kubectl CLI within your GitHub Actions workflow to deploy to Kubernetes. By the end, you’ll have a reusable dev-deploy job that checks out your repo, installs kubectl, verifies the cluster, and is ready for your deployment steps.
1. Current Workflow Overview
Below is the existing workflow trigger and environment setup. We trigger on pushes tomain and feature branches, and we expose MongoDB credentials via environment variables.
2. Adding the dev-deploy Job
We’ll append a new job named dev-deploy. It runs after the docker job on ubuntu-latest and prepares kubectl for deployment in the Development namespace.
3. Installing the kubectl CLI
Instead of manually downloading binaries, leverage the verified [azure/setup-kubectl@v3] action from the GitHub Marketplace.
Using the official
azure/setup-kubectl action ensures you get signed binaries and can pin a specific version for reproducible builds.4. Fetching Kubernetes Cluster Details
After installing, verify connectivity by checking the client version and listing all nodes:5. Full dev-deploy Job Snippet
Here’s the complete YAML for the dev-deploy job:
5.1 Step-by-Step Summary
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Checkout Repo | actions/checkout@v4 | Clones your repository to the runner. |
| Install kubectl CLI | azure/setup-kubectl@v3 | Installs a specific version of kubectl. |
| Fetch Kubernetes Cluster Details | kubectl version --short | Validates CLI version and cluster connectivity. |
6. Workflow Execution
When you push these changes, GitHub Actions will executeunit-testing, code-coverage, and docker first. Once they succeed, dev-deploy runs.
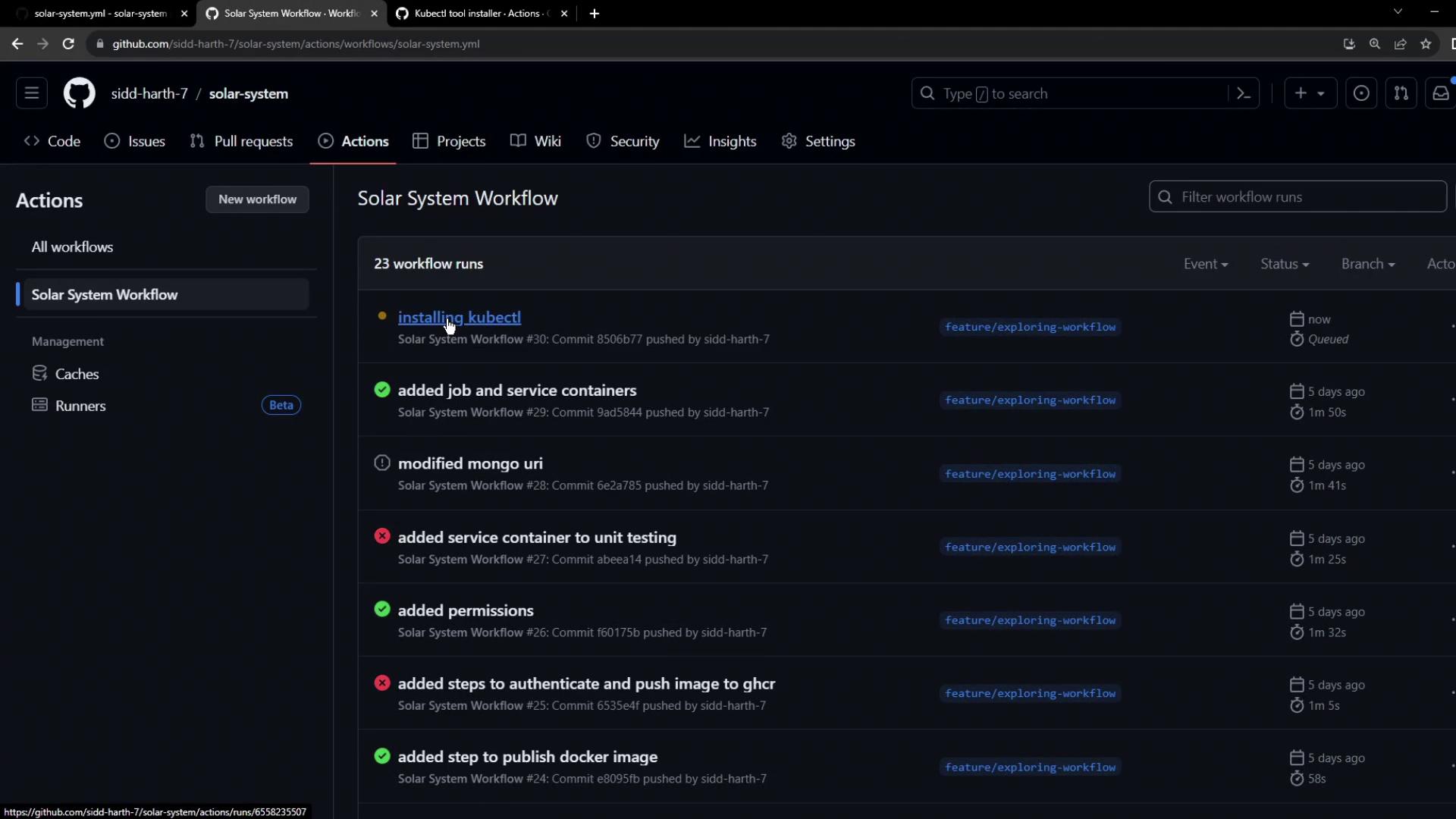
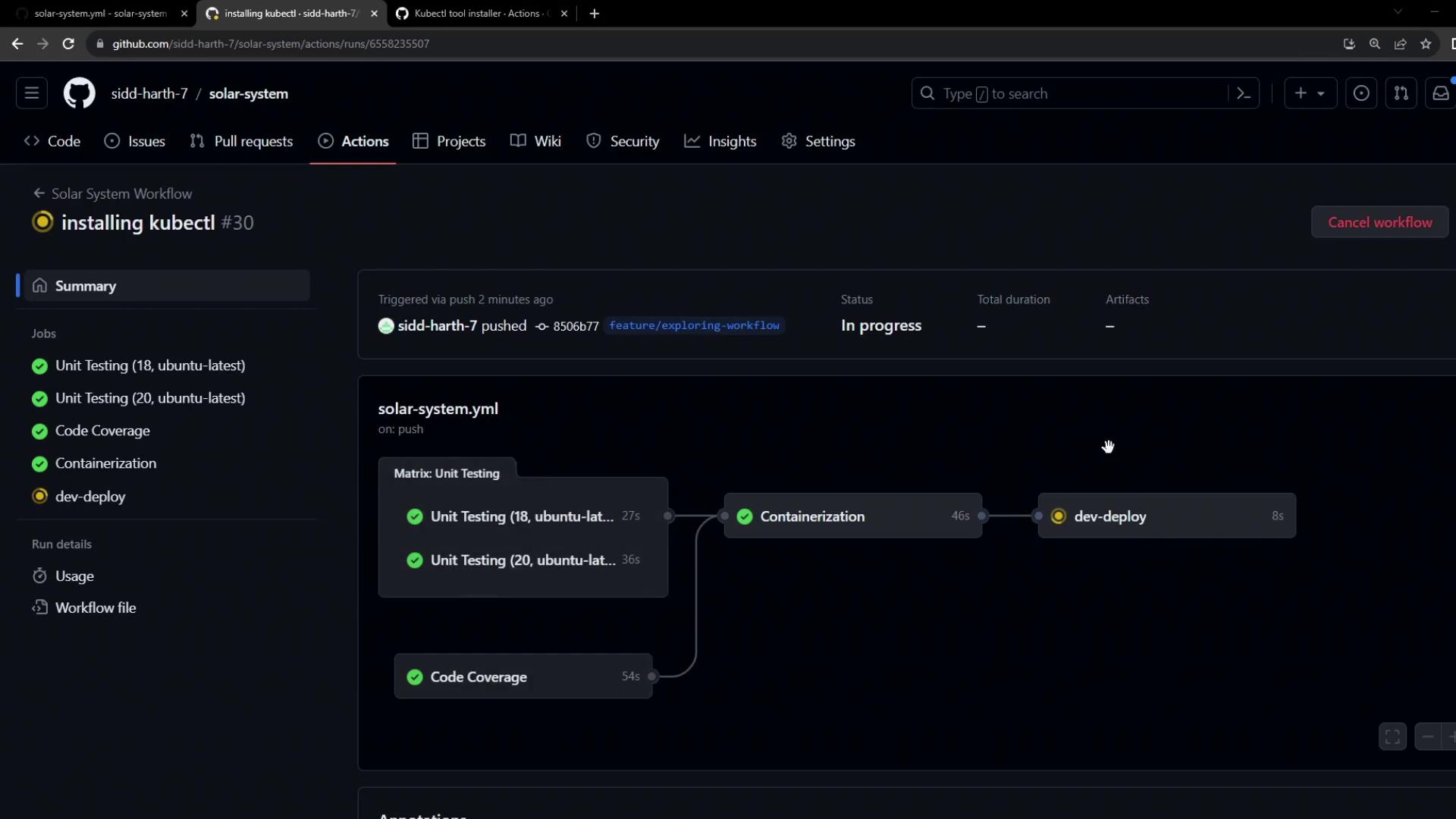
7. Troubleshooting Connection Errors
If you encounter:kubectl has no valid context because no kubeconfig is set.
You must provide a
kubeconfig file via secrets or variables and configure it in your workflow. Without it, kubectl cannot authenticate to your cluster.Example kubeconfig
kubeconfig as a secret and load it before your kubectl steps.