GKE - Google Kubernetes Engine
Managing Security Aspects
GKE shared responsibility model
Securing workloads on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) involves a multi-layered strategy that spans container images, runtimes, cluster networking, and API server access. Applying the principle of least privilege ensures users and applications receive only the permissions they need.
Shared Responsibility Model Overview

This diagram highlights how Google secures the underlying infrastructure and control plane, while customers handle cluster configuration and workload security.
Google Cloud Responsibilities
Google manages and hardens the infrastructure that underpins GKE clusters, including physical hardware, firmware, operating systems, storage, and networking. Core responsibilities include:
- Encrypting data at rest and in transit
- Designing custom hardware and enforcing physical security
- Preventing unauthorized modifications with Shielded Nodes
- Following a secure software development lifecycle
Google also hardens and patches:
- Node OS images (Container-Optimized OS and Ubuntu)
- Kubernetes node components and the GKE control plane
- Control plane VMs (single-tenant Compute Engine instances)
Control Plane Components Managed by Google
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| API Server | Validates and configures Kubernetes API objects |
| Scheduler | Assigns pods to nodes based on resource needs |
| Controller Manager | Enforces desired cluster state |
| Cluster Certificate Authority | Issues and rotates TLS certificates |
| Secrets Encryption | Encrypts Kubernetes Secrets at rest |
| Audit Logging | Captures cluster activity for compliance |
Note
Container Threat Detection is available through Security Command Center for real-time monitoring of container vulnerabilities.

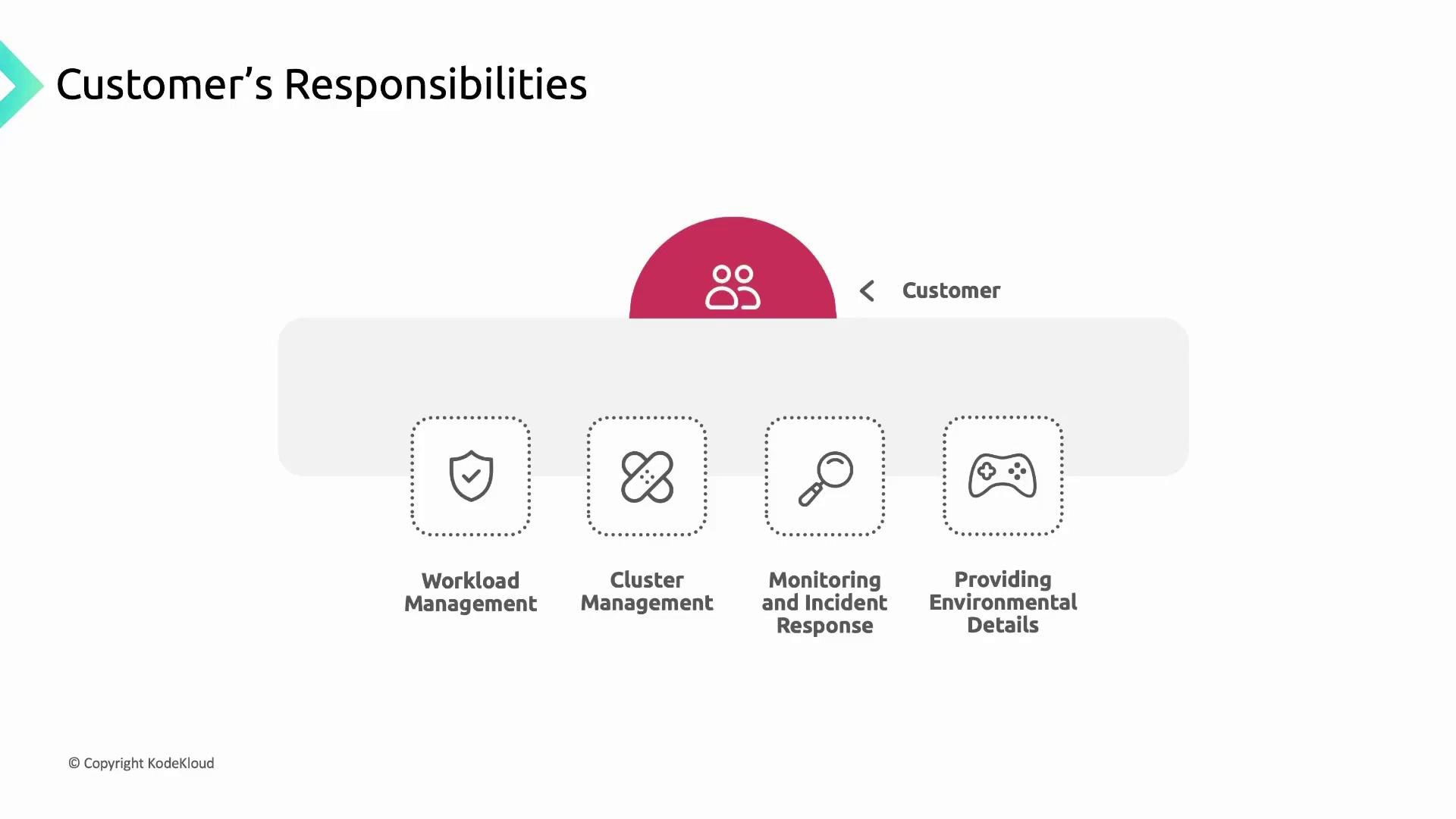
Customer Responsibilities
Customers must secure and manage everything they deploy in GKE:
- Application source code, build pipelines, and container images
- RBAC/IAM policies to control cluster access
- Container workloads (Pods, Deployments) and associated data
- Ensuring application availability, performance, and security
Cluster Lifecycle Management
| Task | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Version upgrades | Enable auto-upgrade (default) or apply manual upgrades |
| Patch management | Stay current with GKE release notes and security bulletins |
| Feature adoption | Test new features in non-production clusters |
Warning
Running unsupported cluster versions exposes you to known vulnerabilities. Always upgrade to a supported GKE version.
Monitoring and Incident Response
- Use the Security Posture Dashboard and Cloud Operations suite
- Configure alerts for suspicious activity and resource anomalies
- Provide environmental details to Google Support when troubleshooting
References
Watch Video
Watch video content