LoadBalancer, GKE automatically provisions and configures the appropriate Google Cloud load balancer, streamlining your networking setup.
Load Balancer Types in GKE
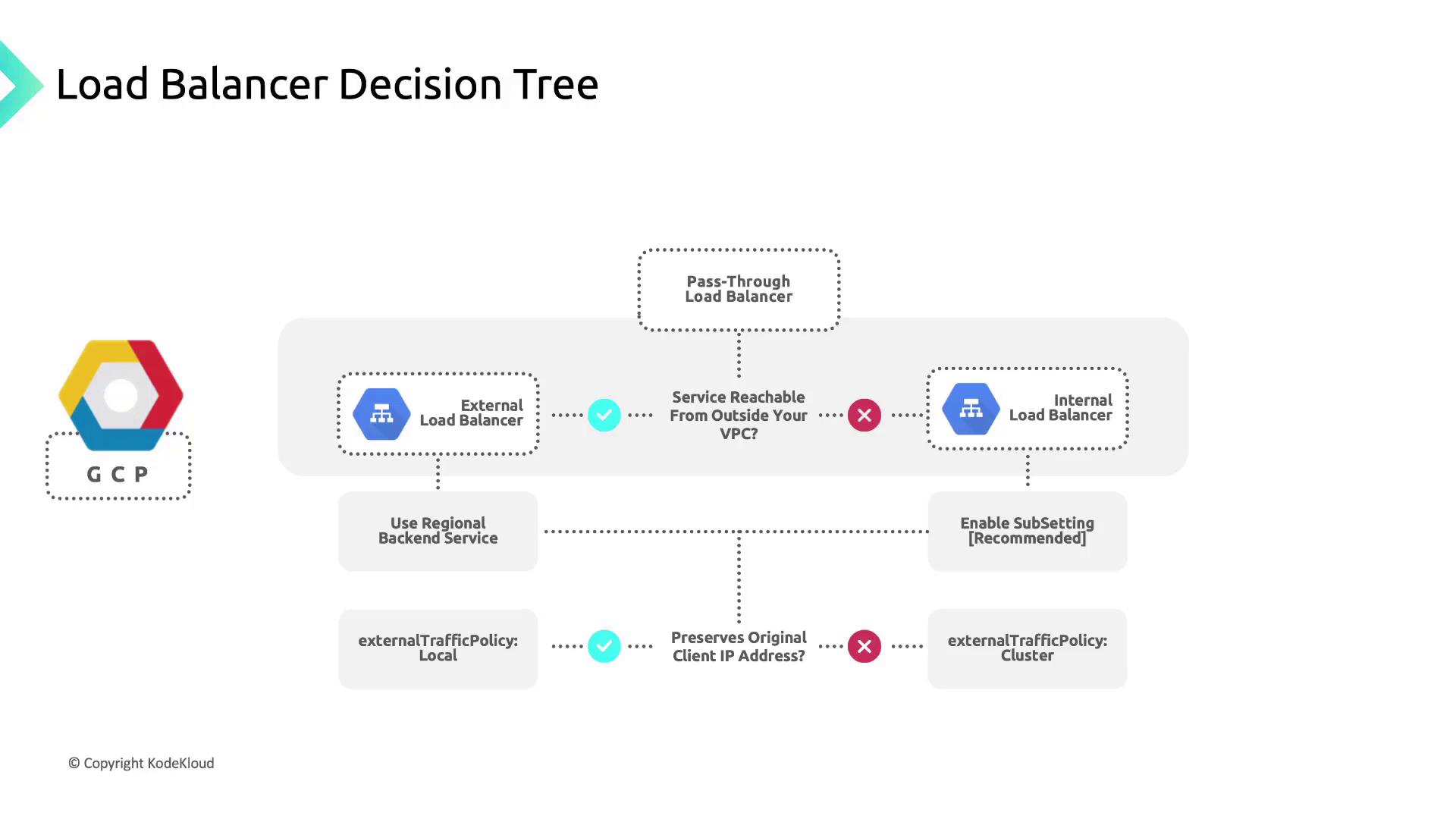
GKE supports two main load balancer types. Choose the one that matches your application’s accessibility and security requirements:| Load Balancer Type | IP Scope | Use Case | Visibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| External Load Balancer | Public IP | Internet-facing services | Global/Public |
| Internal Load Balancer | VPC-private IP | Internal microservices, multi-tier apps | VPC/Internal only |
External Load Balancer
An External Load Balancer Service provisions a publicly accessible IP address. It routes traffic from clients outside your VPC to pods running in your GKE cluster—ideal for web applications, APIs, and services that require Internet exposure.Internal Load Balancer
An Internal Load Balancer Service uses an IP address from your VPC’s subnet. This setup routes traffic privately within the VPC or across peered networks, perfect for multi-tier architectures or services that must remain internal.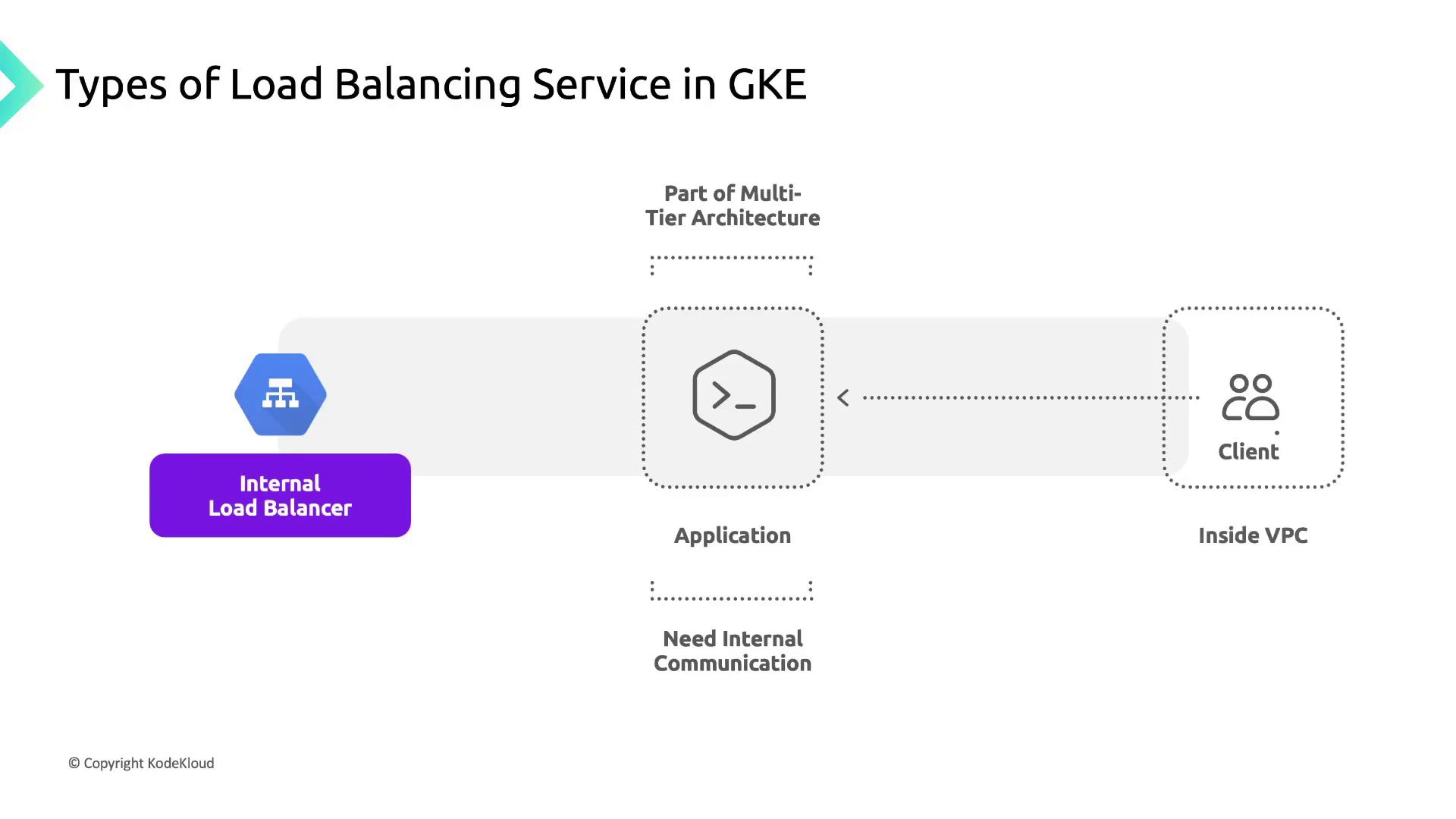
Internal Load Balancer Services do not allocate a public IP. Ensure your subnets and firewall rules allow traffic between your services and clients within the VPC.
Configuring a LoadBalancer Service
The behavior of your load balancer is driven by fields in the Kubernetes Service manifest. Below is a sample configuration followed by key parameter descriptions.| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
type | Must be set to LoadBalancer to provision a Google Cloud load balancer. | LoadBalancer |
loadBalancerIP | (Optional) Assigns a reserved static IP address. | 10.0.0.50 |
externalTrafficPolicy | Defines how client source IPs are handled. | Cluster or Local |
annotations | Configure advanced features (e.g., GKE subsetting for internal L4 load balancing). | cloud.google.com/load-balancer-type |
Reserving a static IP using
gcloud compute addresses create ensures your LoadBalancerIP remains unchanged after service updates or rescheduling.External Traffic Policy
Control how the load balancer forwards requests and preserves source IP:| Policy | Preserves Client IP | Node SNAT | Traffic Routing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster | No | Yes | Any node with healthy pods can receive and proxy traffic. |
| Local | Yes | No | Only nodes with ready pods receive traffic (Direct Server Return). |
-
Cluster (default):
- Source IP is replaced by the node’s IP (SNAT).
- Distributes traffic evenly across all healthy pods.
-
Local:
- Preserves the original client IP.
- Direct Server Return ensures responses go back directly to clients, reducing latency.
GKE Subsetting for Layer-4 Internal Load Balancing
GKE subsetting optimizes internal load balancers by limiting the backend nodes to only those running active pods for a service:- Creates a Network Endpoint Group (NEG) per service per zone.
- Registers only nodes with at least one ready pod.
- Improves performance and scales efficiently in large clusters.
In a zonal cluster with 3 nodes and 2 internal services:
- Enabling subsetting creates 2 NEGs per zone.
- Each NEG contains only the nodes hosting the corresponding service.
- Traffic is distributed solely to relevant nodes, optimizing resource usage.