Securing the Control Plane
The control plane orchestrates your cluster, managing nodes, pods, and services. GKE secures it by running on a hardened Container-Optimized OS with SELinux, AppArmor, and kernel hardening. All communication with the API server is encrypted using TLS, and certificates are rotated automatically. Access is audited for traceability.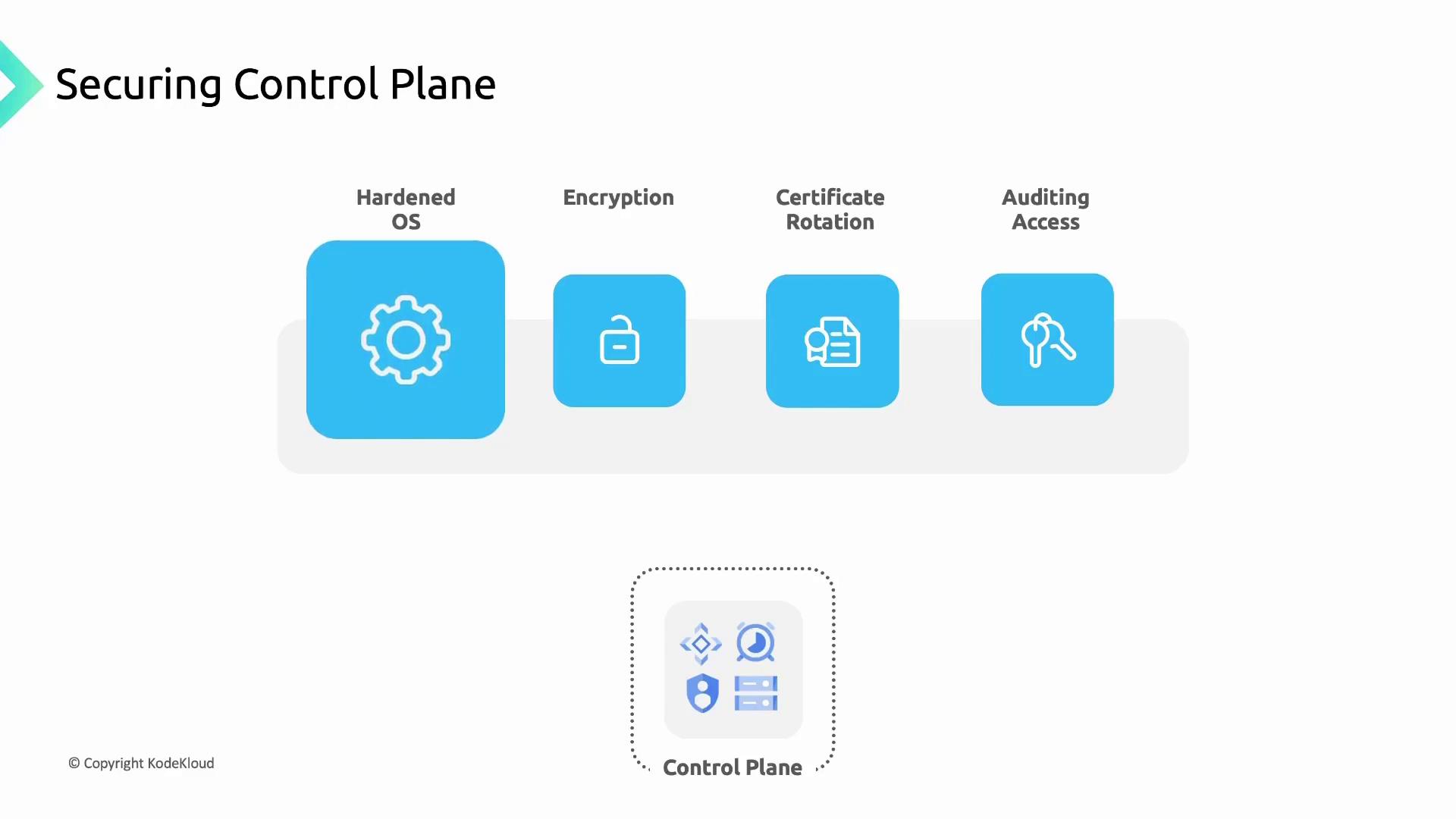
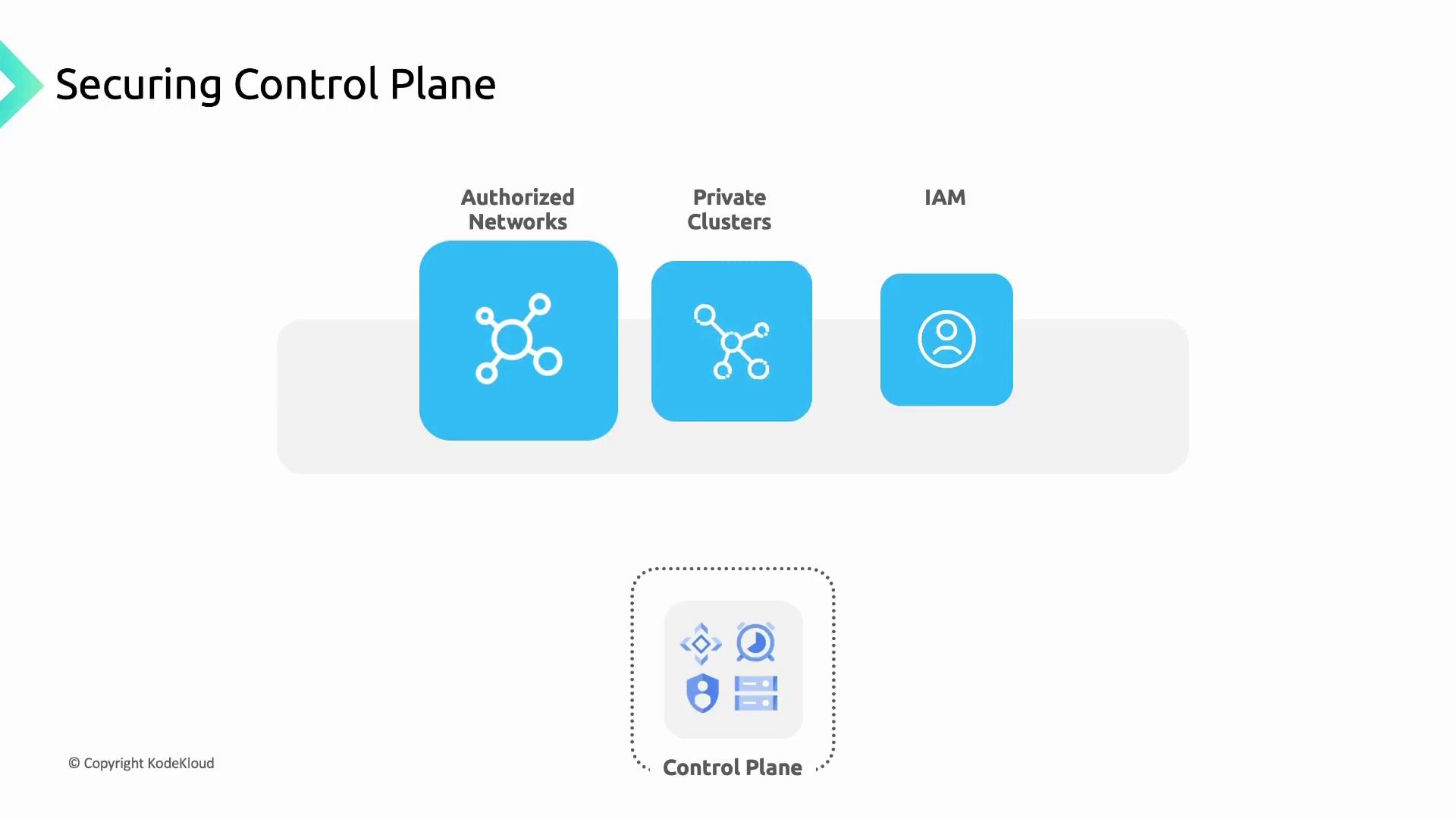
- Authorized Networks: Restrict API endpoint access to whitelisted IP ranges.
- Private Clusters: Use private IPs for nodes and the API server, isolating them from the public internet.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Assign fine-grained roles and permissions to limit who can perform actions on the control plane.
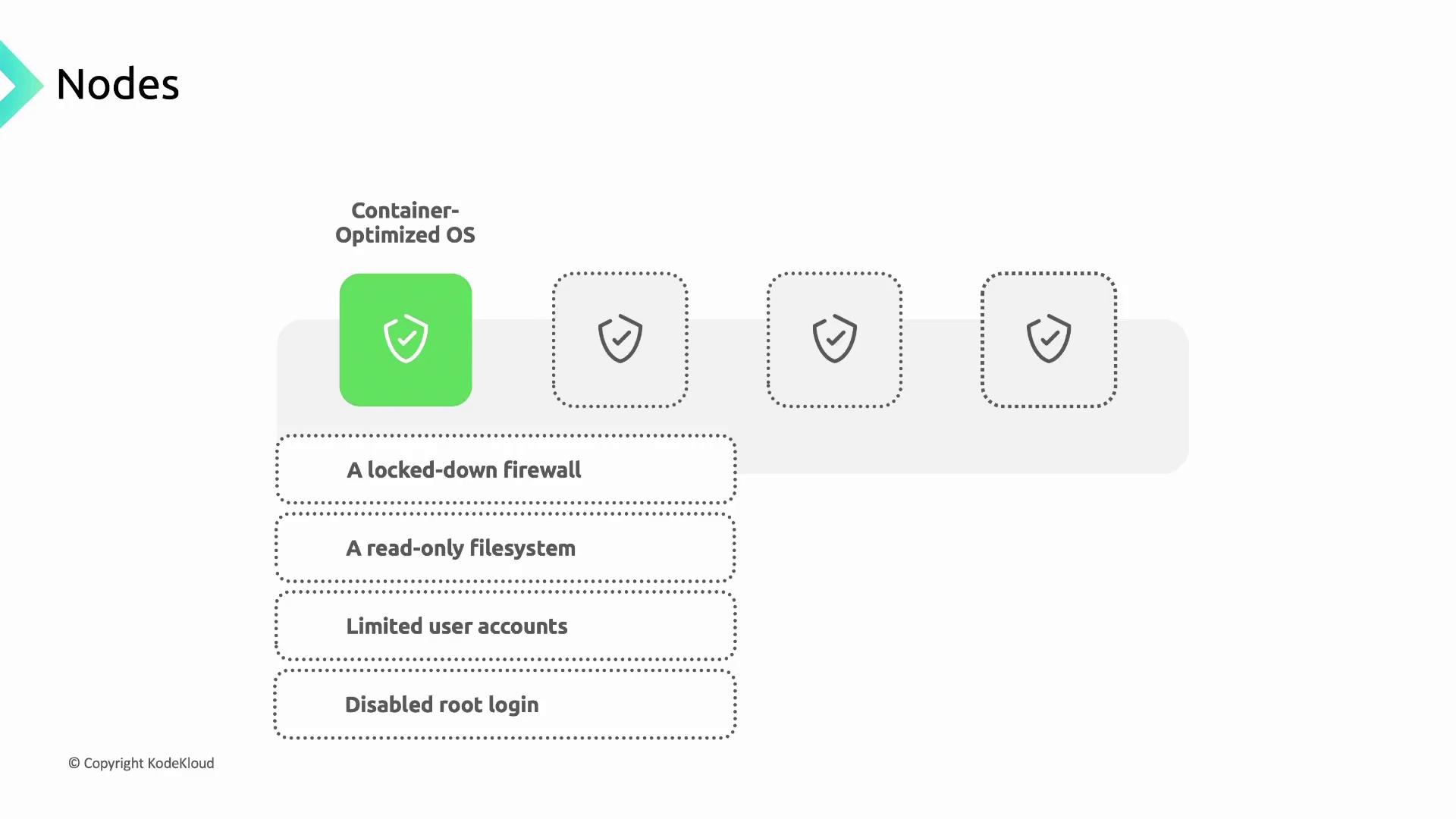
Securing Worker Nodes
Worker nodes run your containerized workloads and must be locked down:- Container-Optimized OS: Google-maintained, read-only root filesystem with a built-in firewall and no root SSH access.
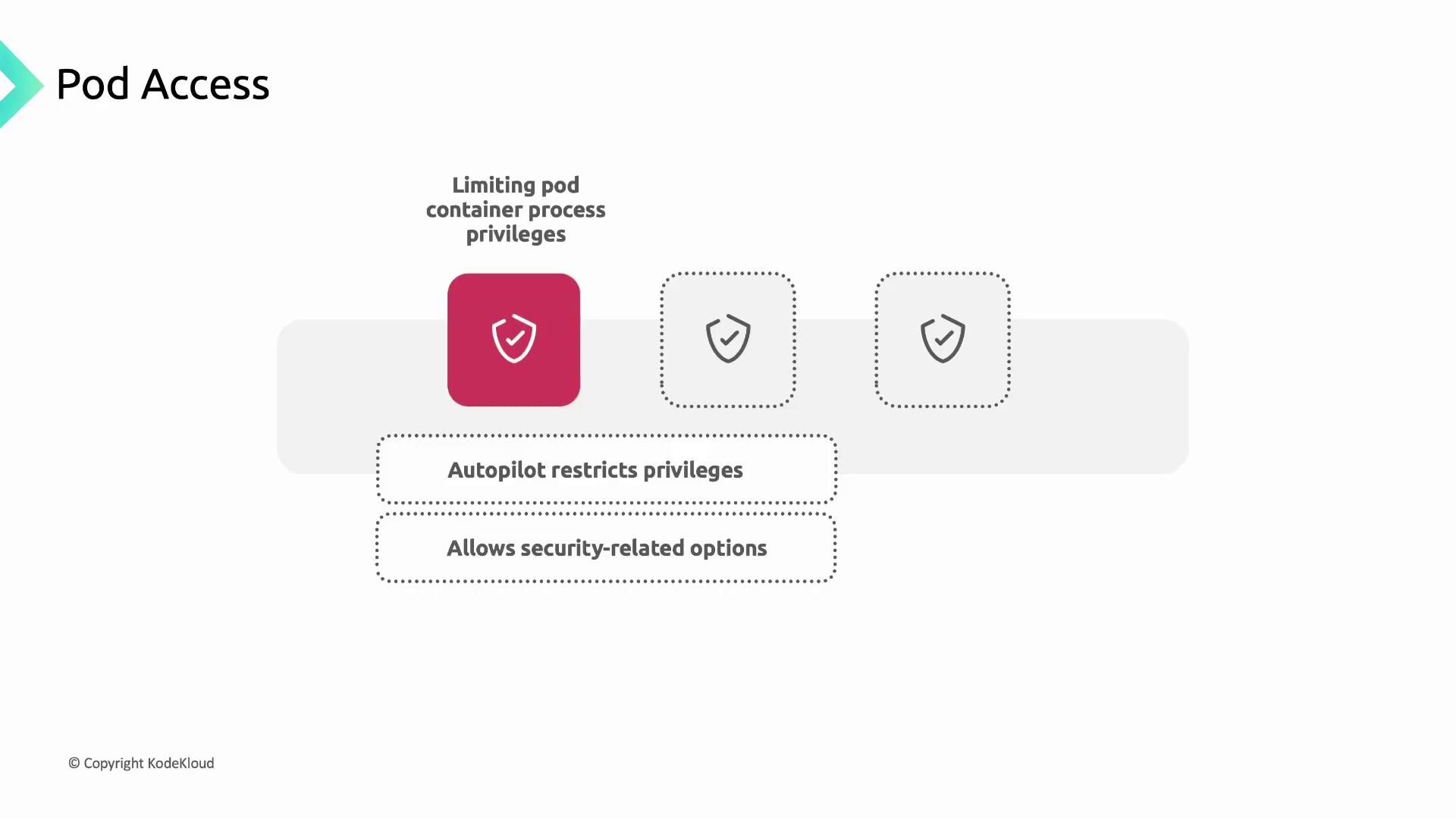
- Autopilot Enforcement: Autopilot clusters apply these OS controls by default.
- Limited Accounts: Only essential user accounts exist with privileges scoped to required operations.
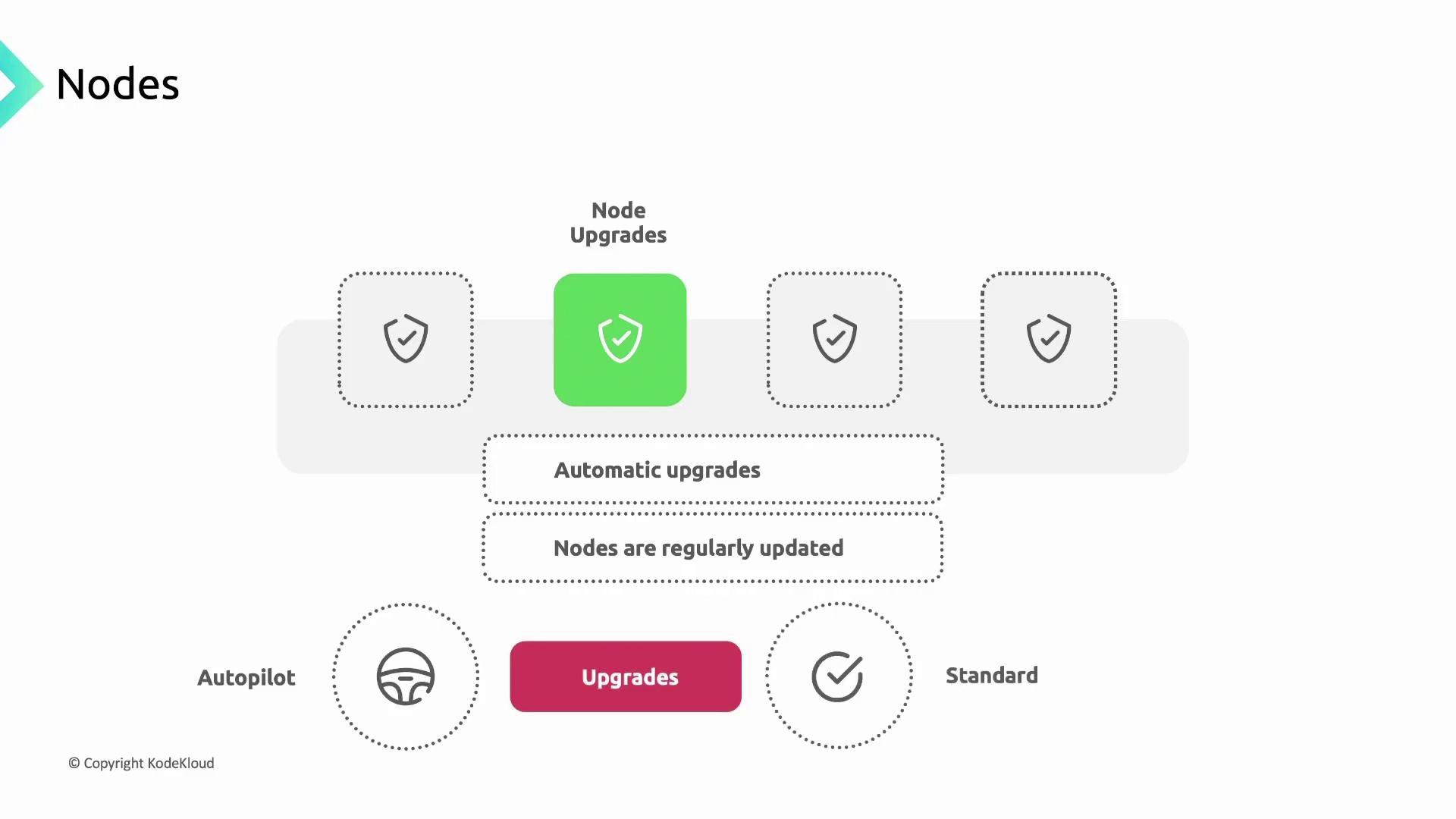
Node Upgrades
Regular updates close security gaps and ensure compatibility:- Autopilot Clusters: Automatic node upgrades are enabled by default.
- Standard Clusters: Choose between automatic or manual upgrades with customizable windows.
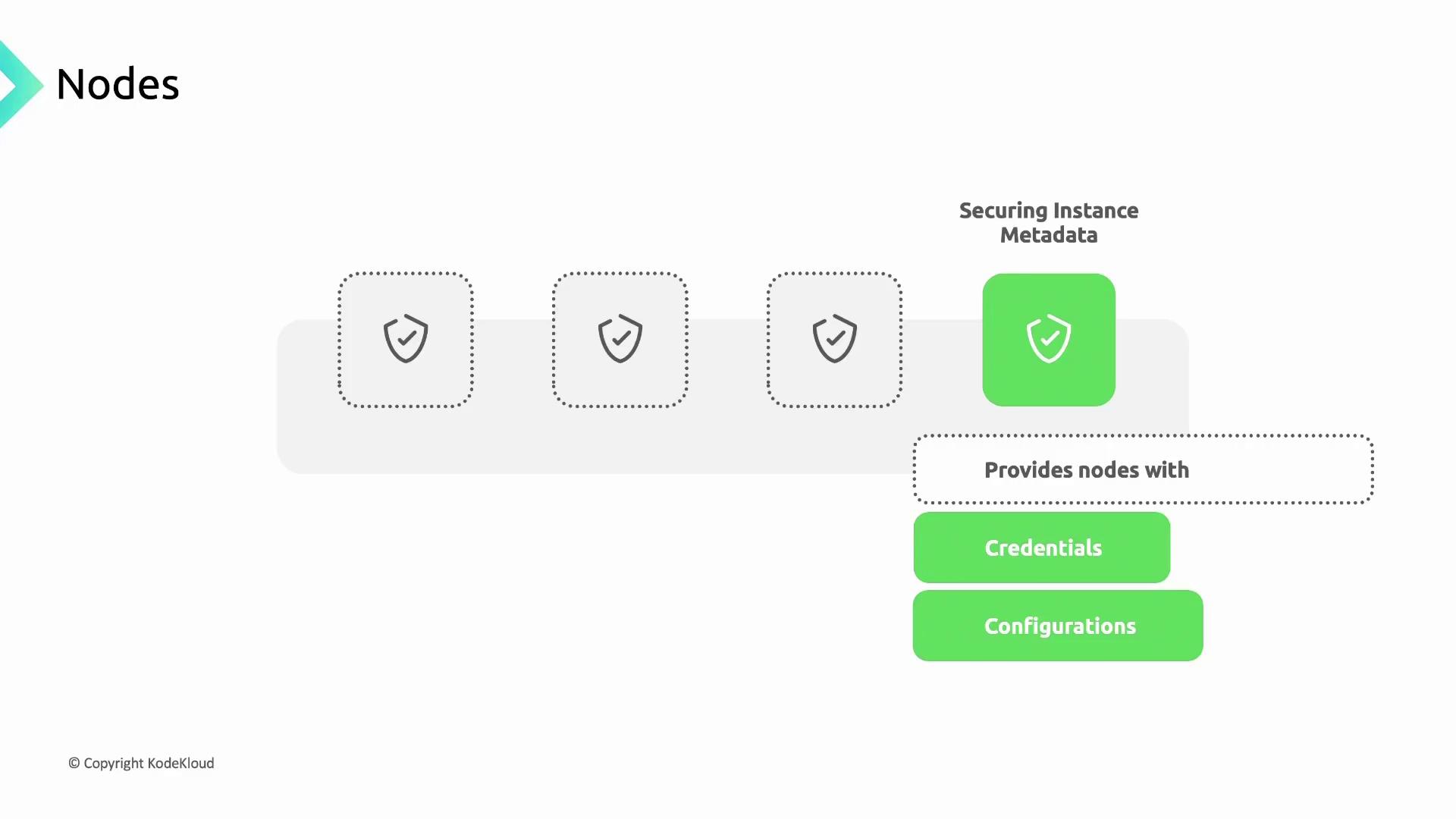
Protecting Instance Metadata
By default, nodes fetch credentials and configuration from the Compute Engine metadata server. Pods shouldn’t inherit node service account keys. Enabling Workload Identity filters metadata access, exposing only pod-level credentials.Workload Identity replaces node-level metadata access, preventing privilege escalation from pods to node credentials.
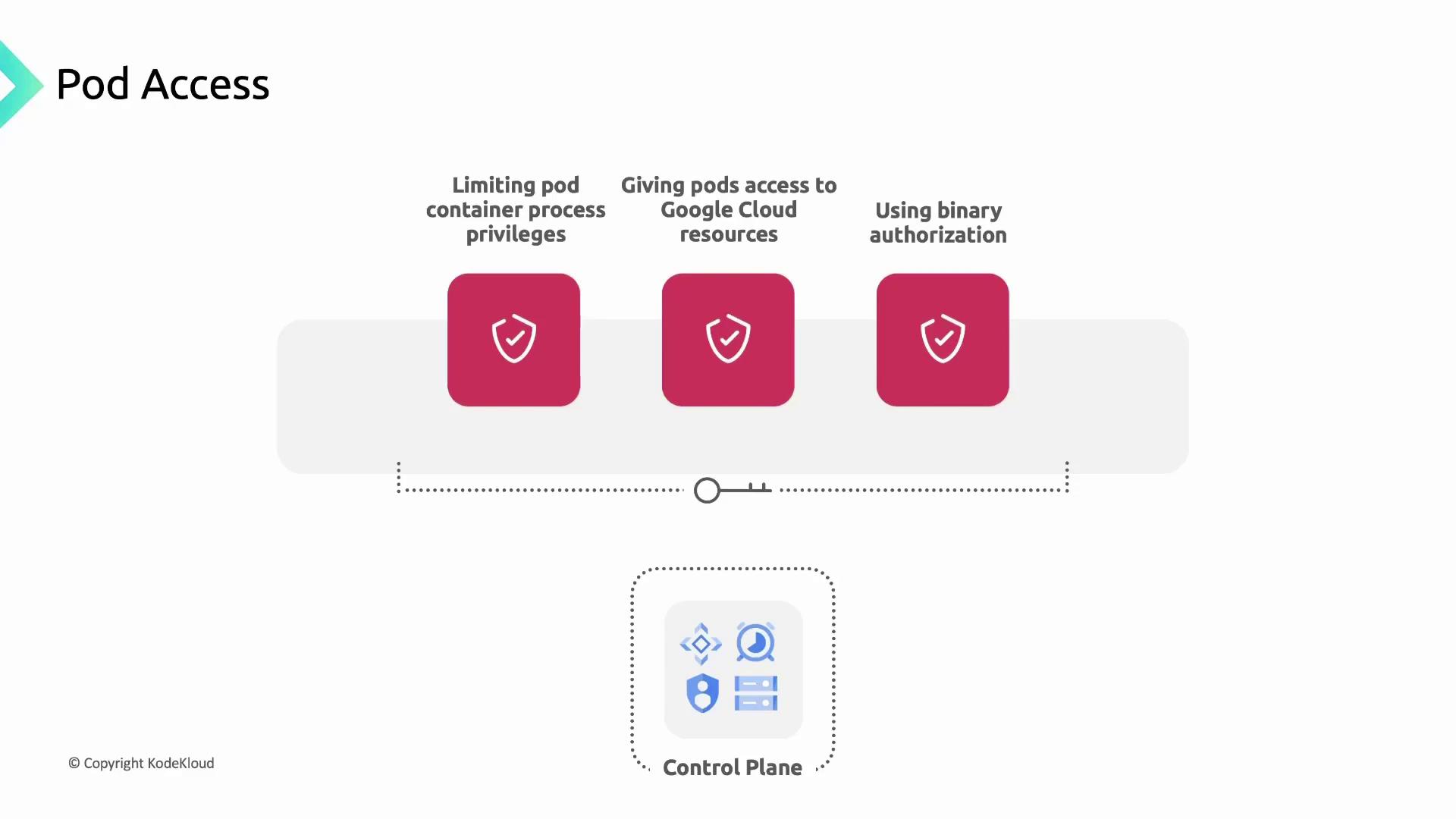
Managing Pod Access and Credentials
Apply the principle of least privilege to your workloads:- Security Contexts: Define user IDs, restrict Linux capabilities, and disable privilege escalation.
- Workload Identity: Map Kubernetes ServiceAccounts to IAM ServiceAccounts for granular permissions.
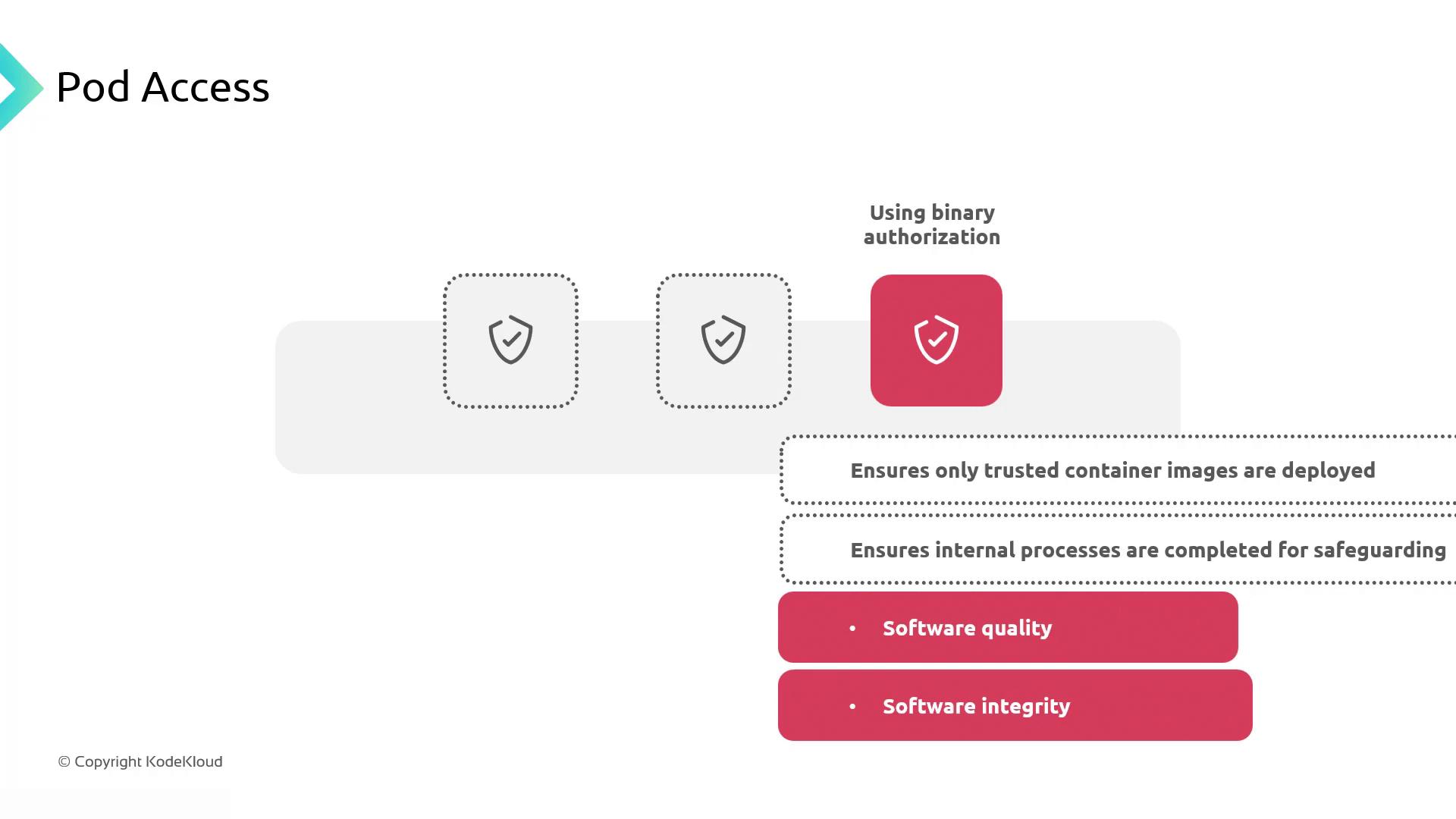
- Binary Authorization: Enforce image signing and attestation before deployment.
Network Security with Network Policies
Kubernetes Network Policies control traffic based on pod labels, enforcing a zero-trust network. For example, restrict anapp=my-app pod to only communicate with db=my-db pods:
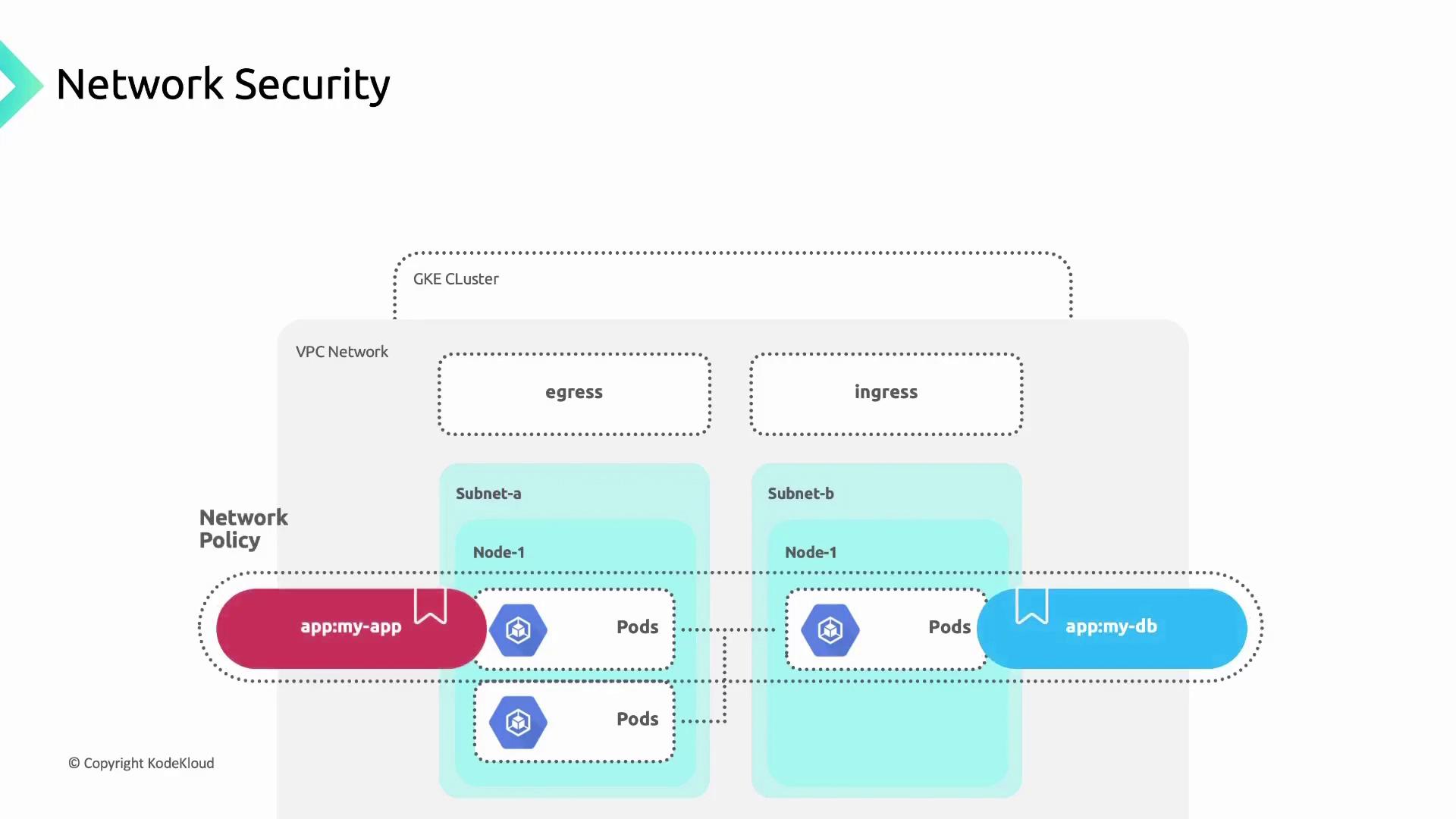
Without a default deny policy, unintended traffic might still flow. Always set a global deny-all policy if no rules match.