Taints and Tolerations Analogy
Imagine a birthday party with two zones: a colorful play area for kids and a quiet lounge for adults. You hand out blue bracelets to kids and green bracelets to adults so everyone stays in the right spot. In GKE:- Nodes are the party zones.
- A taint on a node labels its “zone” (e.g., Music Area, Reading Area).
- A pod’s toleration is its bracelet—pods with a matching toleration can be scheduled on that node.
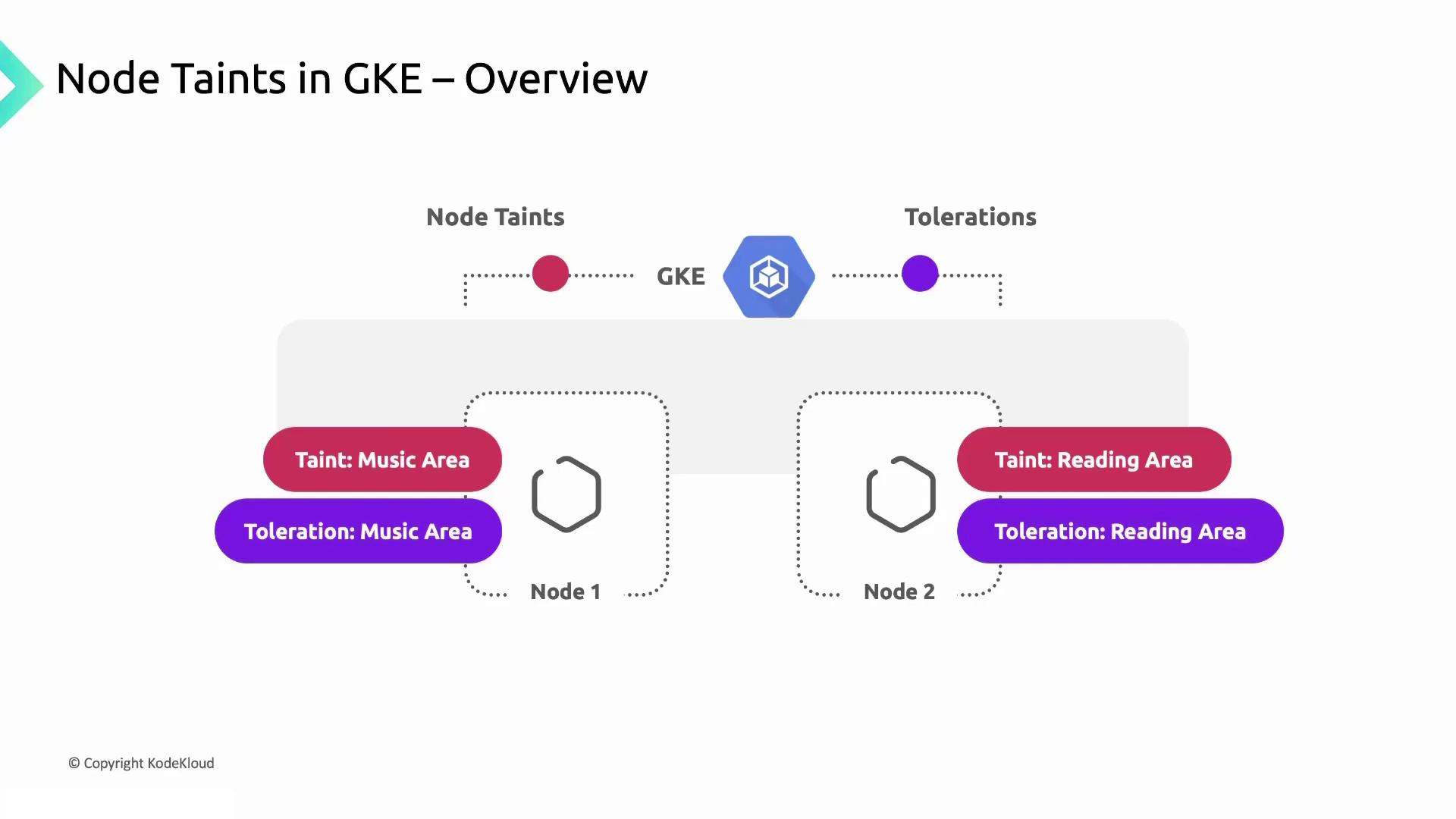
music-area toleration will only run on nodes tainted for music, just like kids gathering in their play zone. Pods tolerating reading-area run on the quiet nodes.
Autopilot vs. Standard Clusters
Depending on your cluster mode, taint configuration changes:| Cluster Mode | Node Management | Taint Setup | Automation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autopilot | Fully managed by GKE | Taints applied automatically | GKE assigns taints at scale |
| Standard | User-defined node pools | You add taints when creating pools | You must update taints manually |
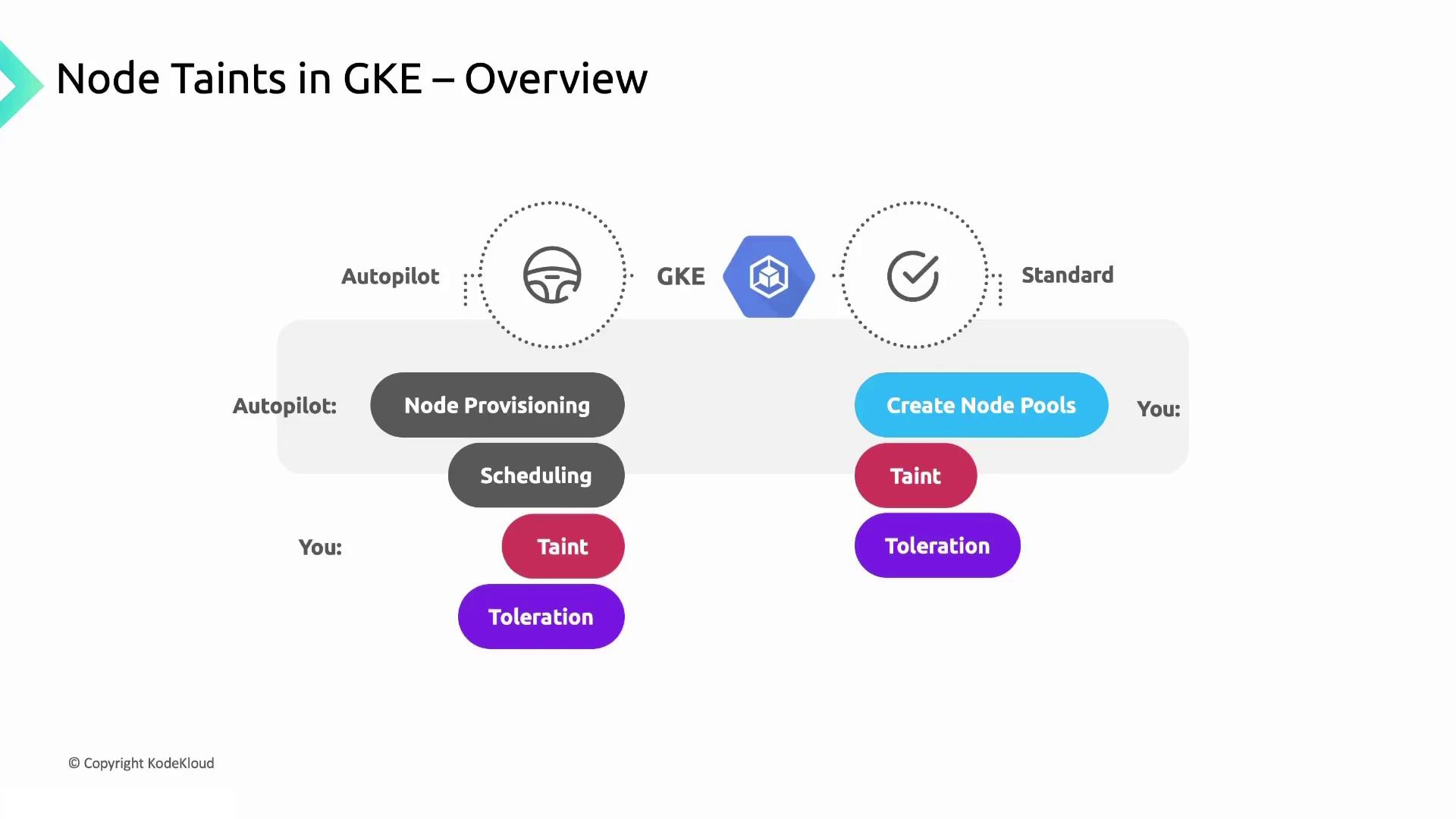
- In Autopilot, GKE handles node lifecycles and taints based on pod requirements.
- In Standard mode, you configure node pools, labels, and taints yourself.
Why Use Node Taints?
Taints help isolate workloads with specific needs—whether resources, hardware, or compliance: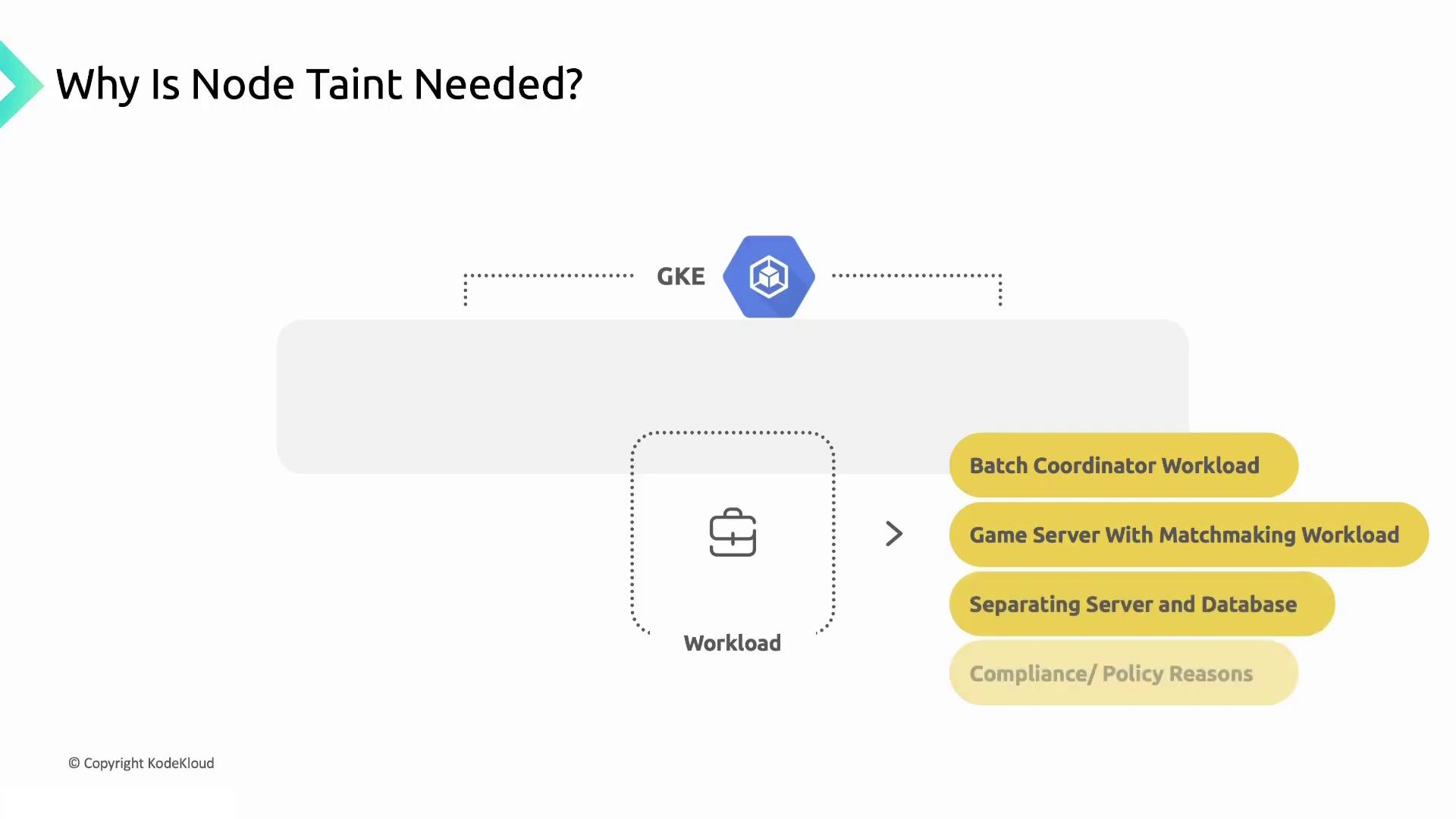
Batch Coordinator Workloads
Time-sensitive, resource-intensive jobs should run on dedicated nodes to avoid interference.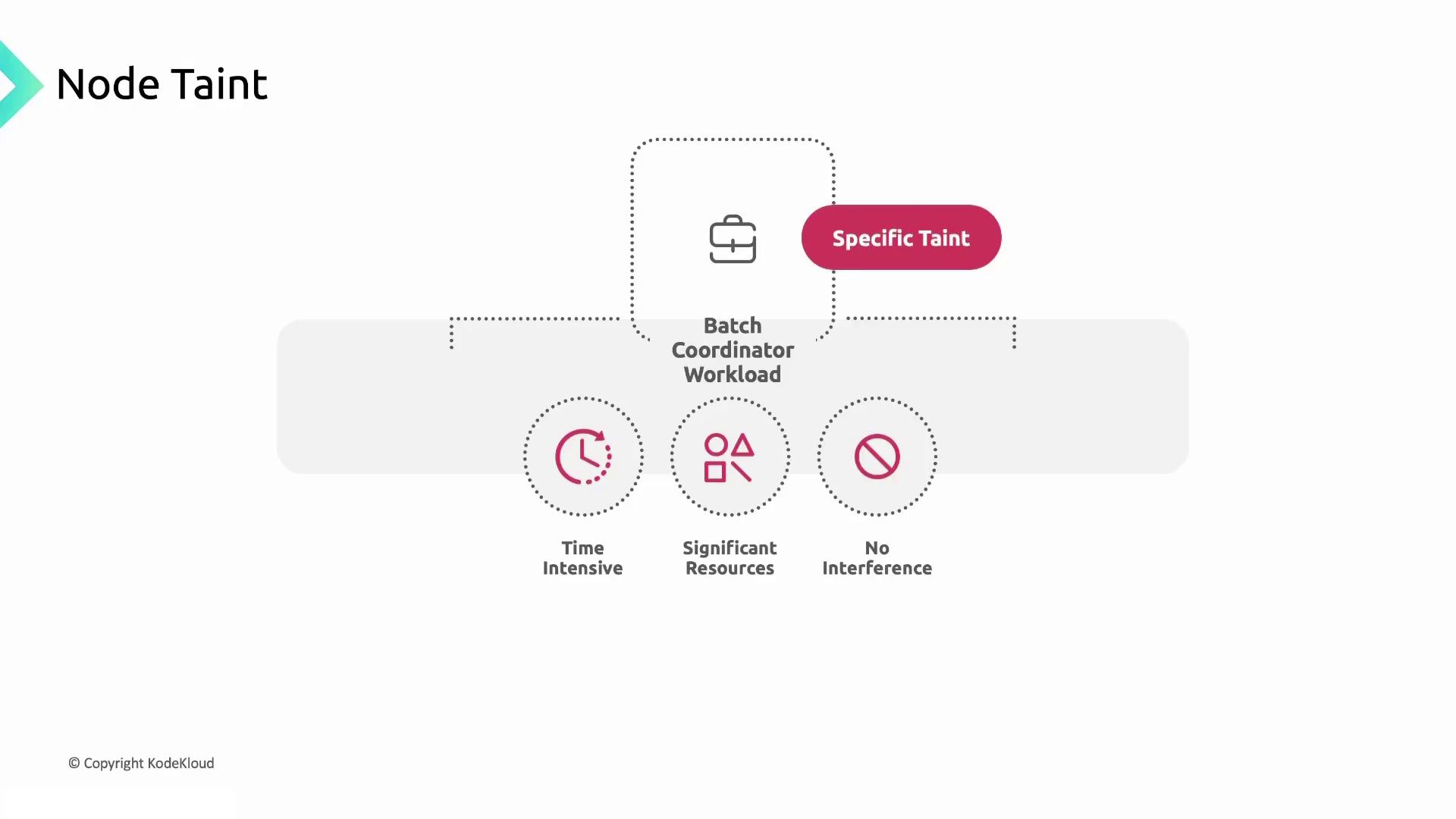
Game Server Matchmaking
Low-latency and specialized hardware are critical for matchmaking. A unique taint guarantees these pods land on the right machines.
Server–Database Separation
By tainting web servers and database nodes differently, you prevent resource contention and improve performance.- Web server nodes:
server-role=web:NoSchedule - Database nodes:
server-role=db:NoSchedule
Compliance and Policy Requirements
Some workloads must adhere to privacy regulations or internal policies. Assign compliance-specific taints to enforce workload isolation.
Node taints are not a security boundary. For untrusted workloads or strict isolation, use network policies, dedicated clusters, or virtualization.
Applying Node Taints in GKE
You can apply taints directly withkubectl or configure them in GKE for greater reliability:
- GKE Console / gcloud
kubectl taint- Terraform or other IaC tools
Example: Tainting with kubectl
If you remove a taint via
kubectl on a managed node pool, GKE will not reapply it after a restart. Always define critical taints at the pool or cluster level in GKE.