needs keyword. By the end of this guide, you’ll configure:
- A build job that installs dependencies and generates an output file.
- A test job that runs only after the build job completes.
- A deploy job that runs after successful testing.
1. Default Workflow: Parallel Job Execution
By default, GitHub Actions runs all jobs in parallel if no dependencies are declared. Here’s an example workflow that attempts to build, test, and deploy simultaneously:dragon.txt isn’t created yet.
2. Chain test_job_2 to build_job_1
Use needs: build_job_1 so that test_job_2 waits for build_job_1 to finish successfully:
The
needs keyword accepts a single job name or an array. You can hover over needs in VS Code with the GitHub Actions plugin to see usage details.3. Chain deploy_job_3 to test_job_2
Add needs: test_job_2 to ensure deploy_job_3 runs only after testing passes:
Job Dependency Summary
| Job Name | Depends On | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| build_job_1 | – | Install cowsay and create dragon.txt |
| test_job_2 | build_job_1 | Verify that dragon.txt contains “dragon” |
| deploy_job_3 | test_job_2 | Output contents of dragon.txt |
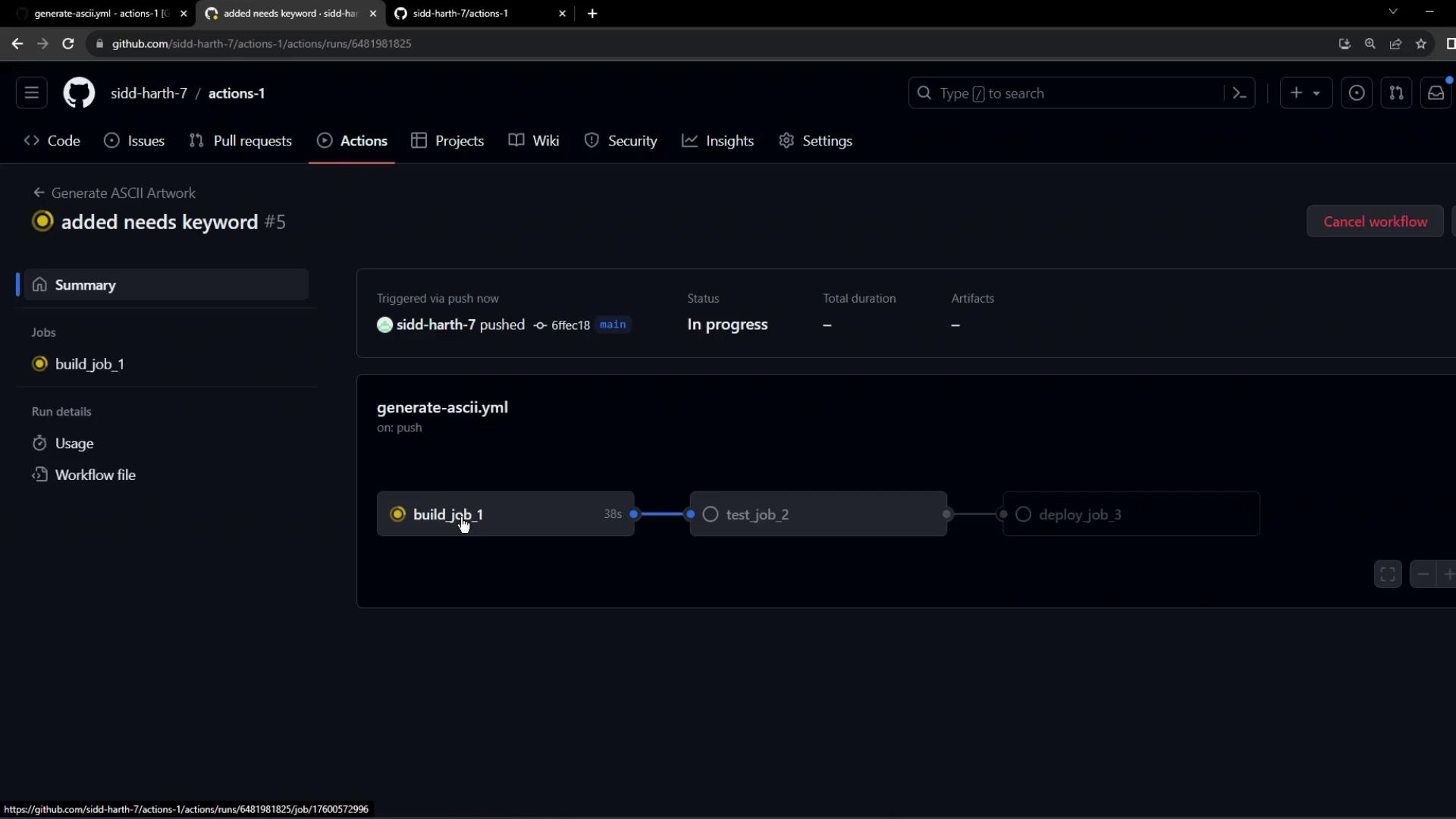
4. Visualize the Dependency Graph
After pushing these changes, GitHub Actions will queuebuild_job_1 first, followed by test_job_2, then deploy_job_3.
5. Troubleshooting: Fresh VM and Missing Files
Each job runs on a clean virtual machine. If you don’t persist files between jobs, later steps will fail: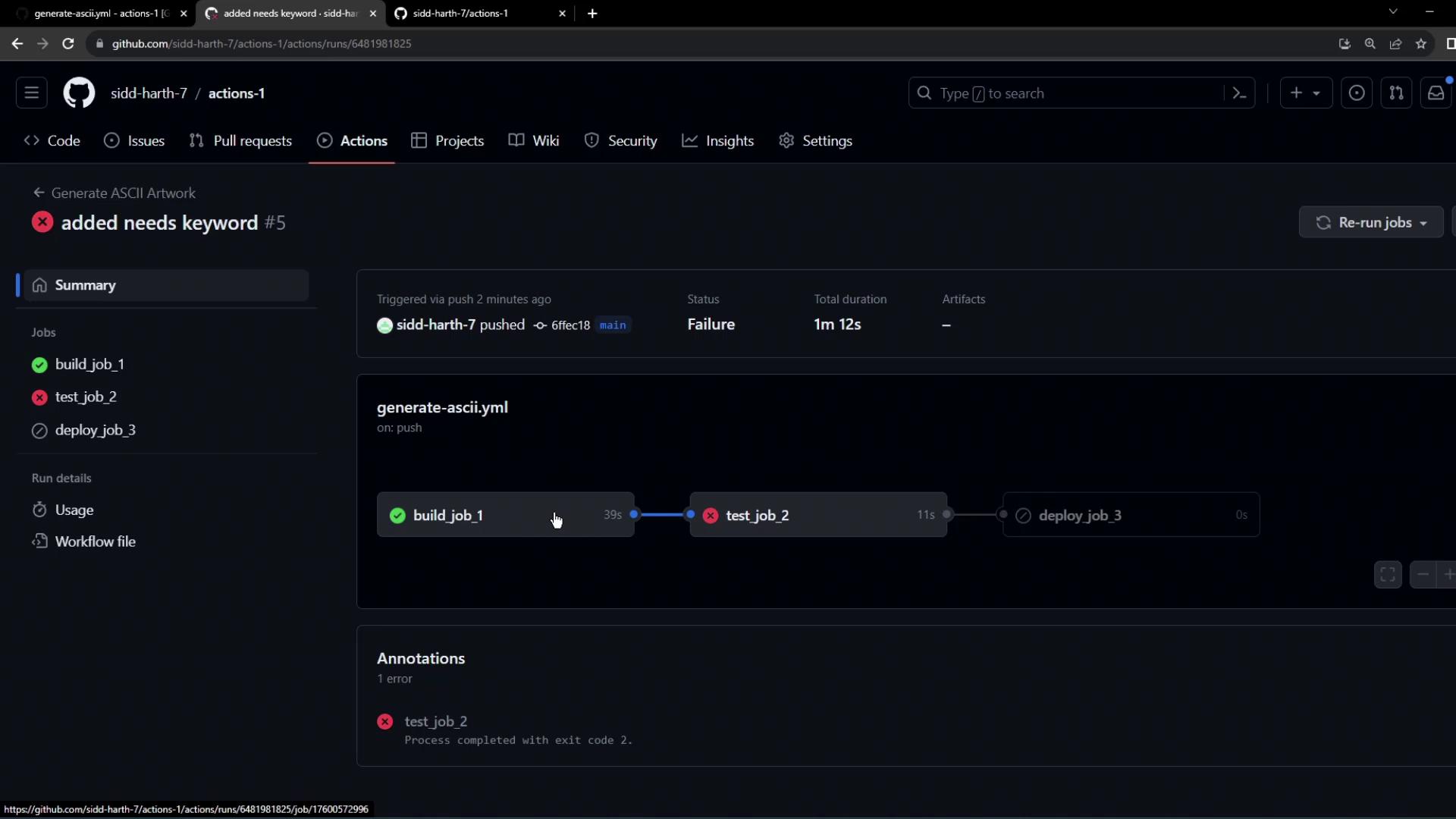
Jobs do not share the filesystem by default. Use artifacts or workspaces to pass files between jobs.