1. Lift-and-Shift Migration to IaaS
If you have an on-premises DBMS, a quick way to migrate is to lift and shift your database to an Azure Virtual Machine (VM). You install and run your choice of DBMS—such as Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, MariaDB, or MySQL—just as you did on-prem. Key responsibilities remain on you:- Operating system upgrades and security patches
- Database server updates and compatibility testing
- Full VM and DBMS administration
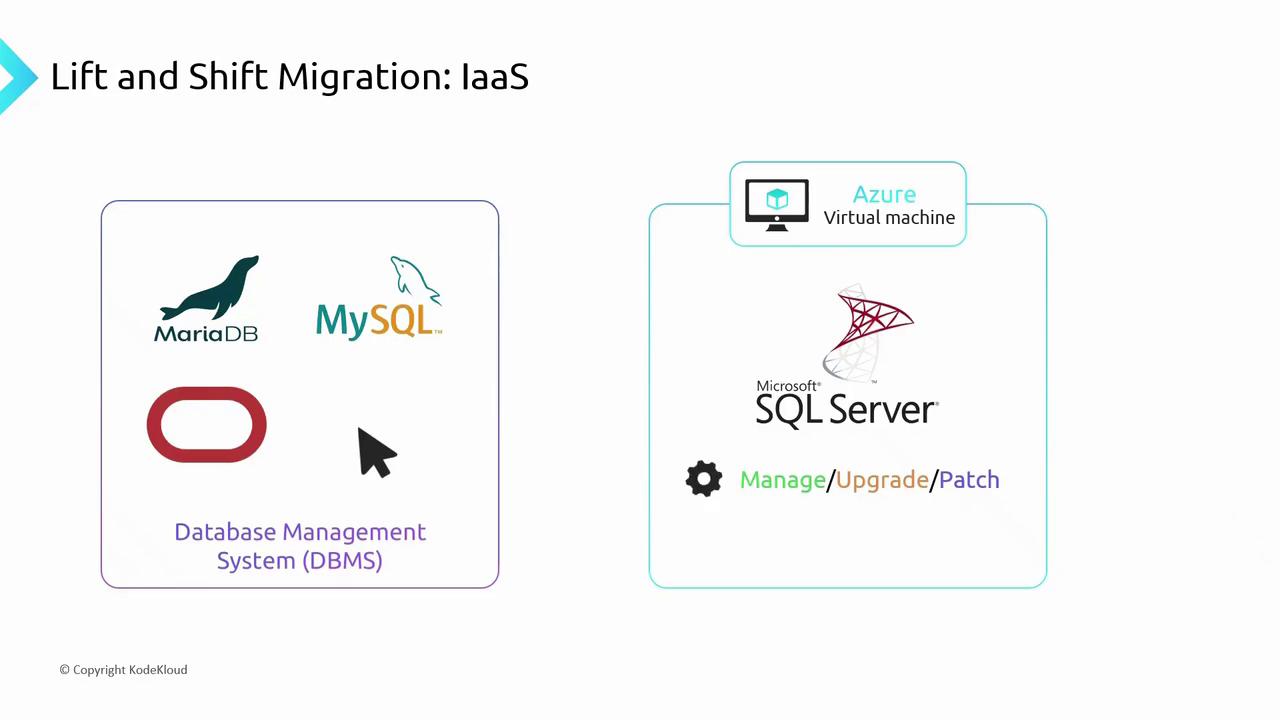
- Access control (who can read or write data)
- Data ingestion pipelines into your DBMS
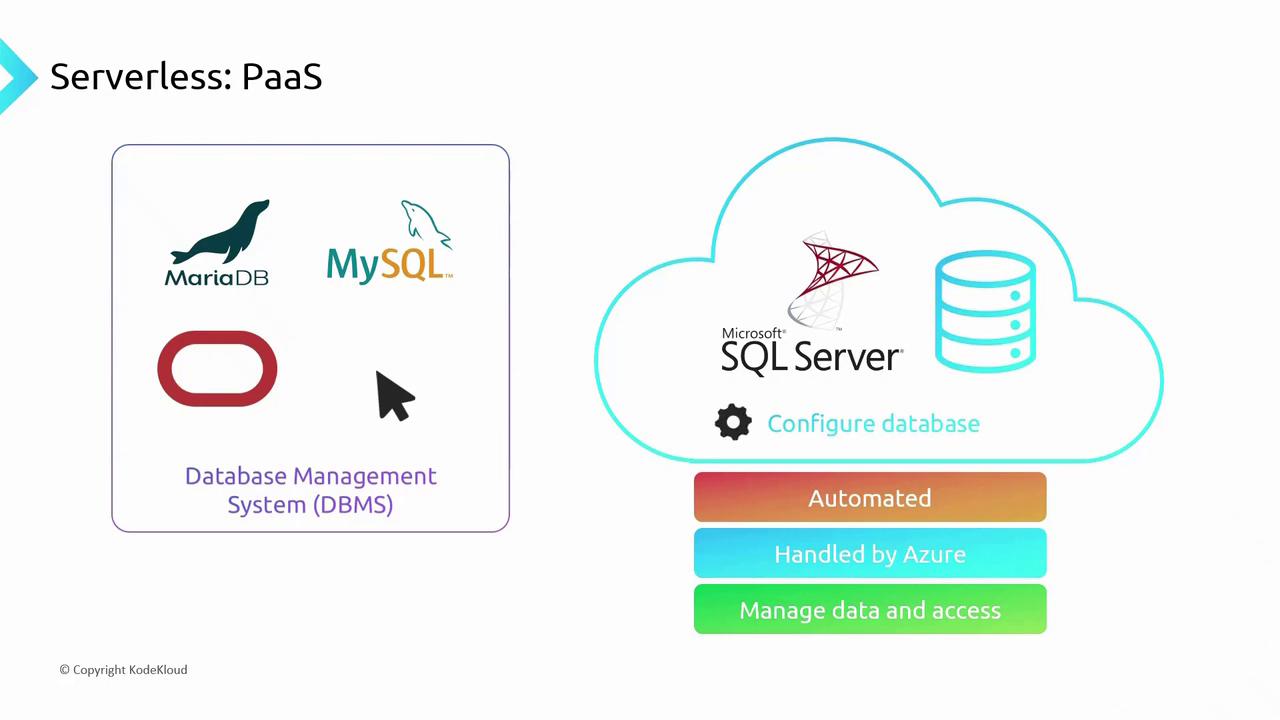
2. Serverless PaaS for Relational Databases
To minimize infrastructure management, opt for a serverless, fully managed database service in Azure. With PaaS:- Azure automates OS and DBMS patching/upgrades
- You don’t provision or manage VMs
- You focus on schema design, access policies, and data ingestion
Serverless databases automatically scale compute and storage based on demand, helping you optimize costs and performance.
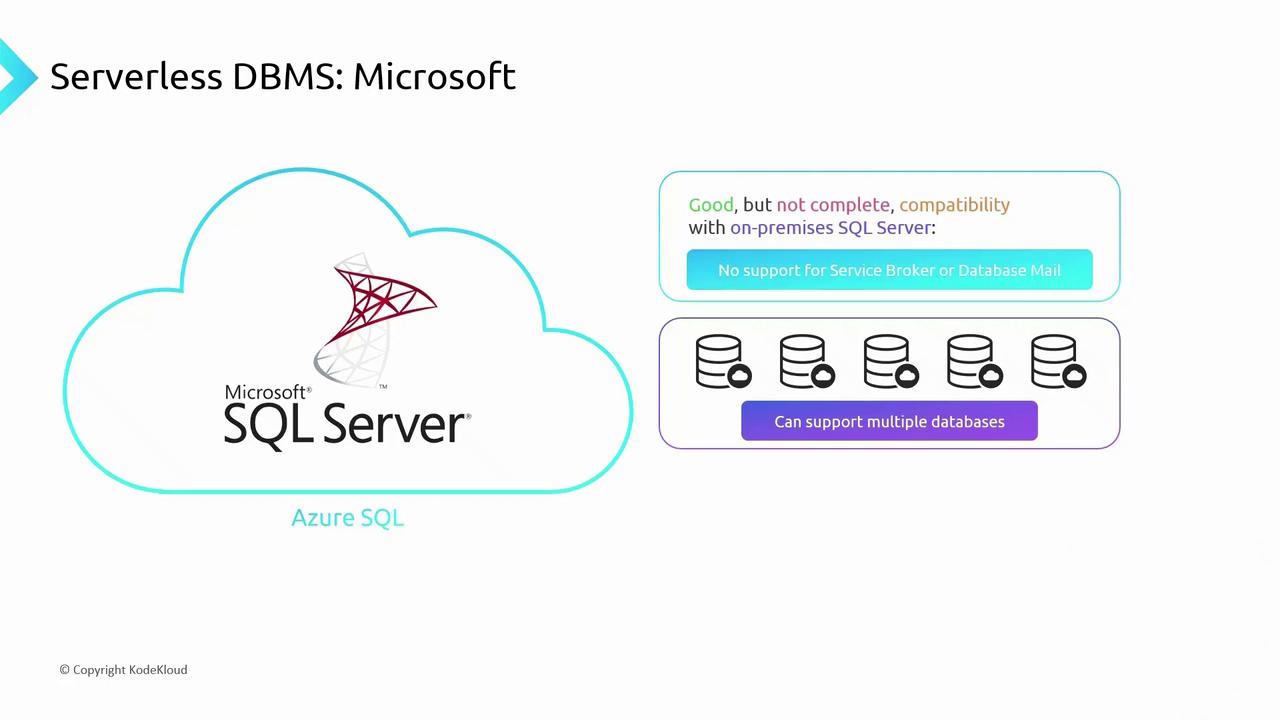
2.1 Azure SQL Database Family
The Azure SQL family delivers multiple serverless and PaaS options compatible with on-premises SQL Server workloads. Keep in mind:Features such as Service Broker and Database Mail aren’t supported in Azure SQL Database and some Managed Instances. If these are critical, consider SQL Server on a VM.
| SKU | Use Case | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Azure SQL Database | Single database, web/app backends | Rapid provisioning, built-in geo-replication |
| Azure SQL Managed Instance | Lift & modernize existing SQL workloads | Near 100% compatibility, custom maintenance |
| Elastic Pools | Multiple DBs with varying demands | Shared resources, cost-effective scaling |
| Azure SQL Edge | IoT and edge computing | Real-time analytics, time-series processing |
2.1.1 Azure SQL Database
A fully managed single-database service ideal for OLTP workloads that need fast setup and built-in high availability.2.1.2 Azure SQL Managed Instance
Provides almost full SQL Server compatibility, enabling easy database porting and control over patching schedules.2.1.3 Elastic Pools
Share compute and storage among multiple databases with complementary usage patterns—perfect when one database peaks by day and another by night.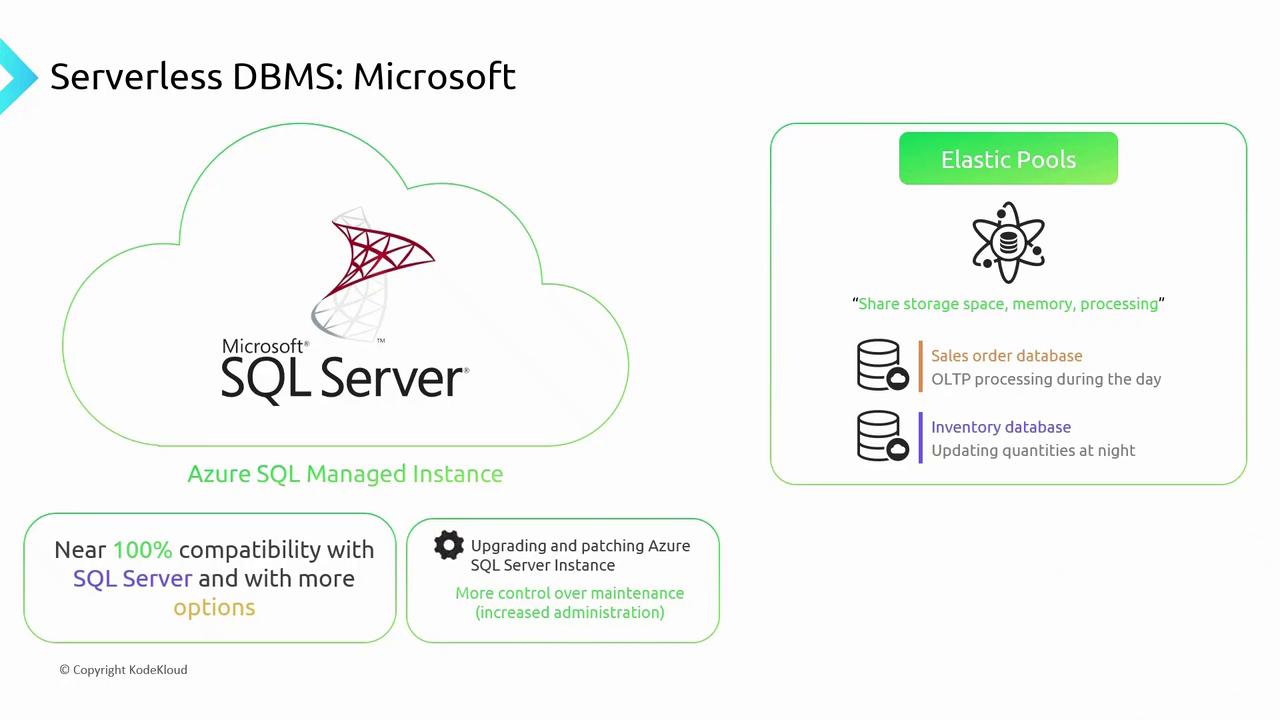
2.1.4 Azure SQL Edge
Optimized for IoT scenarios and edge computing, it ingests continuous telemetry streams and supports real-time analytics with sliding time windows.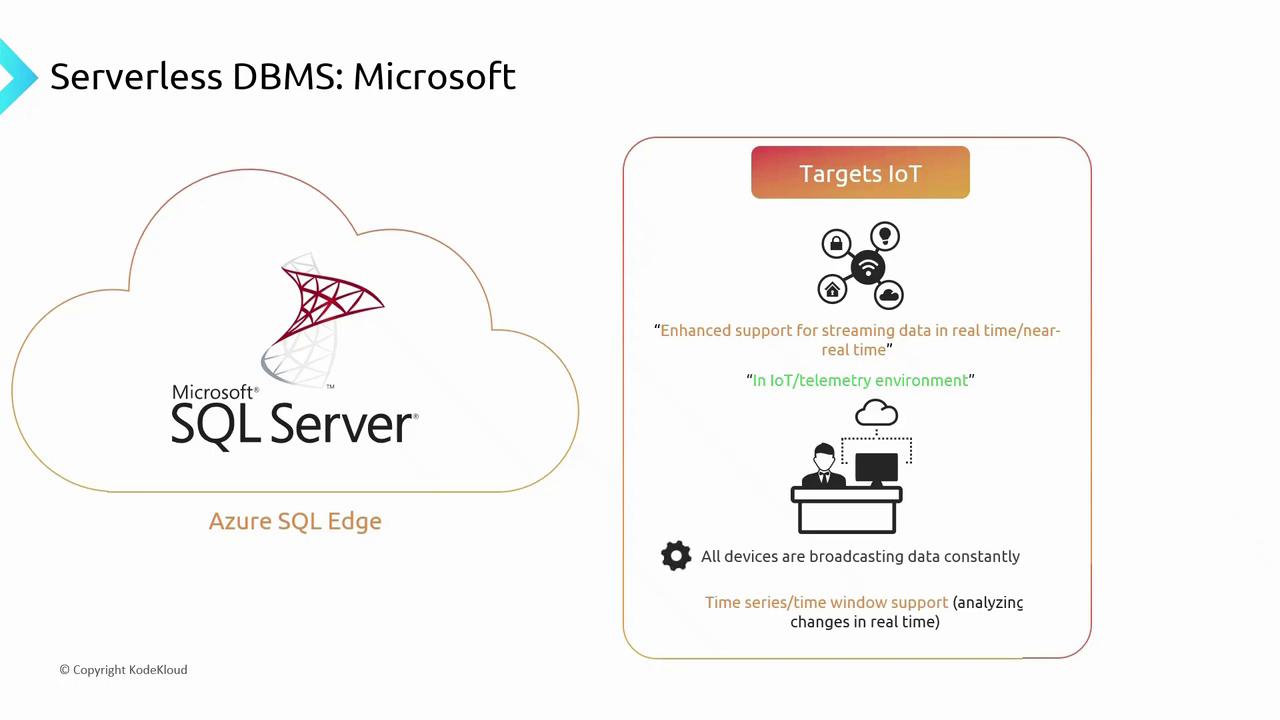
3. Open Source & Third-Party Options
Azure also offers fully managed services for popular open-source relational databases:- Azure Database for PostgreSQL
- Azure Database for MySQL
- Azure Database for MariaDB
