- Project-specific logic not covered by existing Actions
- Integration with internal or legacy services
- Complex orchestration with conditional steps or custom dependencies
- Strict compliance or security policies requiring in-house solutions
Leverage community Actions whenever possible to reduce maintenance overhead. Create a custom Action only when you need functionality that isn’t already available.
- Publishing an npm package when a new Git tag is created
- Sending SMS or Slack alerts upon critical issue creation
- Deploying custom security policies or infrastructure templates
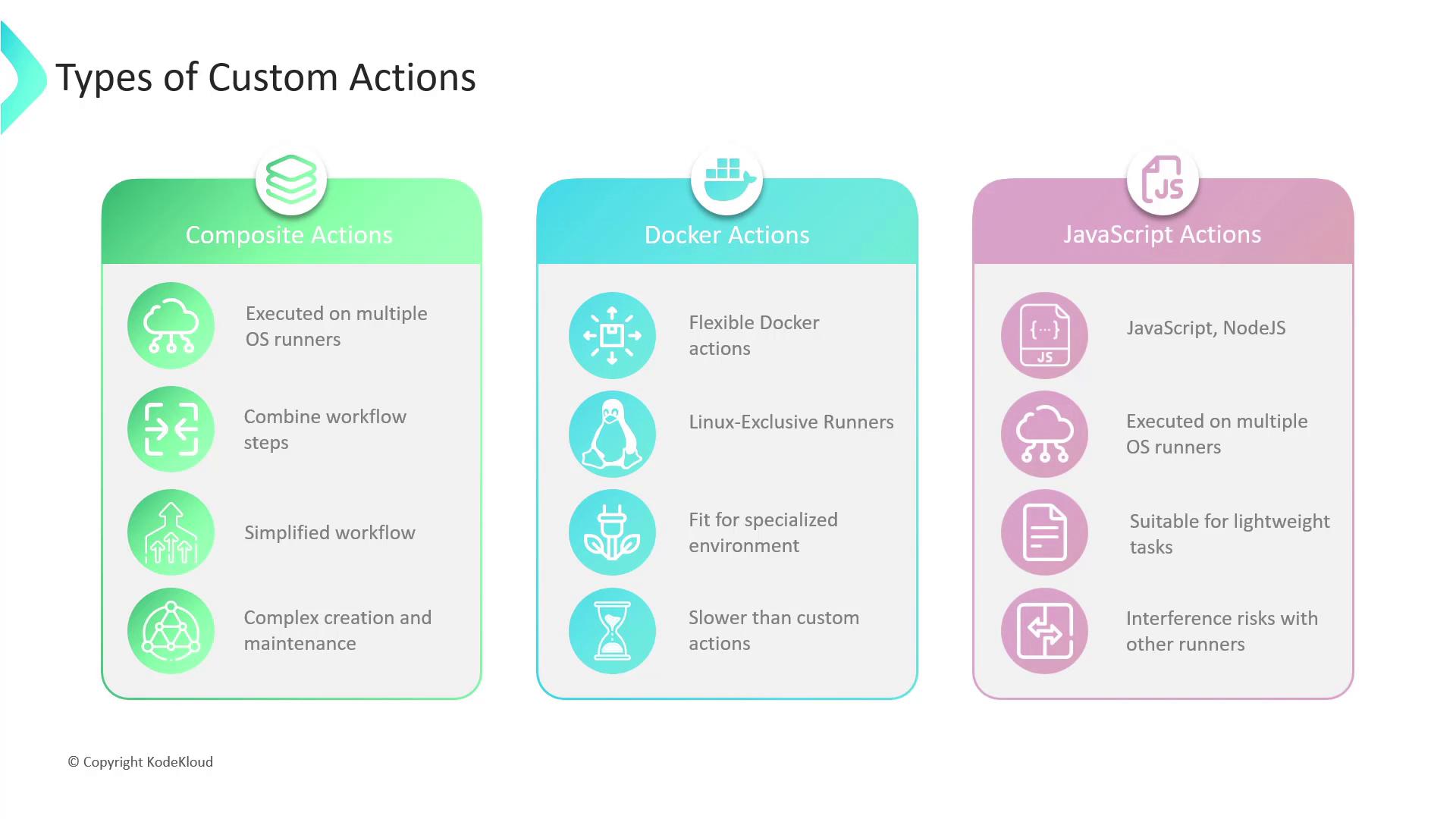
| Action Type | Runner Support | Isolation | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composite Actions | Linux, macOS, Windows | Low (host) | Bundling repeated workflow steps |
| Docker Container | Linux only | High (container) | Complex environment or OS dependencies |
| JavaScript Actions | Linux, macOS, Windows | Medium | Fast, lightweight scripting tasks |
Composite Actions
Composite Actions let you encapsulate multiple workflow steps into a single reusable unit.- Pros: Simplifies workflows, DRY principle, cross-platform
- Cons: Can become hard to maintain if too many steps are bundled
Docker Container Actions
Container Actions run inside a Docker environment defined by you.- Pros: Full OS control, consistent environment, ideal for complex dependencies
- Cons: Linux only, requires Docker knowledge, startup overhead
Docker container Actions run exclusively on Linux runners. Make sure your workflow requirements align with Linux-only execution.
JavaScript Actions
JavaScript Actions execute directly on the runner via Node.js.- Pros: Fast startup, cross-platform, simple scripting
- Cons: Less isolated—be mindful of side effects on the host runner
| Criteria | Composite | Docker Container | JavaScript |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast | Moderate | Fastest |
| Isolation | Low | High | Medium |
| Cross-platform support | Yes | No | Yes |
| Maintenance overhead | Moderate | High | Low |