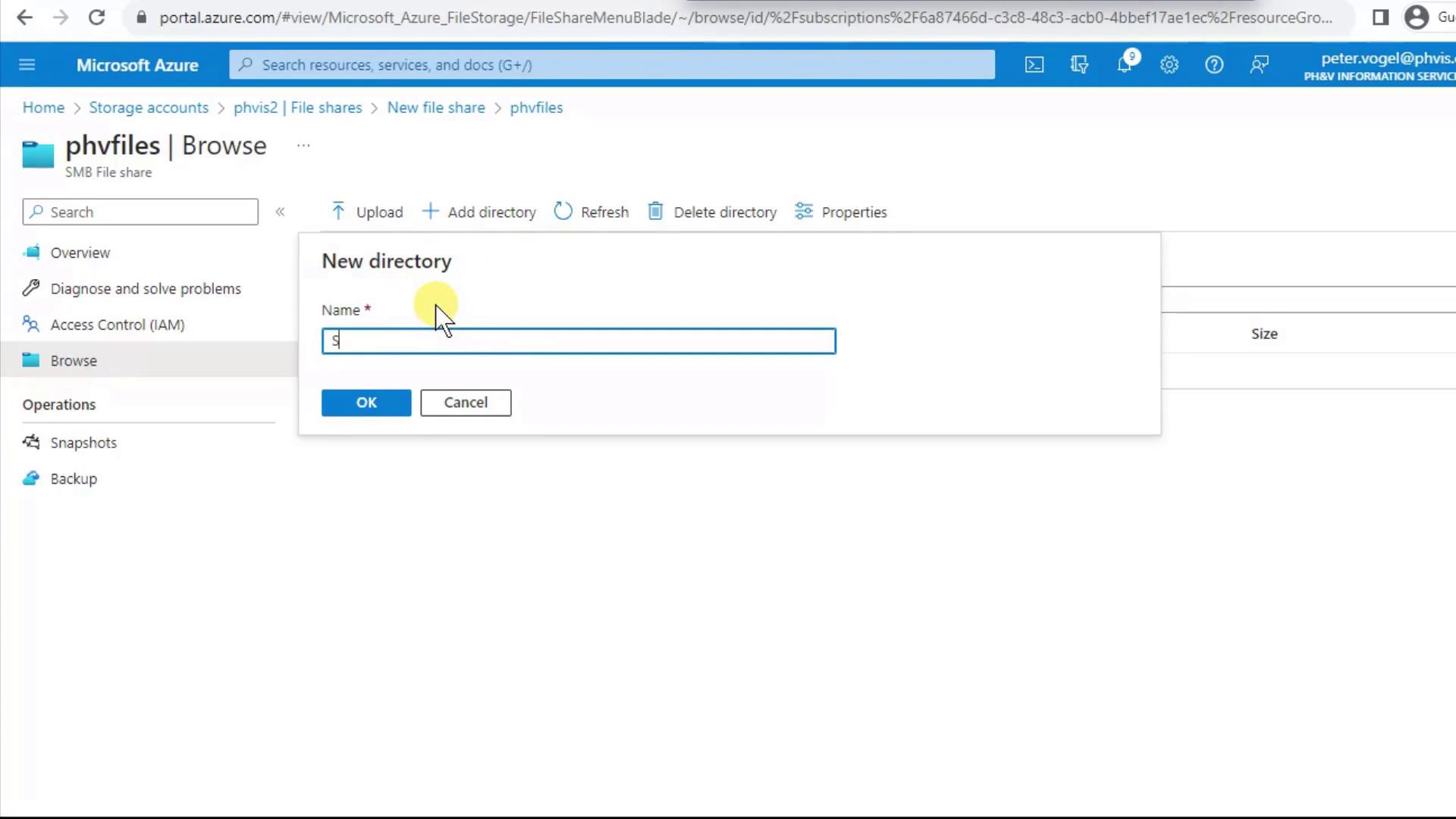
With your share in place, you can add folders and files directly from the portal.- Click Add Directory, enter a name (e.g.,
Folder), and confirm. - Browse into
Folderand repeat Add Directory to create subfolders. Azure Files supports uppercase, lowercase, spaces, and most SMB-compatible characters.
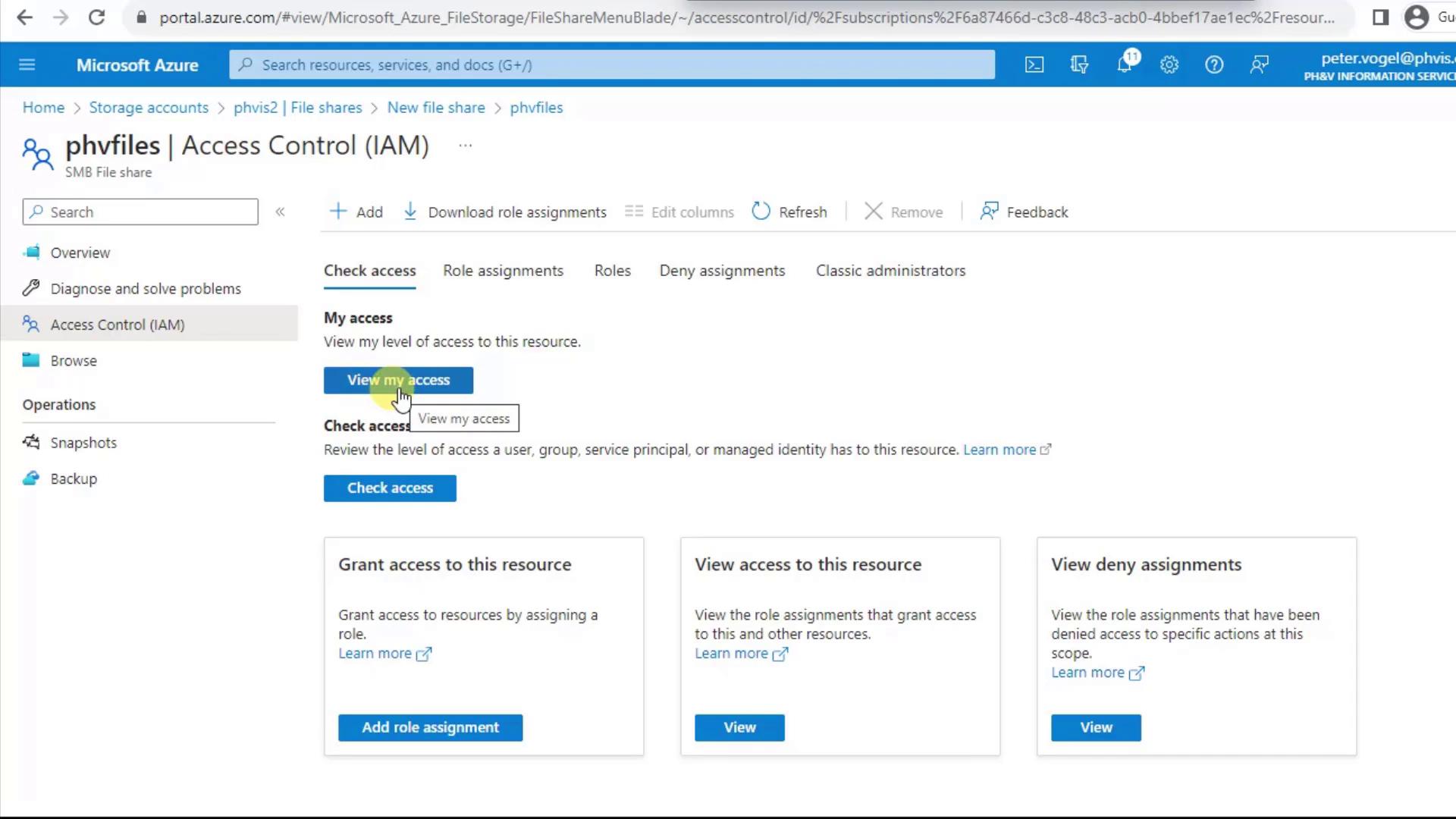
5. Manage Access Control (IAM)
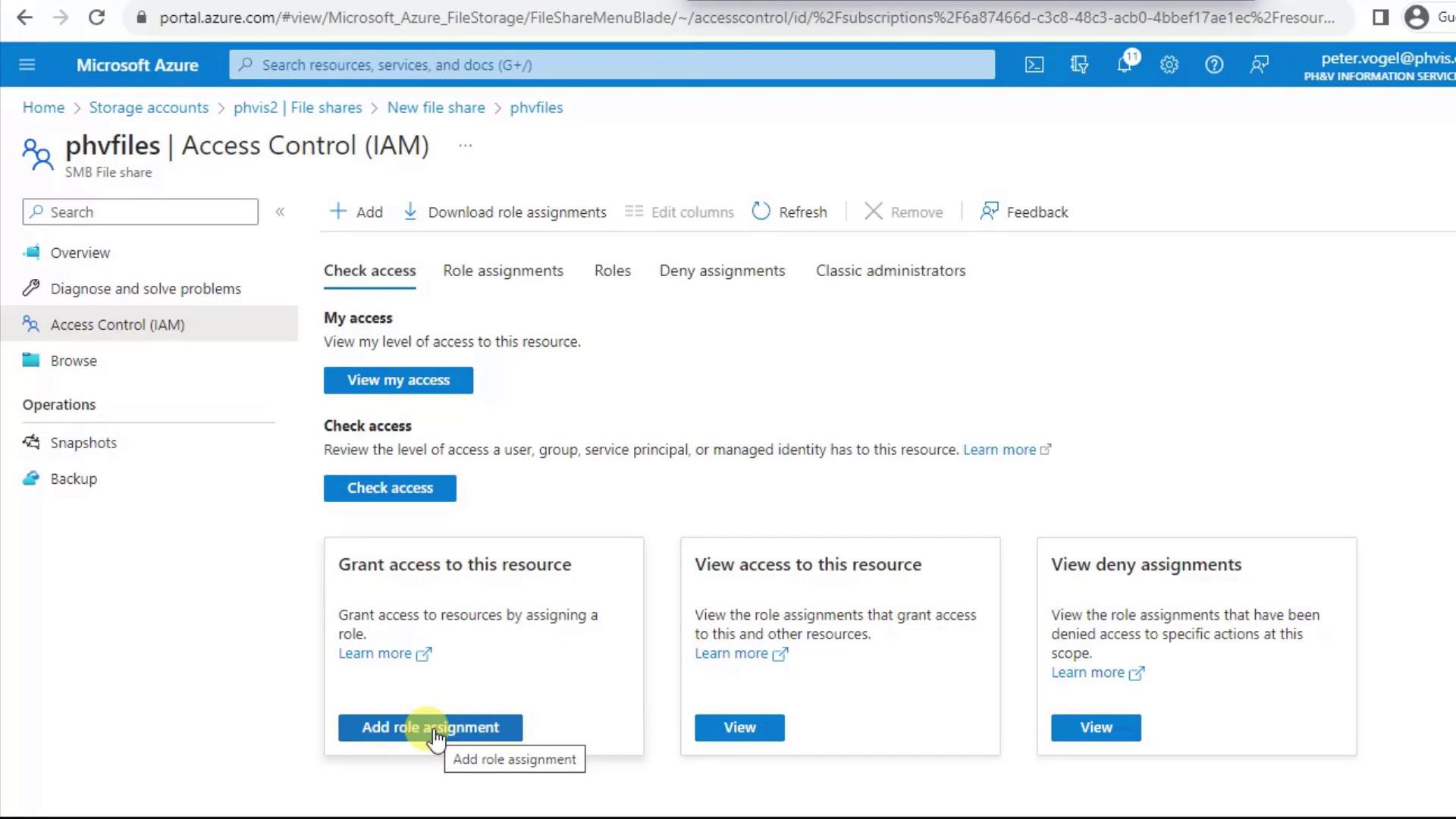
Control who can view and modify your file share via Access Control (IAM) in the left menu:- Check Access shows the effective permissions for any user or service principal.
- Add role assignment lets you grant built-in roles (e.g., Storage File Data SMB Share Contributor) at the share level.
That completes the setup of your Azure File Share. You can now mount it on Windows, Linux, or macOS clients, integrate with Azure File Sync, or manage it via REST API and SDKs.