- Create a feature branch for isolation
- Configure a
cloudbuild.yamlfor automated builds - Set up and verify a Cloud Build trigger
- Monitor builds in the Cloud Build dashboard
- Inspect Docker images in Artifact Registry
1. Create a New Git Branch
First, ensure you’re working in a dedicated feature branch. This keeps yourmain branch clean and allows safe testing of CI/CD changes.
2. Add the Cloud Build Configuration
In the root of your repository, create acloudbuild.yaml file. Cloud Build uses this file to define build steps, images to push, and other options.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| steps.name | Docker builder image used for the build |
| steps.args | Arguments passed to docker build (tagging and context path) |
| images | Destination(s) in Container/Artifact Registry to push to |
Ensure the Cloud Build API and Artifact Registry API are enabled in your Google Cloud project.
3. Commit and Push Changes
Once yourcloudbuild.yaml is in place, commit and push your changes:
main branch and merge it once approved.
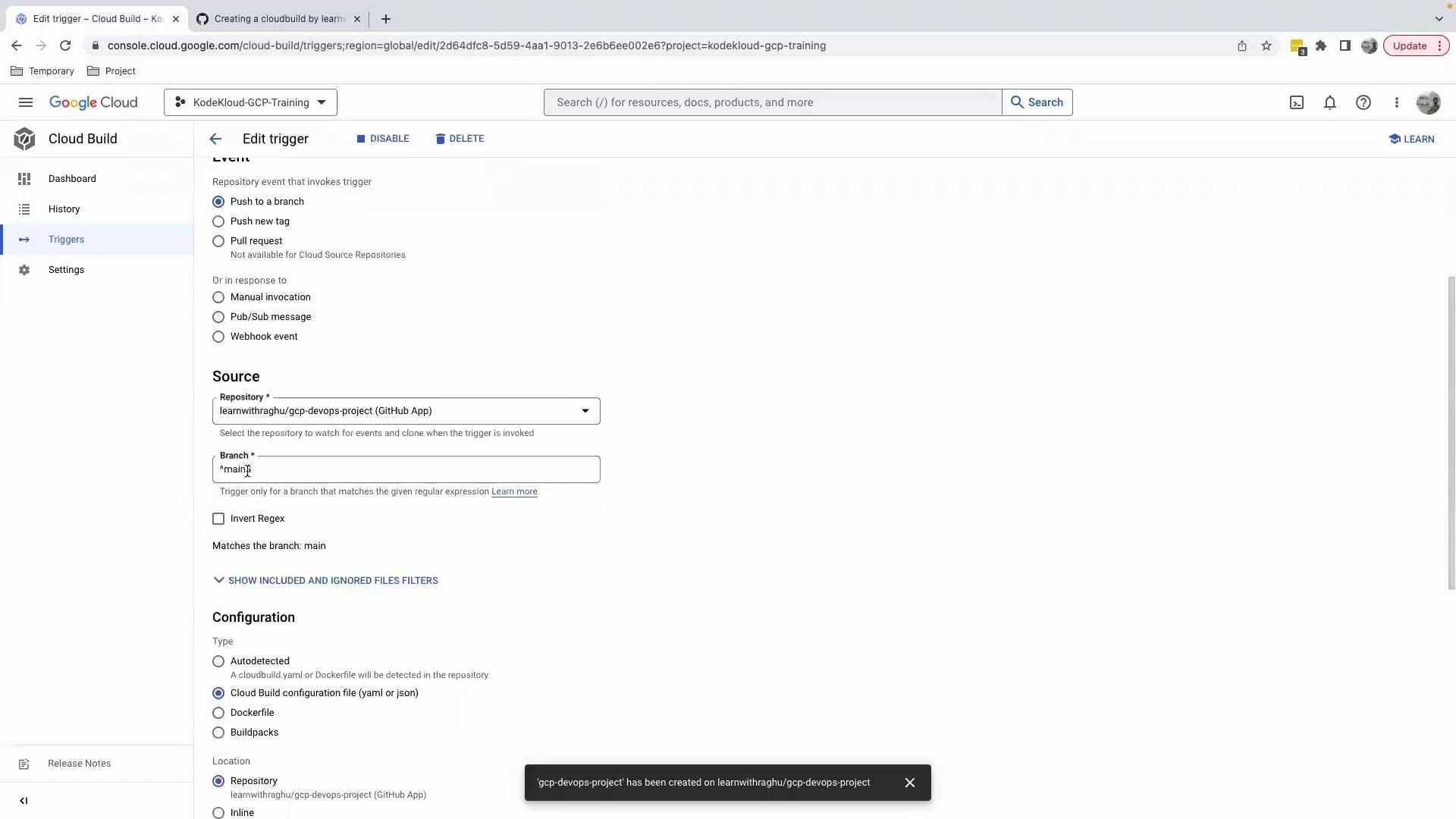
4. Configure and Verify Your Cloud Build Trigger
In the Google Cloud Console, navigate to Cloud Build › Triggers and confirm:- Event: Push to the
mainbranch - Source: Your repository
- Build Configuration: Use
cloudbuild.yamlin the root of the repository
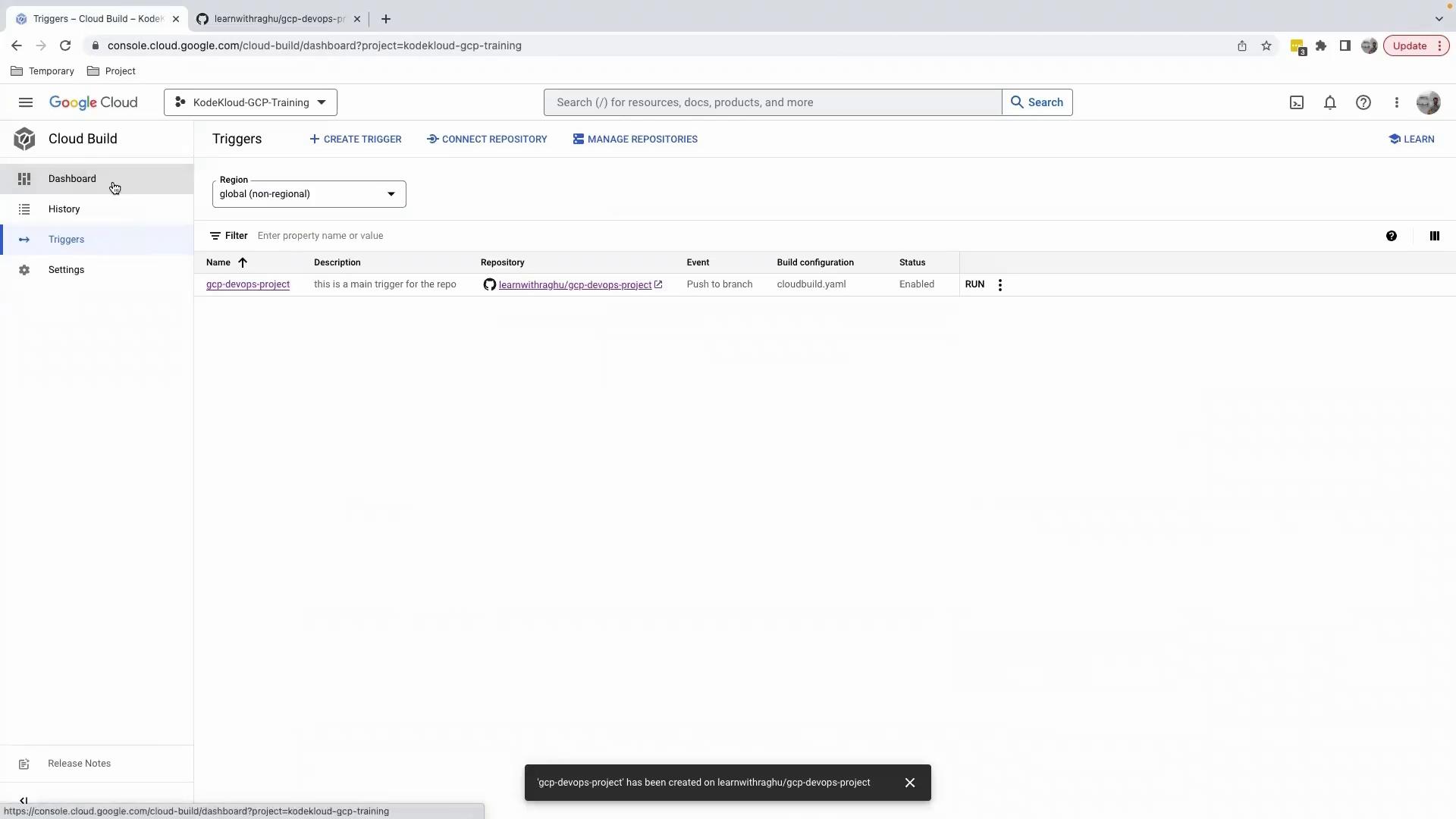
5. Merge and Monitor the Build
After merging your PR, Cloud Build will automatically start a build. To track progress:- Go to Cloud Build › Dashboard.
- Click on the latest build in History to view real-time logs.
Merging directly to
main triggers a build. Make sure your cloudbuild.yaml is correct to avoid broken pipelines.6. Inspect Your Artifacts
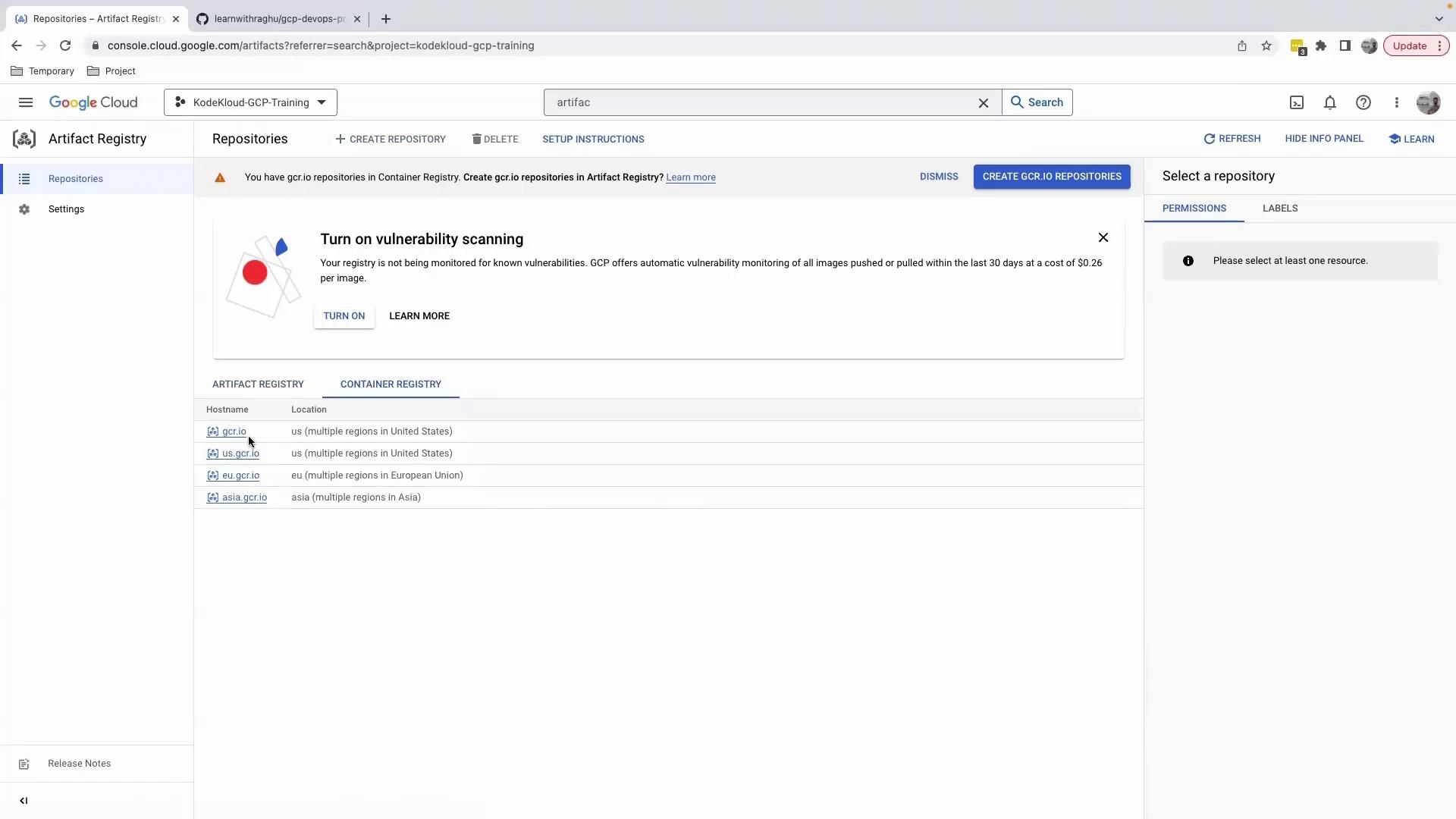
Once the build completes, open Artifact Registry:- Enable Artifact Registry if prompted (may take a minute).
- Click Container Registry to view your
gcr.iorepositories.
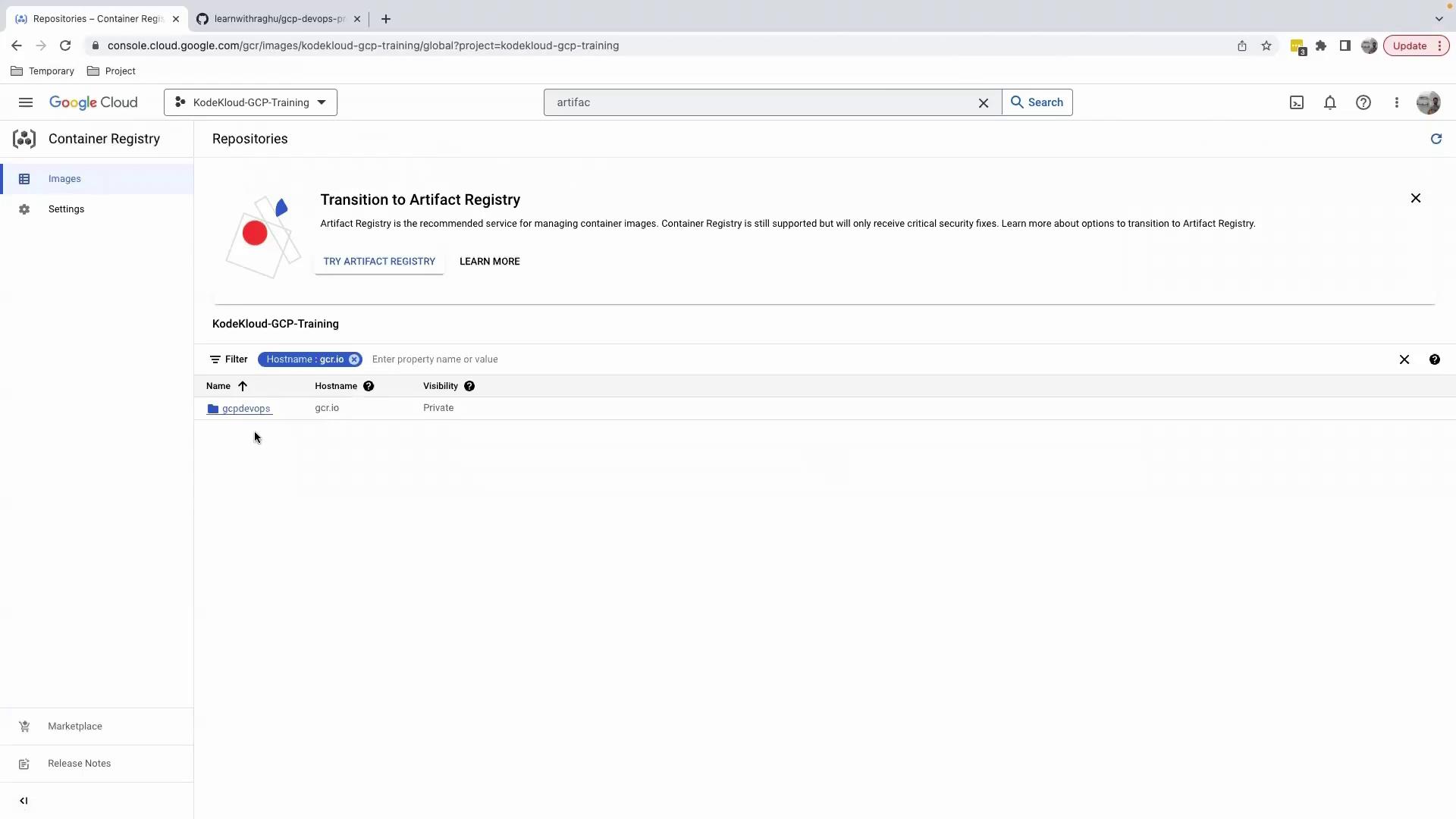
gcpdevops repository:
Recap and Next Steps
You’ve now:- Set up a feature branch and added
cloudbuild.yaml - Configured a Cloud Build trigger on pushes to
main - Monitored build logs and verified successful pushes to Artifact Registry