DevSecOps - Kubernetes DevOps & Security
DevSecOps Pipeline
OWASP ZAP Basics
In this lesson, we’ll explore how to use OWASP ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy) for dynamic application security testing (DAST) of a Spring Boot REST API. You’ll learn about scan types, how to run an API scan with Docker, and how to interpret the results.
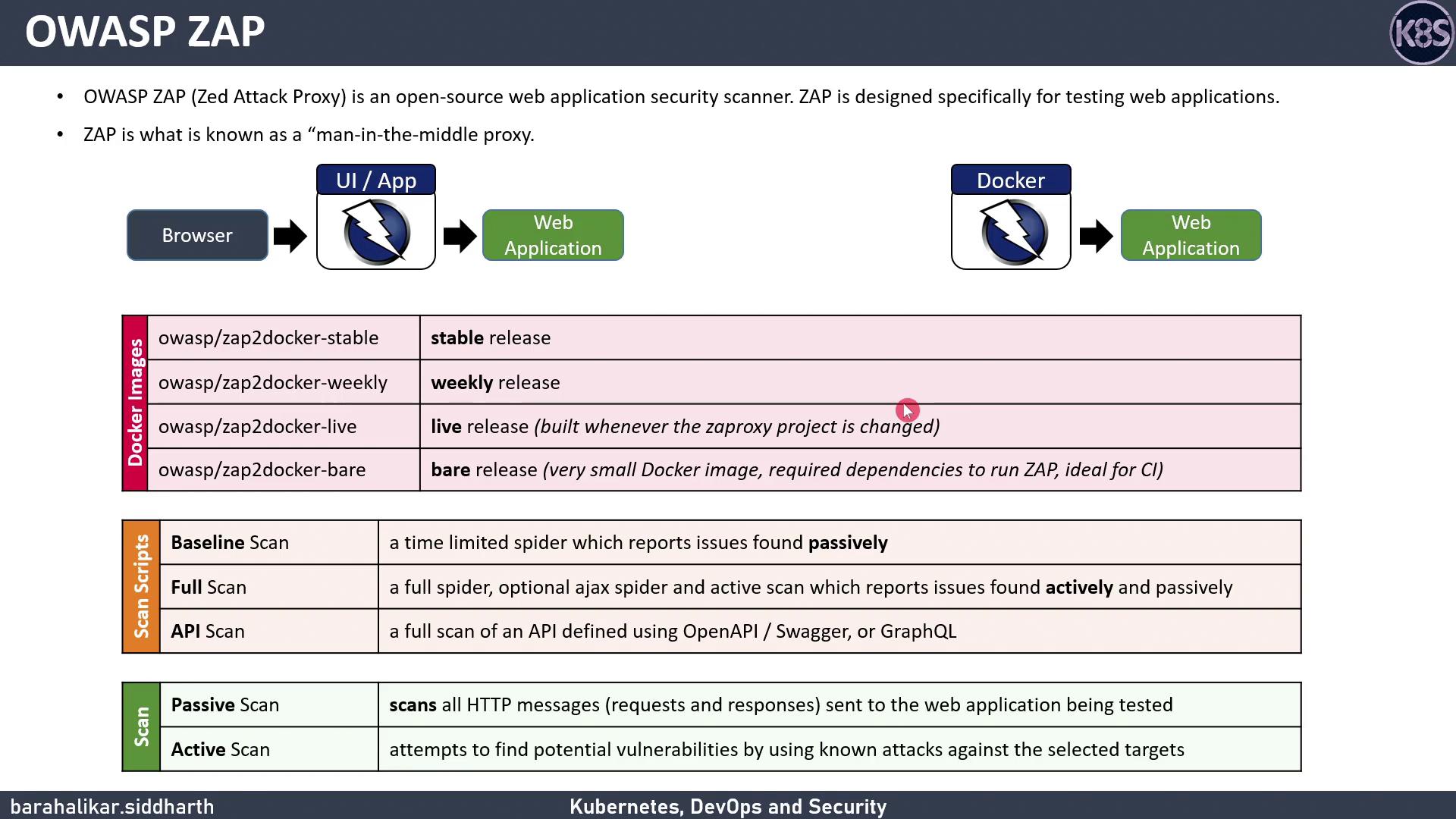
What Is OWASP ZAP?
OWASP ZAP is an open-source web application security scanner that sits between your client and target application as a “man-in-the-middle proxy.” It can:
- Intercept and modify HTTP(S) requests and responses
- Perform passive scans to detect vulnerabilities without modifying traffic
- Launch active scans to probe for common attack vectors
- Import API definitions (OpenAPI, Swagger, SOAP, GraphQL) for targeted testing
You can install ZAP in multiple ways:
- Standalone GUI or CLI
- Docker image on Docker Hub
ZAP Scan Types
| Scan Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Time-limited spidering + passive analysis | Smoke test before deployment |
| Full | Ajax spidering + both passive and active scans | Comprehensive web application test |
| API | Imports API definitions + active scan tuned for APIs (skips irrelevant tests like XSS) | REST/GraphQL/SOAP API testing |
Note
API scans skip UI-related tests (e.g., XSS) and focus on HTTP error codes or unusual content types.
Running the API Scan with Docker
Since our Spring Boot service exposes only REST endpoints, we’ll use the API scan. This example mounts your working directory to collect reports and any custom rules.
docker run \
-v $(pwd):/zap/wrk/:rw \
-t owasp/zap2docker-weekly \
zap-api-scan.py \
-t http://$HOST_URL:$PORT/v3/api-docs \
-f openapi \
-c custom_rules.conf \
-r zap-report.html
$HOST_URLand$PORTshould point to your running Spring Boot application.-c custom_rules.confis optional; omit if you don’t need overrides.
Warning
Ensure the API definition is reachable (no authentication required) when running scans. Firewall or incorrect URLs can cause false failures.
Sample Scan Output
PASS: Hash Disclosure [10007]
PASS: Cross-Domain Misconfiguration [10098]
PASS: Weak Authentication Method [10105]
PASS: Reverse Tabnabbing [10108]
PASS: Modern Web Application [10109]
PASS: Private IP Disclosure [2]
PASS: Session ID in URL Rewrite [13]
PASS: Script Passive Scan Rules [50001]
PASS: Insecure JSF ViewState [90001]
PASS: Charset Mismatch [90011]
PASS: Loosely Scoped Cookie [90023]
WARN NEW: Application Error Disclosure [90022] x 2
WARN: http://192.168.18.23:5000/update (500 INTERNAL SERVER ERROR)
WARN: http://192.168.18.23:5000/?_debugger=__yes&cmd=paste (500 INTERNAL SERVER ERROR)
FAIL-NEW: 0
FAIL-INPROG: 0
WARN-NEW: 6
PASS: 45
This summary shows how many tests passed, failed, or generated warnings. You can use these metrics to gate your CI/CD pipeline.
Docker Command Arguments
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -v | Mount current directory for reports and custom configs | -v $(pwd):/zap/wrk/:rw |
| -t | Target API definition URL (include protocol) | -t http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs |
| -f | Format of API definition: openapi, soap, or graphql | -f openapi |
| -c | Custom rules configuration file | -c custom_rules.conf |
| -r | Output report format: report.html, report.md, report.xml, report.json | -r zap-report.html |
References
Watch Video
Watch video content