Grant only the minimum permissions required—this enforces security and reduces the risk of accidental data exposure.
- Users
Need read or read/write access to files, blobs, or file shares for day-to-day operations. - Administrators
Manage storage accounts, assign or revoke permissions, configure backups, and define data governance policies. - Data Engineers
Provision and configure storage resources without direct access to the data itself.
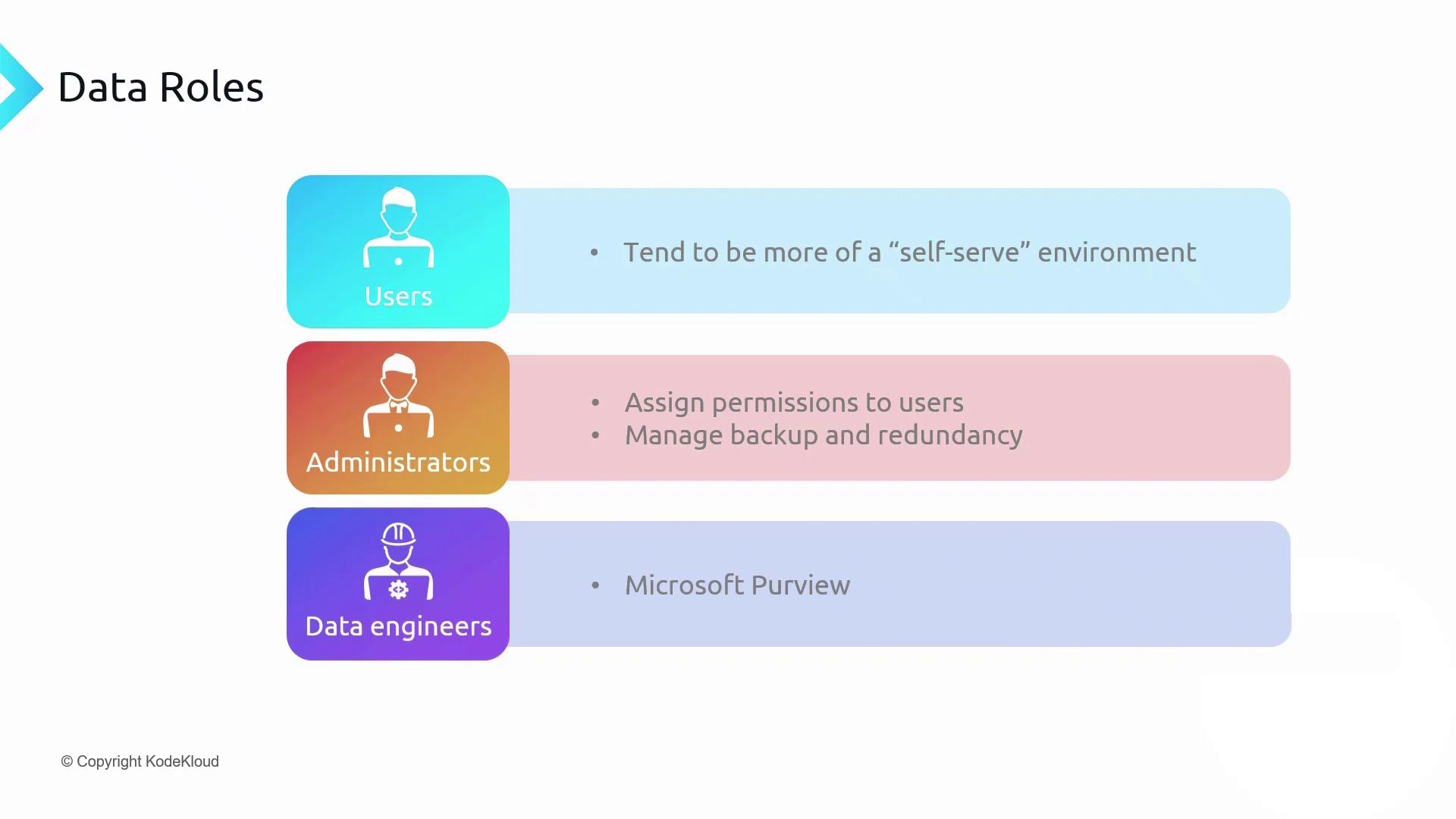
User Responsibilities
Users operate in a self-service environment. They receive scoped permissions on the storage objects they need, enabling independent work without frequent administrative requests.- Read data from files, blobs, or containers
- Modify or upload new data when granted write access
- Access only the shares or containers explicitly assigned to them
Administrator Responsibilities
Administrators oversee the lifecycle and compliance of storage resources:- Assign and revoke RBAC permissions (
Storage Blob Data Reader,Storage Blob Data Contributor) - Configure and manage automated backups for point-in-time restores
- Integrate with Microsoft Purview to define retention and classification policies
Incorrect or overly broad RBAC assignments can lead to unintended data exposure. Always audit role assignments regularly.
Data Engineer Responsibilities
Data Engineers handle provisioning and configuration tasks without accessing content directly:- Create and configure storage accounts and file shares
- Optimize performance tiers based on workload patterns
- Automate deployments using Azure CLI or Terraform
We’ve explored unstructured data storage on Azure and the roles needed to manage it securely.
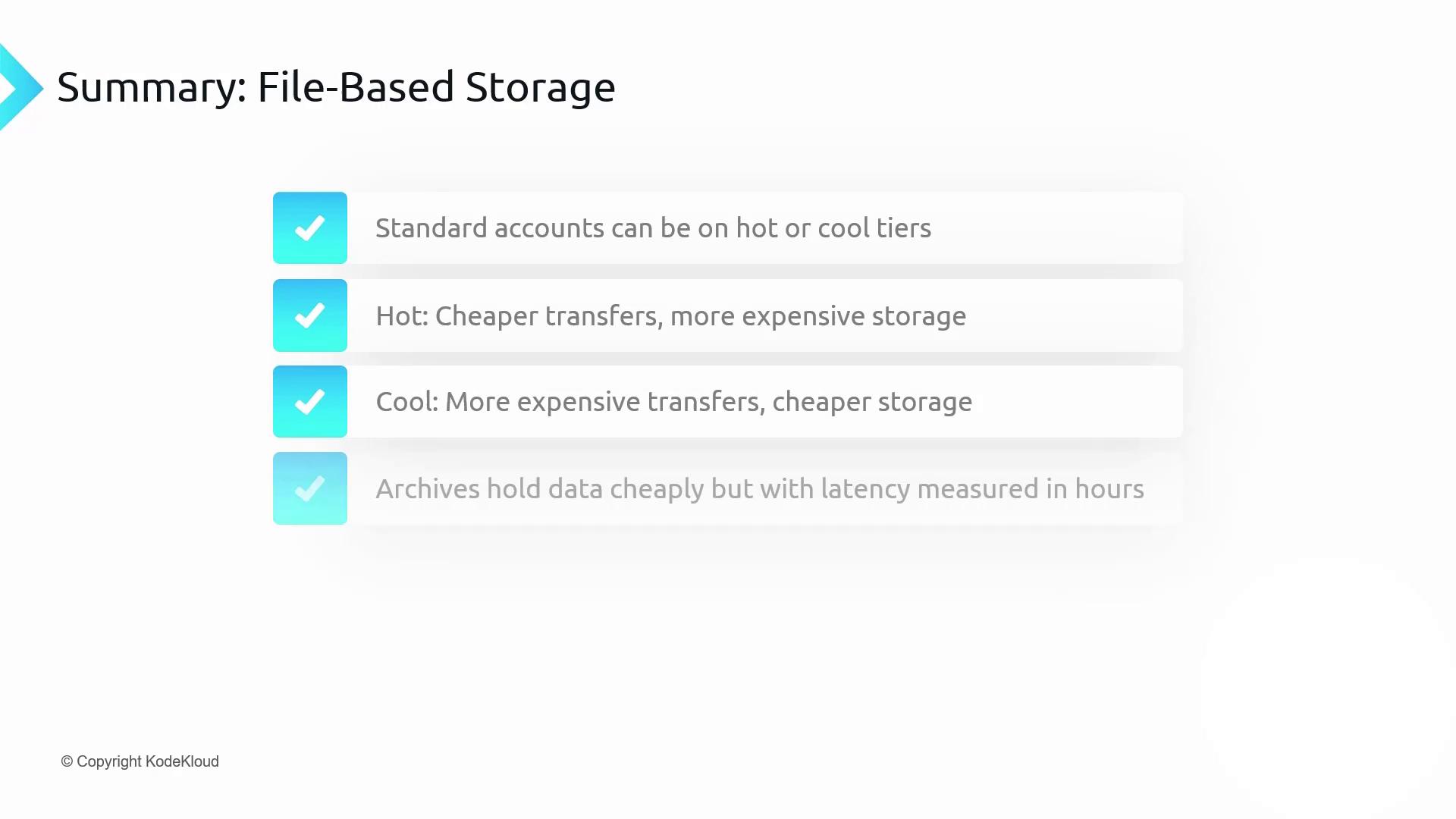
- File and object storage support binary files and common text formats (CSV, JSON, XML).
- Azure storage accounts host both Azure Files and Azure Blob Storage.
- Premium accounts use SSDs for low-latency I/O.
- File shares utilize the SMB protocol for broad OS compatibility.
Storage Account Tiers Comparison
| Tier | Storage Cost | Access Cost | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot | Higher | Lower | Frequently accessed data |
| Cool | Lower | Higher | Infrequently accessed, but not archival |
| Archive | Lowest (hours to retrieve) | Highest (latency) | Long-term retention with rare retrieval |