NodePort services.
Why Use Flux 2 for Monitoring?
Using Flux 2 to manage your monitoring stack as GitOps ensures:- Declarative configuration
- Automated drift detection and remediation
- Version control of all resource definitions
1. Prepare the Flux Monitoring Manifests
Flux maintains example manifests for the Kube Prometheus Stack in its repository undermanifests/monitoring/kube-prometheus-stack:
a. HelmRepository
This resource fetches the Helm charts from the Prometheus Community Helm Repository:b. HelmRelease
TheHelmRelease installs version 0.45.x of the kube-prometheus-stack chart into the monitoring namespace. It also configures custom retention and resource requests:
Defining
crds: Create ensures that all CustomResourceDefinitions required by the chart are installed before the HelmRelease.2. Deploy the Flux Resources
In your cluster Git repository (for example,flux-clusters/dev-cluster), create the Flux sources and kustomization:
Make sure the
monitoring namespace does not already exist or is managed by another tool, as Flux will create it.| Resource | Purpose | Flux CLI Example |
|---|---|---|
| GitRepository | Point Flux at a Git repo for manifests | flux create source git ... |
| Kustomization | Apply resources from a source directory | flux create kustomization ... |
| HelmRepository | Download Helm charts from an OCI or HTTP endpoint | Defined in monitoring/kube-prometheus-stack/helmrepo.yaml |
| HelmRelease | Install and manage a Helm chart | Defined in monitoring/kube-prometheus-stack/helmrelease.yaml |
3. Verify Deployment
After Flux syncs, confirm that themonitoring namespace and its resources are created:
4. Expose Prometheus and Grafana
By default, both Prometheus and Grafana services useClusterIP. To access them externally, switch to NodePort:
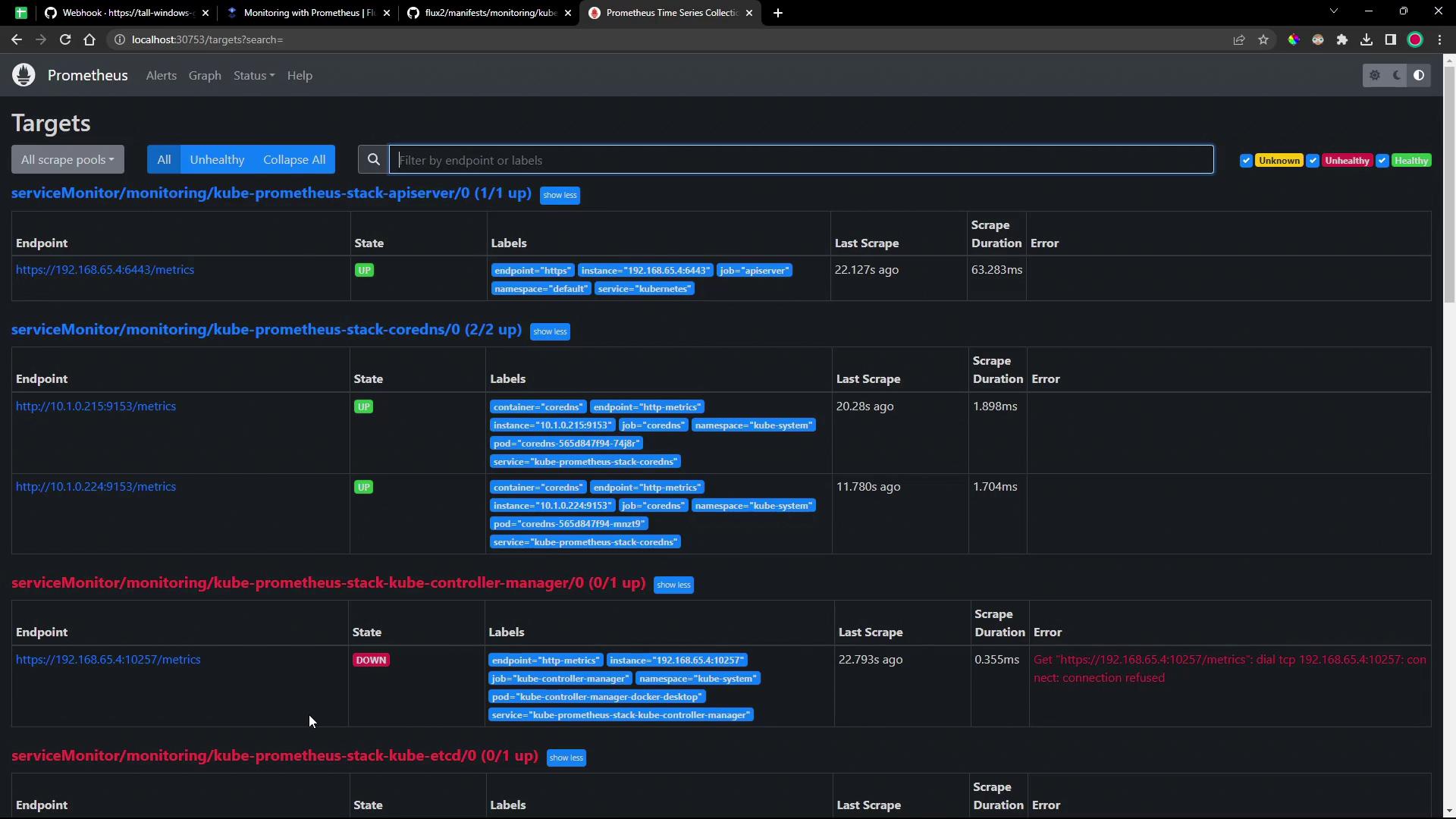
5. Access the Prometheus UI
Open the Prometheus interface in your browser athttp://<node-ip>:30753. The dashboard displays service monitor health:
6. Access the Grafana Dashboard
Visithttp://<node-ip>:31921 and log in with credentials stored in the kube-prometheus-stack-grafana secret:

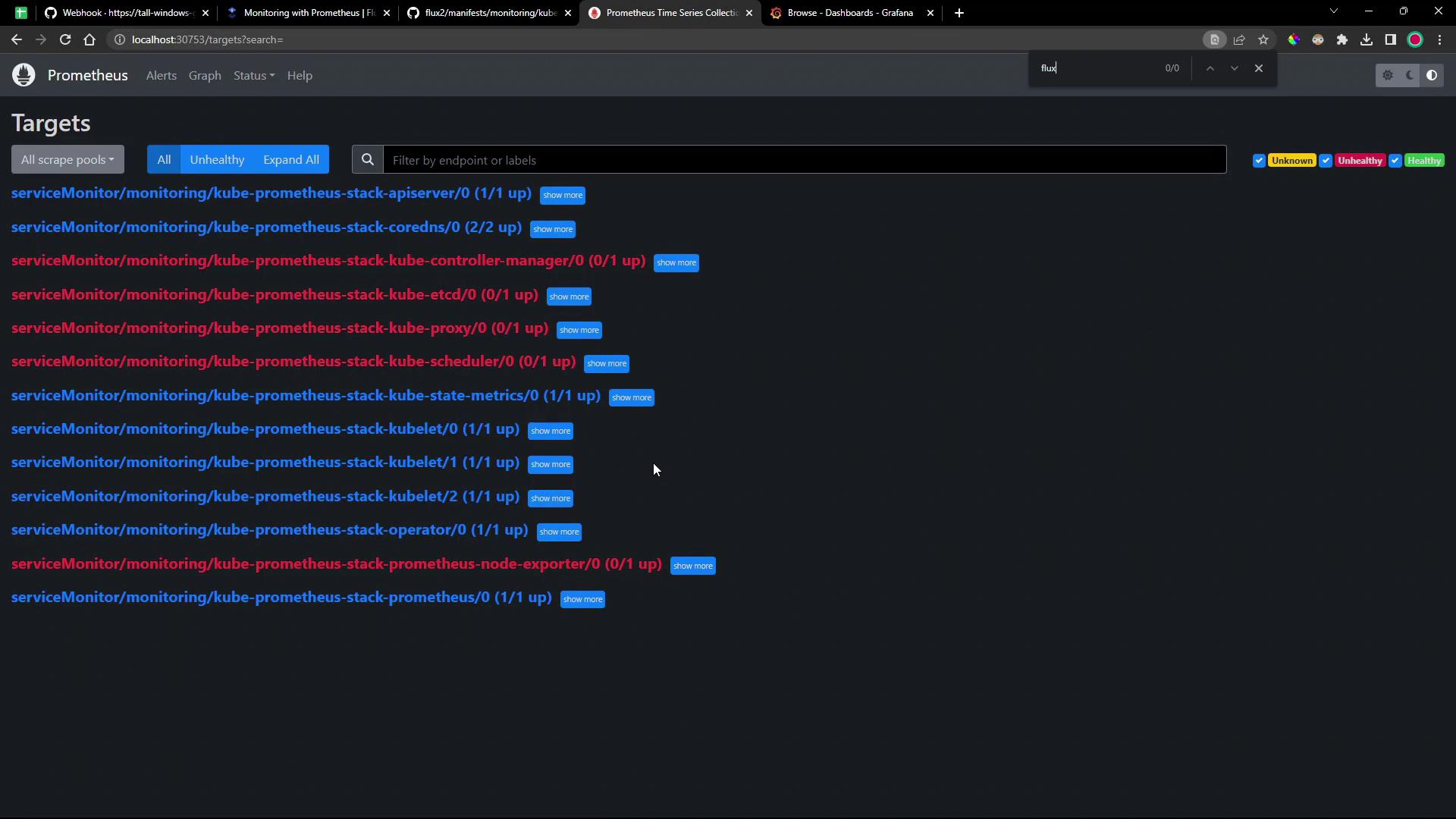
7. Explore Prometheus Targets
Check the Prometheus/targets page to see which endpoints are scraped:
Next Steps
- Configure
ServiceMonitorresources to scrape Flux controllers. - Deploy custom Grafana dashboards for Flux metrics.
- Integrate alerts into your incident management workflow.