Why Use Kubernetes Services?
Kubernetes Services decouple the front-end, back-end, and data-layer Pods, offering:- Stable endpoints: Consistent IPs or DNS names for Pods that may be recreated.
- Load balancing: Distributes traffic evenly across multiple Pods.
- Discoverability: Native service discovery within the cluster network.
- Front-end Pods serving user interfaces
- Back-end Pods processing business logic
- Pods connecting to external data sources
External Access Use Case
By default, Pod IPs (e.g., 10.244.0.2) are only reachable inside the cluster network. To access a web server Pod from your laptop (192.168.1.10) without SSH’ing into the Node (192.168.1.2), you need a NodePort Service which maps a port on the Node to the Pod’s port.| Service Type | Use Case | Example Configuration |
|---|---|---|
| ClusterIP | Internal-only service for Pod-to-Pod communication | type: ClusterIP |
| NodePort | Exposes Pod on a port across all Nodes for external access | type: NodePortnodePort: 30008 |
| LoadBalancer | Provisions a cloud load balancer to distribute external traffic | type: LoadBalancer |
NodePort ranges from 30000 to 32767 by default. You can customize this in the API server flags.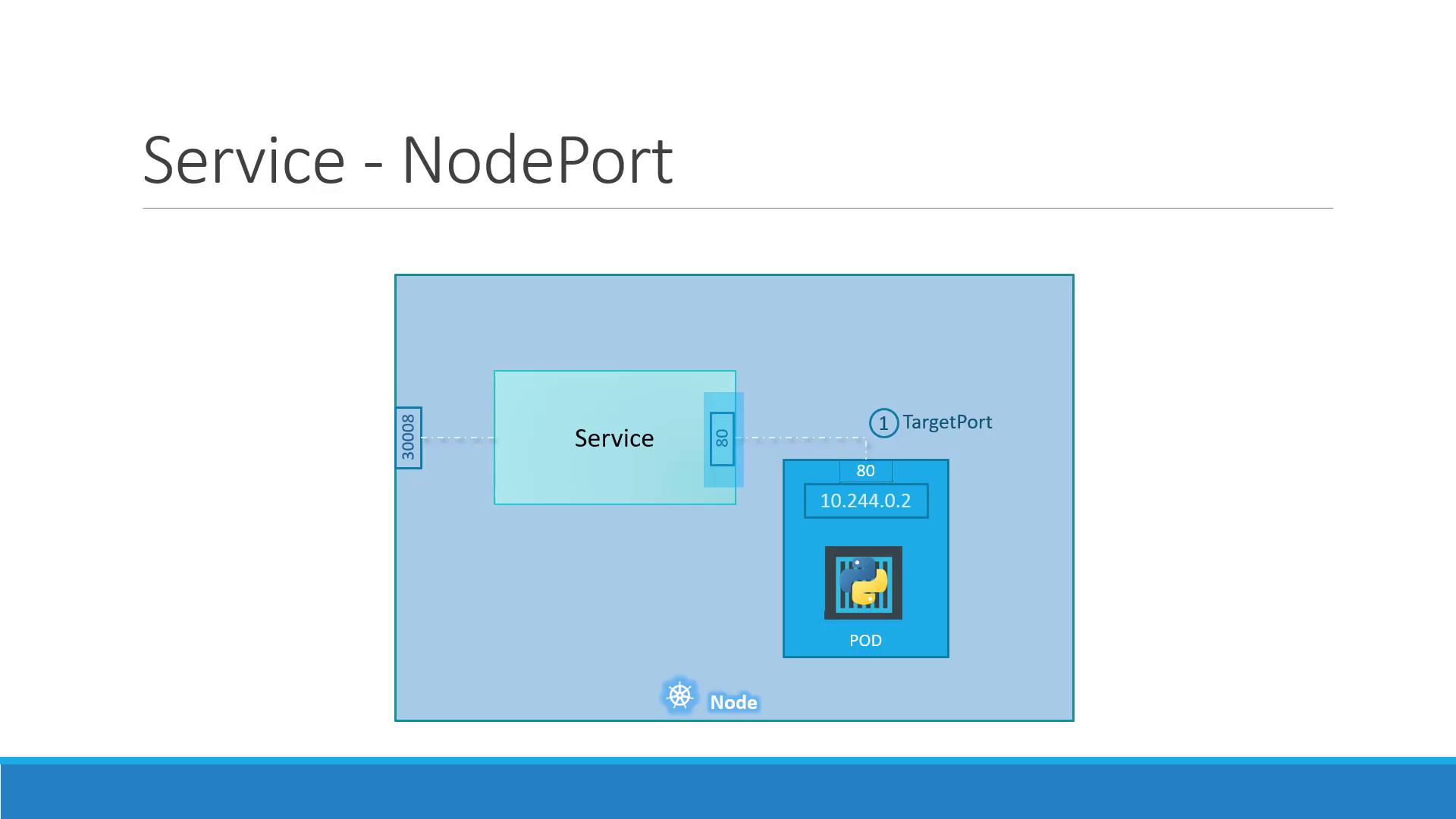
NodePort Service Ports Explained
A NodePort Service uses three port definitions:- targetPort: Port on the Pod (e.g., 80)
- port: Virtual Service port inside the cluster (e.g., 80)
- nodePort: Port on each Node, accessible externally (e.g., 30008)
<NodeIP>:<nodePort> → Service → port → Pod at targetPort.
Defining a NodePort Service
- Create a Pod with labels:
- Define the NodePort Service, matching the Pod labels:
- Deploy and Verify:
Exposing high ports on Nodes can pose security risks. Ensure proper firewall rules and network policies are in place.
Scaling with Multiple Pods and Nodes
In production, you’ll run multiple Pod replicas for high availability. A NodePort Service automatically load-balances incoming traffic across all Pods that match its selector, even when spread across multiple Nodes.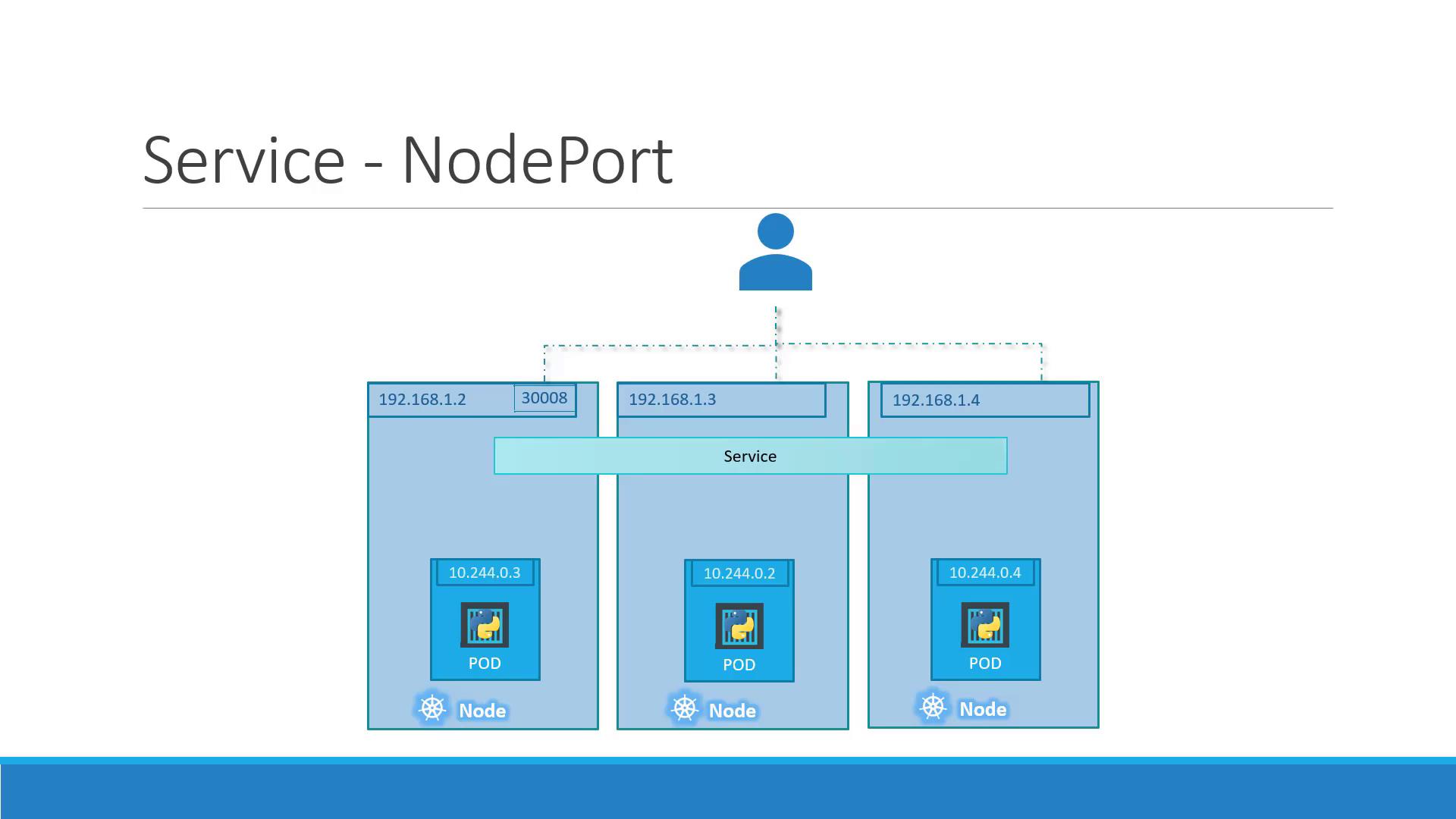
NodeIP:30008 are distributed across all 3 Pods.
Summary
- NodePort Services expose Pod ports on each Node for external access.
- Key fields:
type: NodePort,port,targetPort, andnodePort. - Match Services to Pods via label
selector. - Kubernetes handles load balancing across Pods and Nodes automatically.