- How FluxCD implements GitOps for continuous delivery
- The role of Flux controllers and CLI commands
- Observability and notification integration
How FluxCD Operates in Kubernetes
FluxCD runs as an agent inside your Kubernetes cluster. Users typically interact via the Flux CLI to:- Create Sources
Configure Git repositories, Helm charts, or OCI registries as reconciliation sources. - Define Kustomizations
Apply and manage Kubernetes manifests using Kustomize. - Automate Image Updates
Monitor container registries to automatically bump image tags in Git.
FluxCD follows the GitOps pattern:
- The desired state lives in a Git repository.
- The live state resides in the Kubernetes cluster.
- FluxCD continually syncs them for drift correction.
Core Flux Controllers
FluxCD comprises several controllers that reconcile resources in Kubernetes. Here’s a quick overview:| Controller | Responsibility | Example CLI Command |
|---|---|---|
| Source Controller | Tracks Git repos, Helm repositories, OCI images | flux create source git podinfo --url=https://github.com/stefanprodan/podinfo |
| Kustomize Controller | Applies Kustomize overlays | flux create kustomization podinfo --source=GitRepository/podinfo --path="./deploy" |
| Helm Controller | Installs and upgrades Helm charts | flux create helmrelease nginx --chart=nginx --target-namespace=default |
| Notification Controller | Sends events and alerts via Slack, email, GitHub | Configure via Notification and Alert custom resources |
| Image Automation Controller | Automates container image updates in Git | flux create image policy podinfo --image-ref=ghcr.io/stefanprodan/podinfo |
The GitOps Workflow
FluxCD continuously monitors your Git repositories and the cluster’s live state. When a commit or pull-request merge occurs:- Webhook Trigger (optional)
You can configure Git webhooks to notify FluxCD of new commits immediately. - Reconciliation Loop
Each controller fetches the latest manifests, compares them to the live cluster state, and applies any differences. - Status Reporting
Flux updates resource status back to Git (e.g., annotating commits), and emits events for observability.
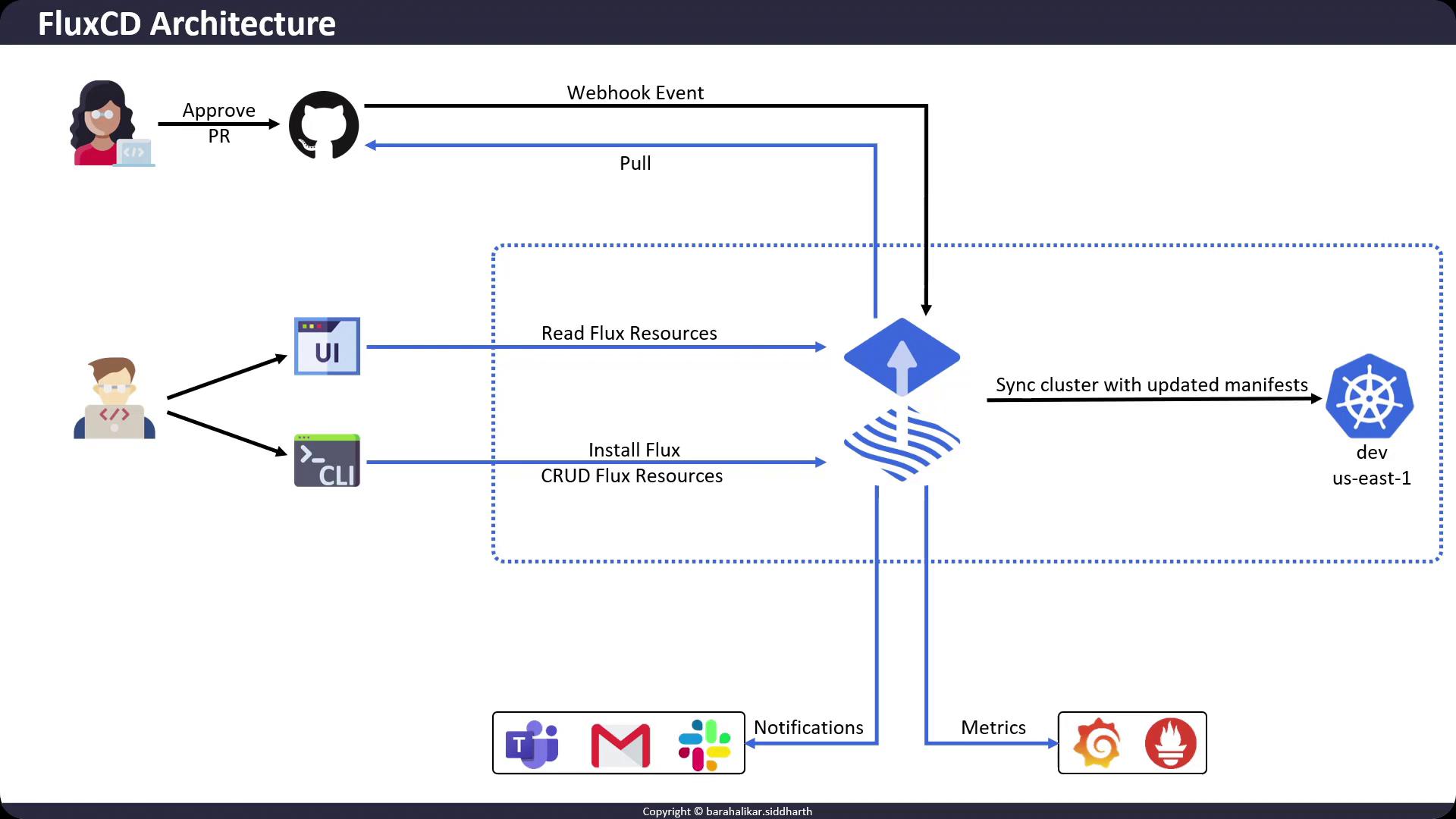
Observability & Notifications
FluxCD offers built-in metrics and alerts to help you monitor delivery pipelines:- Prometheus Metrics
Expose metrics from each controller; scrape with Prometheus for real-time insights. - Grafana Dashboards
Visualize Flux health and reconcile durations. - Notifications Controller
Send alerts on sync failures or promotion events to Slack, email, or GitHub.
Ensure your cluster’s RBAC policies allow Flux to read Secrets and apply CRDs. Misconfigured permissions can prevent controllers from reconciling.