
What Is GitHub Packages?
GitHub Packages is a native package hosting service that lives alongside your repositories. It supports multiple ecosystems, provides fine-grained access control, and integrates directly with GitHub Actions to automate your CI/CD pipelines.
Supported Ecosystems
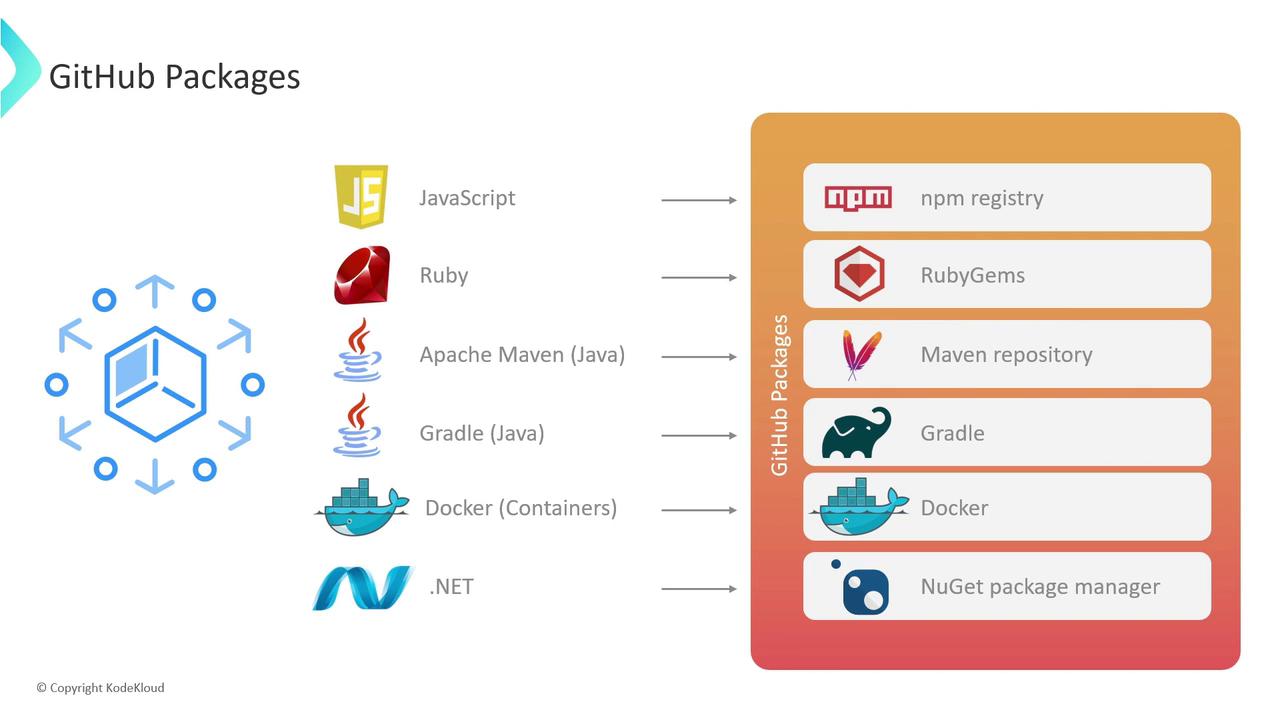
GitHub Packages works with all major package managers and container registries:| Ecosystem | Registry URL | Example Manager Action |
|---|---|---|
| JavaScript | https://npm.pkg.github.com/ | actions/setup-node@v3 |
| Ruby | https://rubygems.pkg.github.com/ | ruby/setup-ruby@v1 |
| Java (Maven) | https://maven.pkg.github.com/OWNER/REPO | actions/setup-java@v3 |
| Java (Gradle) | same as Maven | gradle config in build.gradle |
| Docker | ghcr.io | docker/login-action@v2 |
| .NET (NuGet) | https://nuget.pkg.github.com/OWNER/index.json | actions/setup-dotnet@v2 |
Why Use GitHub Packages?
- Centralized management
Keep code, CI/CD workflows, and packages in one place for consistent versioning. - Secure distribution
Leverage private packages or granular access controls tied to your GitHub org. - Streamlined workflows
Publish & consume packages in the same Actions workflow—no external credentials needed.
Integration with GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions automates build, test, and publish steps to your GitHub Packages registry. Each package manager exposes a unique endpoint: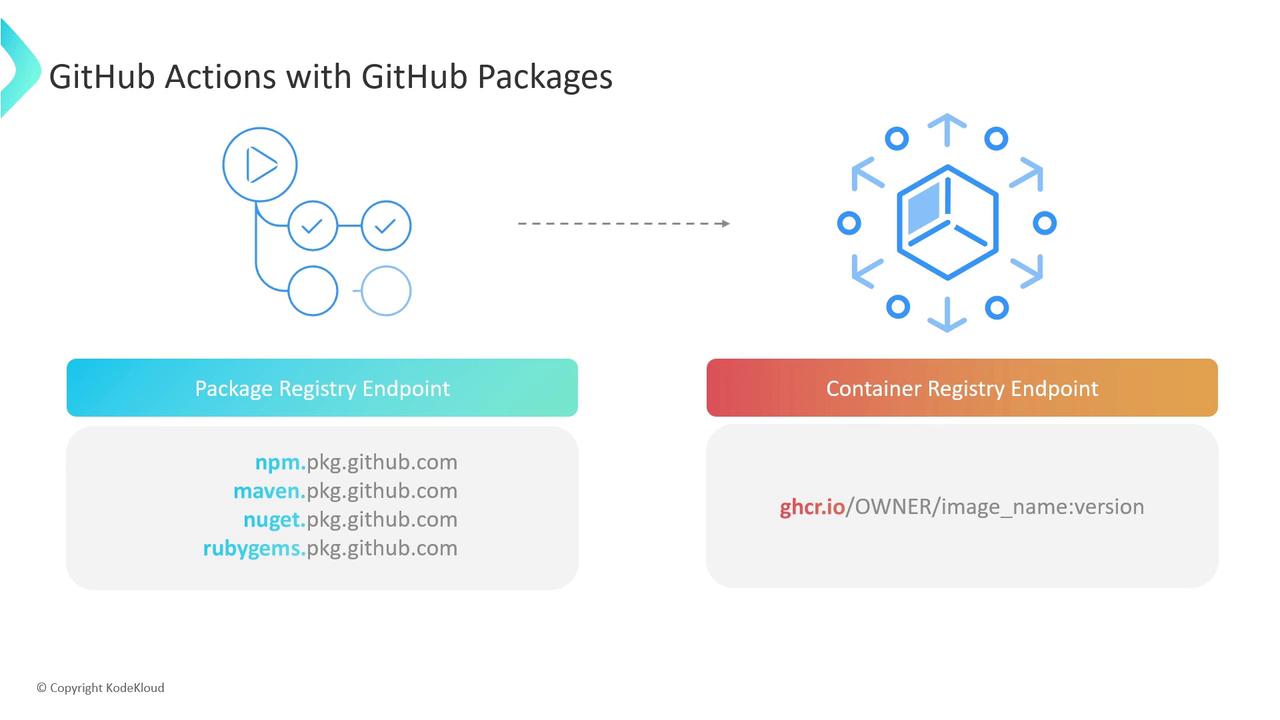
Example Workflows
Publish an npm Package
Build and Push a Docker Image
Deploy a Maven Artifact
Push a .NET NuGet Package
Authentication
All of these workflows rely on the built-inGITHUB_TOKEN. This secret is automatically created for each workflow run and scoped to the repository:
- Grants read/write access to GitHub Packages.
- Requires no extra setup or manual credential management.
- Automatically expires when the workflow completes.
If you need to publish packages across multiple repositories or organizations, consider using a Personal Access Token (PAT) with the appropriate scopes.