- Connecting GitHub for source control
- Adding unit and integration testing stages
- Running vulnerability scans
- Performing dynamic application security testing (DAST)
Ensure you have a GitHub repository connected and a Jenkins server with the Kubernetes plugin installed.
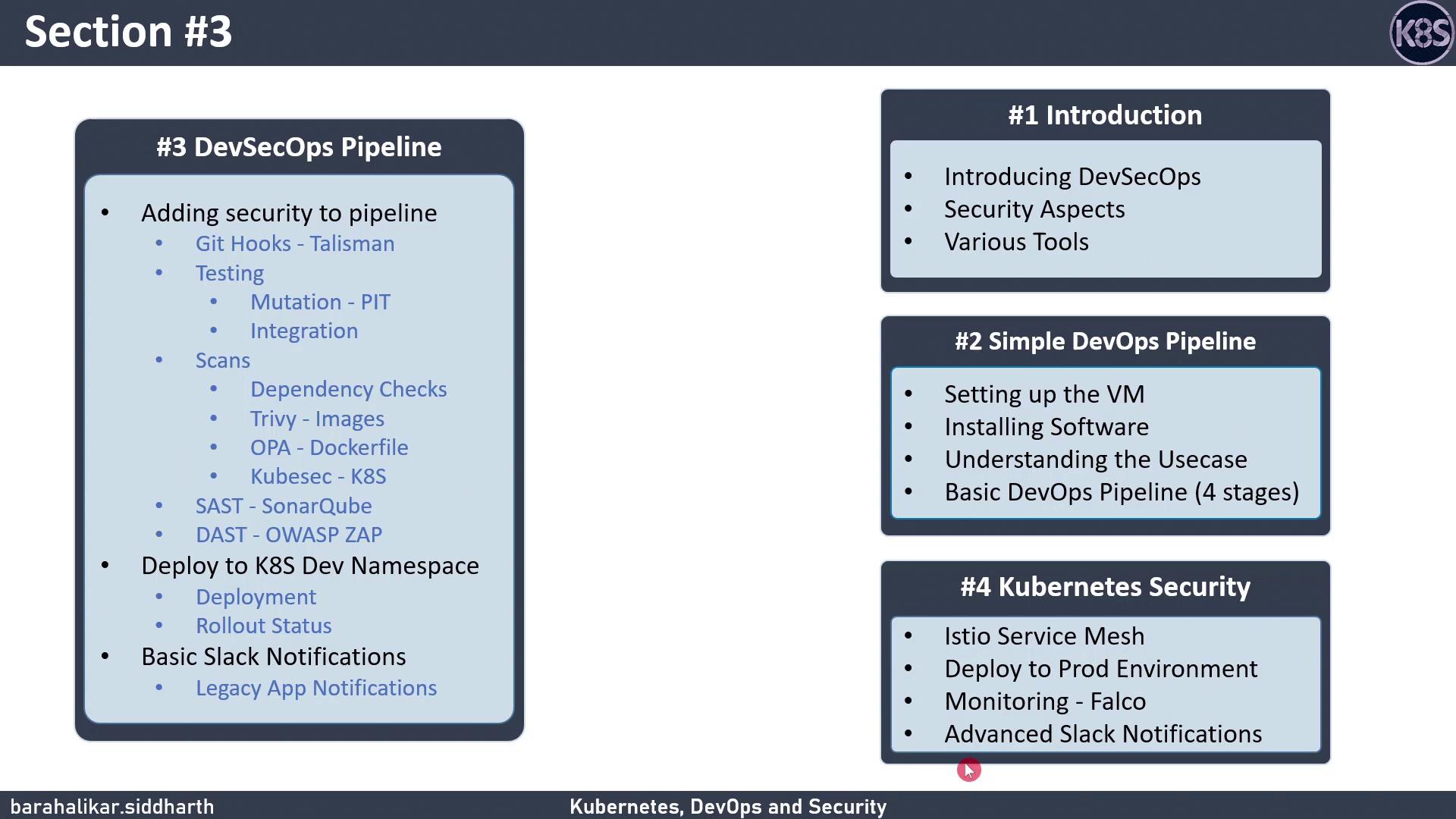
DevSecOps Pipeline Overview
Below is a high-level breakdown of each stage in our DevSecOps pipeline:| Stage | Purpose | Tool(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Source Control | Host and version application code | GitHub |
| Unit Testing | Validate individual functions and modules | JUnit, pytest |
| Integration Testing | Test interactions between services | Postman, Selenium |
| Vulnerability Scanning | Identify security flaws in code and dependencies | OWASP Dependency-Check |
| Dynamic Application Security Testing | Simulate real-world attacks against the running app | OWASP ZAP |
3.1 Verify Kubernetes Rollout Status
After deploying to Kubernetes, confirm that your pods have rolled out successfully:3.2 Configure Jenkins for Slack Notifications
Keep your team informed by sending build alerts to Slack. Add the following to your Jenkinsfile:Make sure the Slack plugin is installed in Jenkins and you have configured your Incoming Webhook URL under Manage Jenkins → Configure System → Slack.