HashiCorp Certified: Vault Associate Certification
Learning the Vault Architecture
Vault Data Protection
Vault secures all data at rest by employing a two-tier key architecture. Your secrets are always encrypted in the storage backend, ensuring that even if an attacker gains full access to the backend, they cannot decrypt your data without the appropriate keys.
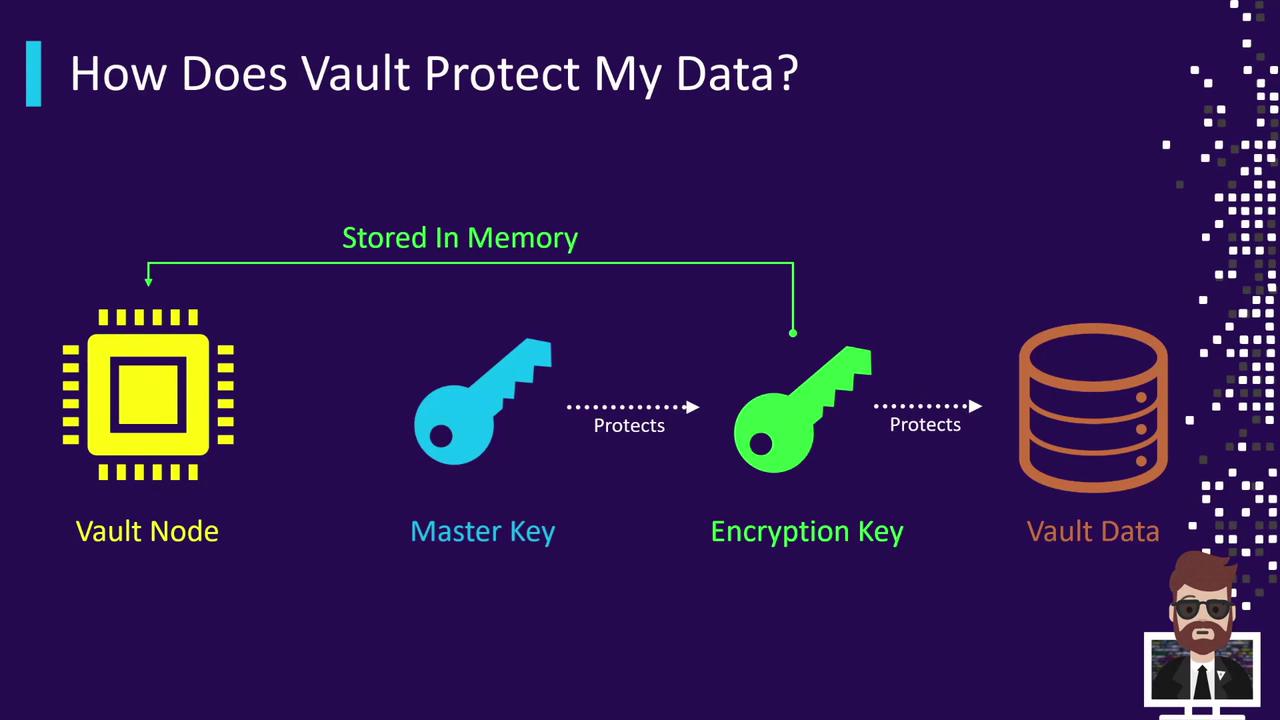
How It Works: Two-Tier Key Flow
- Vault initialization (or a rekey operation) generates the Master Key.
- Vault creates a Data Encryption Key (DEK) used to encrypt/decrypt your actual data.
- The Master Key encrypts the DEK; this encrypted DEK is stored alongside your encrypted data in the backend.
- On unseal, Vault operators supply unseal keys (traditional) or Vault fetches the Master Key from the auto-unseal backend. Vault then decrypts the DEK in memory, allowing seamless data operations.
Warning
If you lose all unseal key shares and have no auto-unseal configured, you will permanently lose access to your data. Always back up unseal keys or configure auto-unseal.
Master Key vs. Data Encryption Key
| Key Type | Role | Storage Location |
|---|---|---|
| Master Key | Encrypts/Decrypts the DEK | - In memory (traditional unseal)<br>- core/master in backend (auto-unseal) |
| Data Encryption Key | Encrypts/Decrypts actual payloads stored in the backend | Encrypted by Master Key, stored in the key ring alongside data |
Master Key Details

- Creation
Generated at Vault initialization or during any rekey operation. - Storage
- Traditional Unseal: Never written to disk; reconstructed in memory from unseal key shares.
- Auto-Unseal: Stored encrypted at
core/masterin the storage backend, protected by your chosen KMS.
- Usage
Encrypts and decrypts the DEK, ensuring only an unsealed Vault node can access data encryption keys.
Data Encryption Key Details
The Data Encryption Key (DEK) is responsible for encrypting payloads in your storage backend.
- Protection
Always encrypted by the Master Key before being written to storage. - Storage
Held in a key ring alongside encrypted data blocks; older keys remain available to decrypt existing data. - Rotation
Vault supports automatic DEK rotation:- New write operations use the latest key in the ring.
- Reads first try the newest key, then fall back to older keys if needed.
Note
Regularly rotate your Data Encryption Key to limit the amount of data encrypted under a single key. See Vault Encryption Key Rotation for details.
Further Reading
Watch Video
Watch video content