In this guide, you’ll learn how to integrate GitHub’s CodeQL code scanning into your CI processes. CodeQL analyzes your source code to uncover security vulnerabilities by running community- and GitHub Security Lab–maintained queries. Results appear on pull requests and in the repository’s Security tab.
What Is CodeQL Code Scanning? Code scanning is a built-in GitHub feature that uses the CodeQL semantic analysis engine. It runs queries against your codebase, surfaces potential security issues, and helps you track and resolve them before they reach production.
Two Ways to Enable CodeQL Method Description Repository Settings Turn on CodeQL under Settings → Security . GitHub Actions Workflow (recommended) Add a .github/workflows/codeql.yml workflow file.
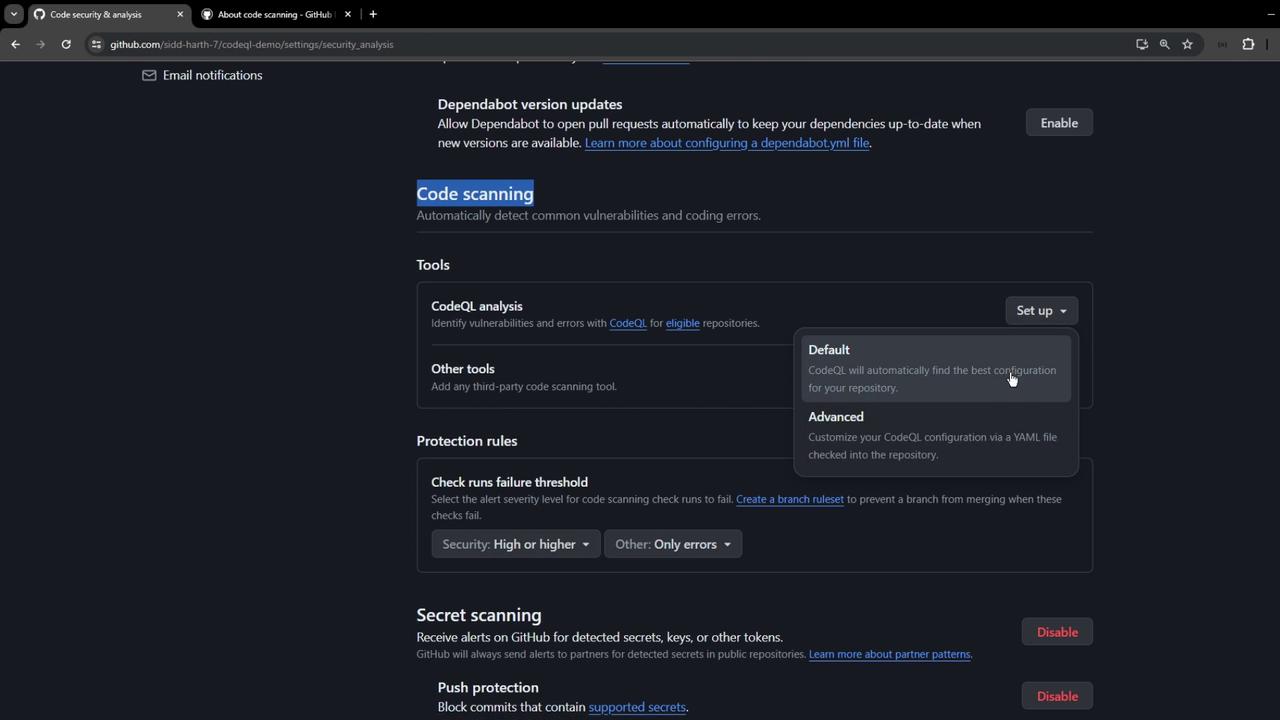
1. Enable via Repository Settings
Navigate to Settings → Security → Code security and analysis .
Scroll to CodeQL analysis and toggle it on.
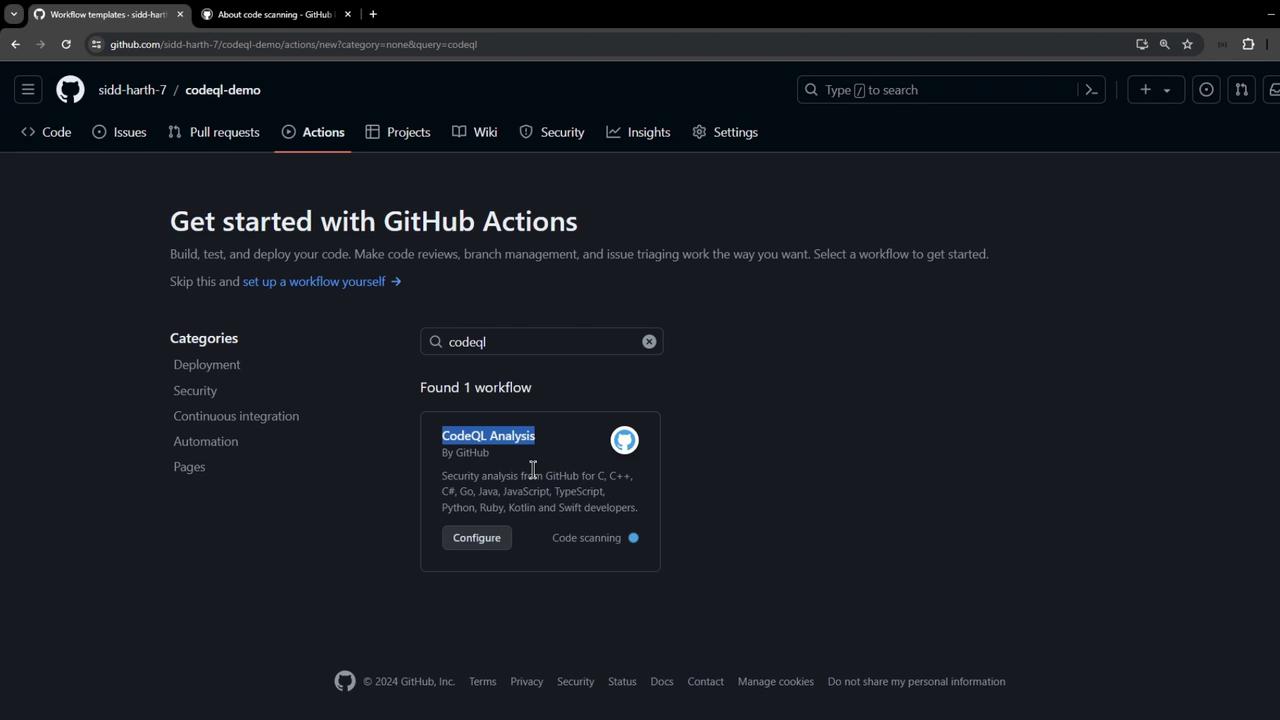
Open the Actions tab.
Search for CodeQL Analysis and select the starter workflow.
This creates .github/workflows/codeql.yml. Below is a minimal example you can customize:
name : "CodeQL" on : push : branches : [ "main" ] pull_request : branches : [ "main" ] schedule : - cron : '30 13 * * 4' # Runs weekly on Thursday jobs : analyze : name : Analyze (${{ matrix.language }}) runs-on : ${{ matrix.language == 'swift' && 'macos-latest' || 'ubuntu-latest' }} timeout-minutes : ${{ matrix.language == 'swift' && 120 || 360 }} permissions : security-events : write actions : read contents : read strategy : fail-fast : false matrix : include : - language : javascript-typescript build-mode : none # Other options: c-cpp, csharp, go, java-kotlin, python, ruby, swift steps : - name : Checkout repository uses : actions/checkout@v4 - name : Initialize CodeQL uses : github/codeql-action/init@v3 with : languages : ${{ matrix.language }} build-mode : ${{ matrix.build-mode }} # queries: security-extended, security-and-quality - name : Build (manual mode) if : matrix.build-mode == 'manual' run : | echo "Replace this with your project's build steps, e.g.:" echo "make build" exit 1 - name : Perform CodeQL Analysis uses : github/codeql-action/analyze@v3 with : category : '/language:${{ matrix.language }}'
Adjust the build-mode and add any custom run commands needed to compile your project before analysis.
Commit this file to trigger your first CodeQL run. Monitor progress in Actions .
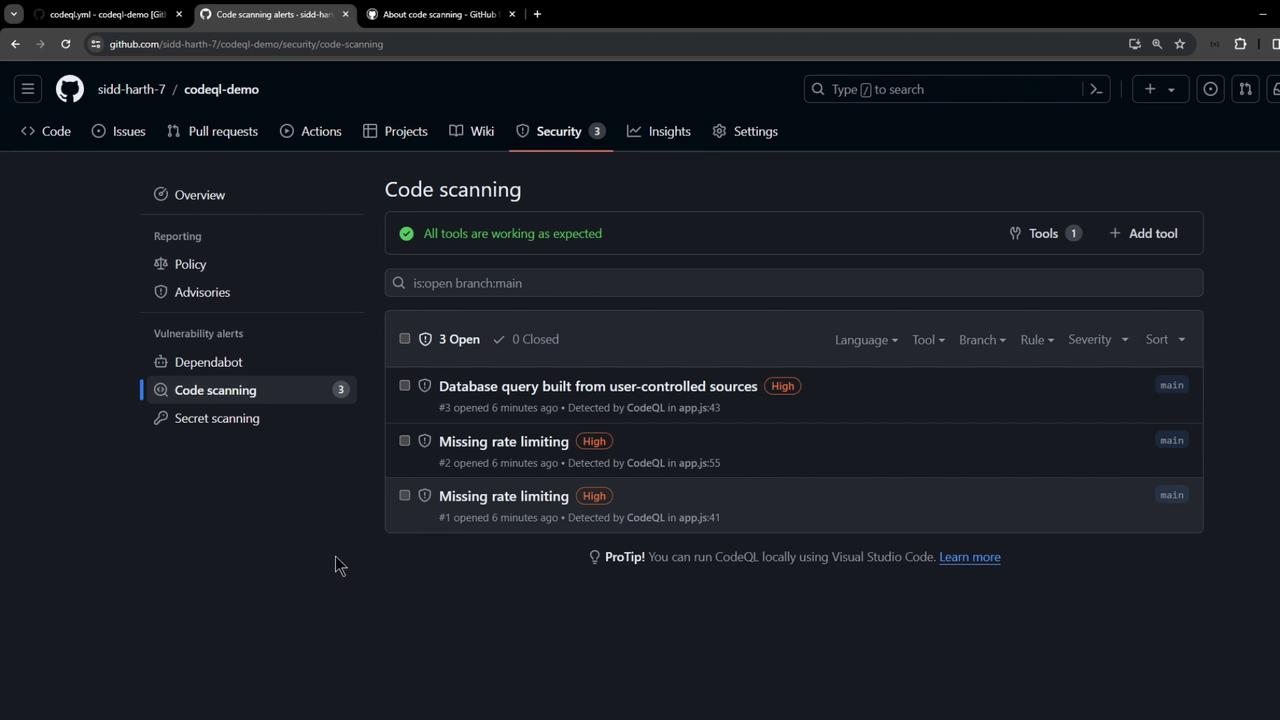
Reviewing CodeQL Results When the workflow completes, findings are uploaded to GitHub. Go to Security → Code scanning to see alerts:
Click an alert to view:
Rule ID
Severity level
CWE identifier
Vulnerable code snippet
Example: Unsafe Database Query app . post ( '/planet' , ( req , res ) => { planetModel . findOne ( { id: req . body . id }, ( err , planetData ) => { if ( err ) { res . status ( 400 ). send ( "Error in Planet Data" ); } } ); });
Directly using req.body.id in a query can lead to injection attacks. CodeQL recommends parameterized queries or sanitization, for instance:
// GOOD: Parameterized query to avoid injection app . get ( '/users/:id' , ( req , res ) => { const id = req . params . id ; pool . query ( 'SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = $1' , [ id ], ( err , results ) => { if ( err ) throw err ; res . json ( results . rows ); } ); });
Best Practices
Run CodeQL on every pull request to catch issues early.
Customize queries via the queries input.
Dismiss false positives or open issues for confirmed vulnerabilities.
Regularly update the CodeQL Action versions (init@v3, analyze@v3).
Links and References By embedding CodeQL into your CI workflow, you automate continuous security analysis with minimal setup—helping you catch and fix vulnerabilities before they hit production.