This guide assumes you’re familiar with GitOps, Docker, Kubernetes, and CI/CD workflows.
Key Concepts Overview
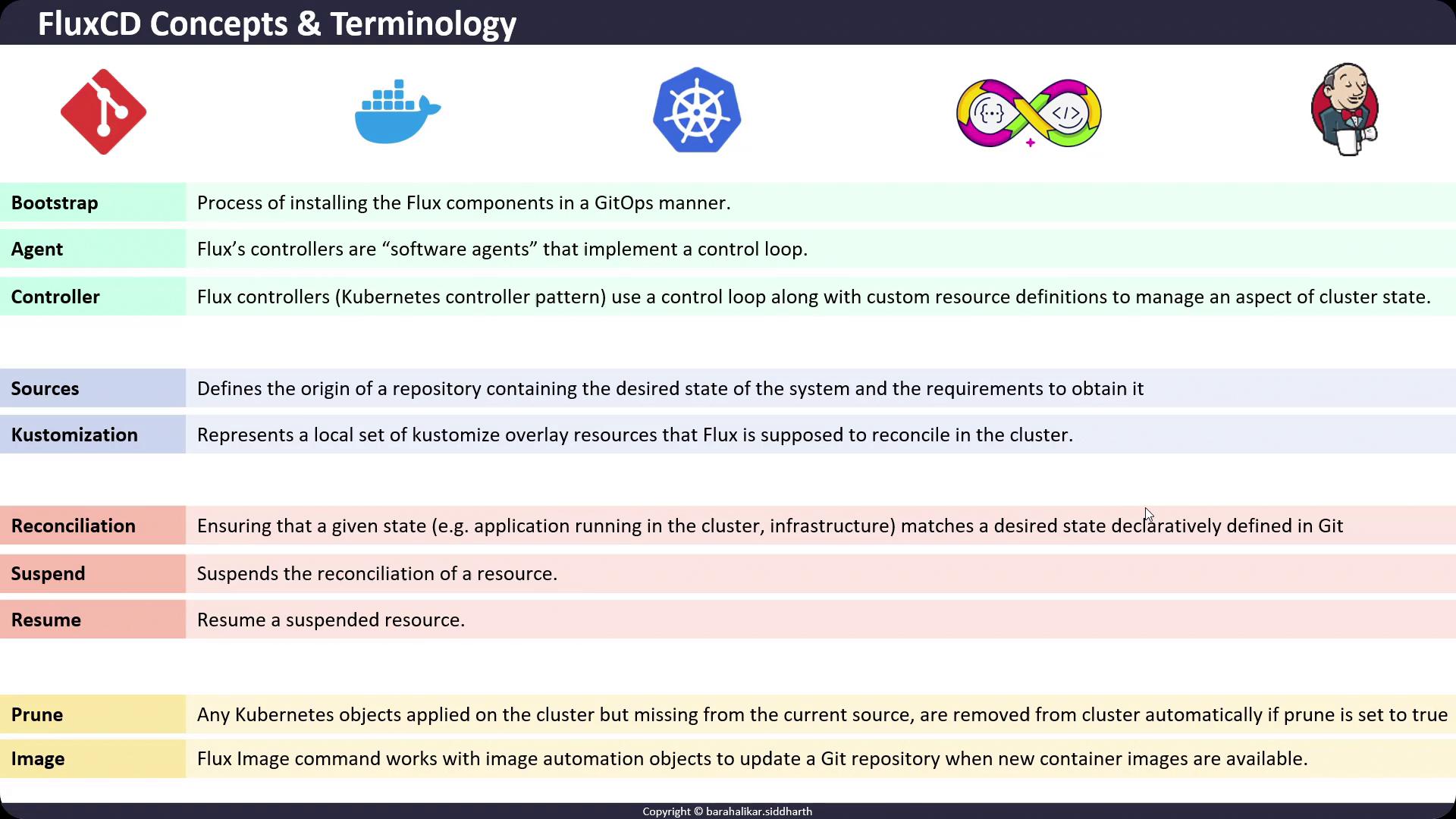
Below is a quick reference of FluxCD’s core components and GitOps terminology.| Concept | Controller / Command | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Bootstrapping | flux bootstrap | Installs Flux controllers and Git repository sources. |
| Agent / Controller | Reconciliation loops | Watches CRDs and aligns cluster state with Git definitions. |
| Source | GitRepository, HelmRepository, OCIRepository | Fetches and tracks external repositories. |
| Kustomization | Kustomization | Applies and reconciles overlays or plain manifests. |
| Reconciliation | Continuous process | Ensures actual cluster state matches Git’s desired state. |
| Suspend & Resume | flux suspend / flux resume | Pauses or restarts automatic reconciliation. |
| Prune | Automatic cleanup | Removes resources no longer defined in the source. |
| Image Automation | flux image | Updates Git when new container images are available. |
1. Bootstrapping
Bootstrapping is the initial step to install Flux components on your Kubernetes cluster.Use the
flux bootstrap command to connect your cluster with a Git repository following GitOps best practices.
2. Agent / Controller
Flux controllers (or agents) implement Kubernetes’ controller pattern:- They run reconciliation loops.
- Watch for custom resources (CRDs).
- Continuously compare and reconcile the cluster’s actual state against Git-defined desired state.
3. Sources
Sources define where Flux retrieves configuration or package artifacts:- GitRepository: Monitors a Git repo for YAML manifests or Kustomize overlays.
- HelmRepository: Tracks Helm charts.
- OCIRepository: Fetches Helm charts or container images from an OCI registry.
4. Kustomization
The Kustomization controller applies a set of overlays or plain manifests:- Applies resources to the cluster.
- Continuously reconciles updates.
- Supports features like patches, generators, and strategic merges.
5. Reconciliation
Reconciliation is Flux’s core mechanism:- Compares the actual state of your cluster with the desired state defined in Git.
- By default, reconciliation runs automatically at each interval.
- You can temporarily suspend or resume this process.
Suspending reconciliation in production may delay critical updates. Always verify before pausing.
6. Suspend & Resume
Use the Flux CLI to manage reconciliation:flux reconcile is required to apply changes.
7. Prune
Pruning ensures your cluster stays clean:- When enabled, Flux automatically deletes Kubernetes resources that are no longer defined in the Git source.
- Helps prevent resource drift and orphaned objects.
8. Flux Image Automation
Theflux image command manages image automation objects:
- Image Reflector Controller: Monitors container registries for new tags.
- Image Automation Controller: Commits updated image references to your Git repository.