HashiCorp Certified: Vault Operations Professional 2022
Build Fault Tolerant Vault Environments
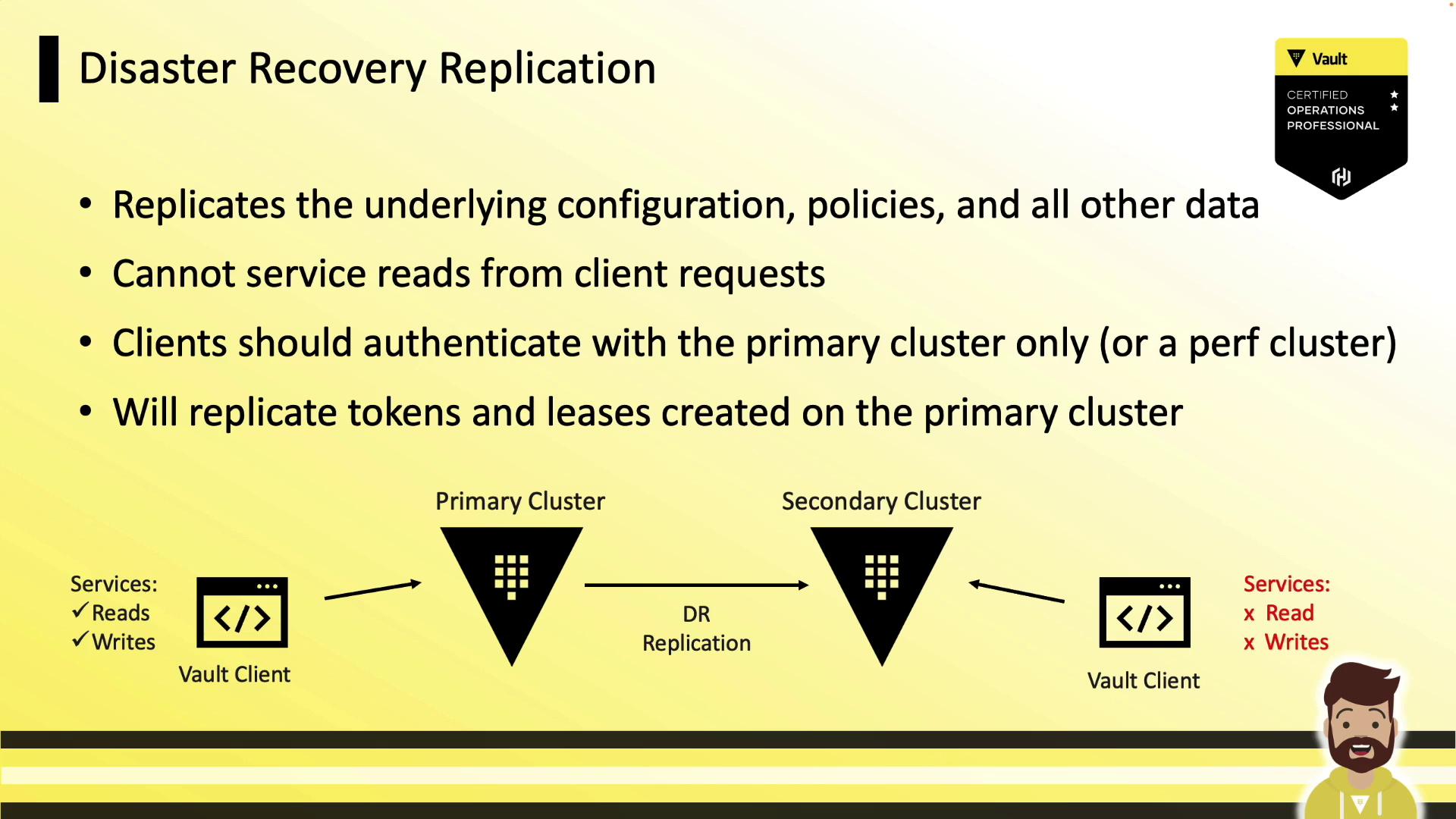
Enable and Configure Disaster Recovery DR Replication
Vault Enterprise’s Disaster Recovery (DR) replication creates a warm-standby cluster that can be promoted instantly if your primary fails. In this guide, you’ll learn how Vault replication works, compare performance and DR modes, review reference architectures, and walk through both CLI and UI setup.
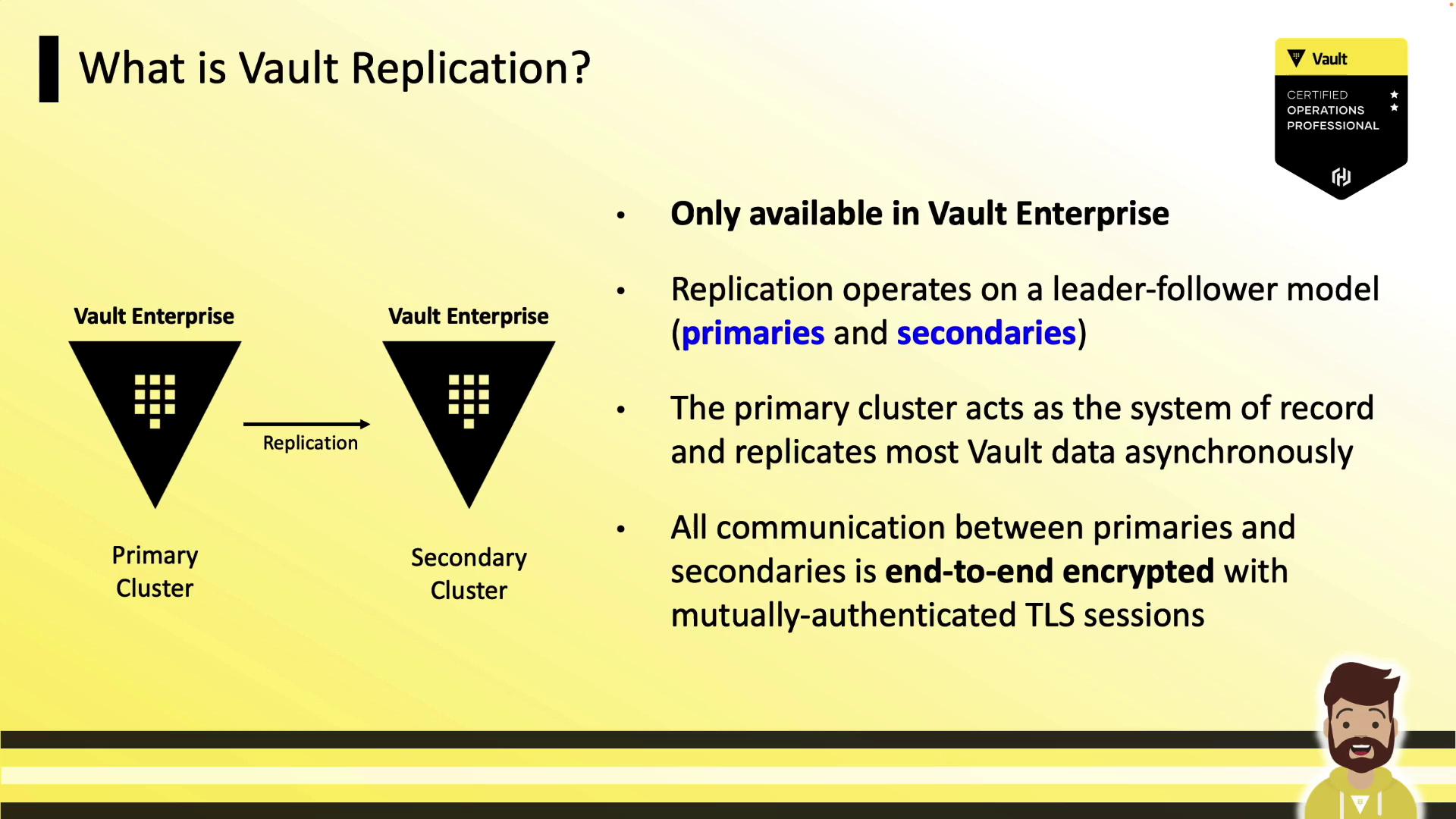
What Is Vault Replication?
Vault replication offers a global, consistent view of your policies, secret engines, auth methods, KV data, and audit configurations—eliminating manual duplication and ensuring high availability across data centers or cloud regions. It uses a leader-follower model with one primary (leader) cluster and one or more secondary (follower) clusters. All inter-cluster communication is end-to-end encrypted with mutual TLS.
Performance vs. Disaster Recovery Replication
Vault Enterprise supports two replication modes. Select the one that matches your use case:
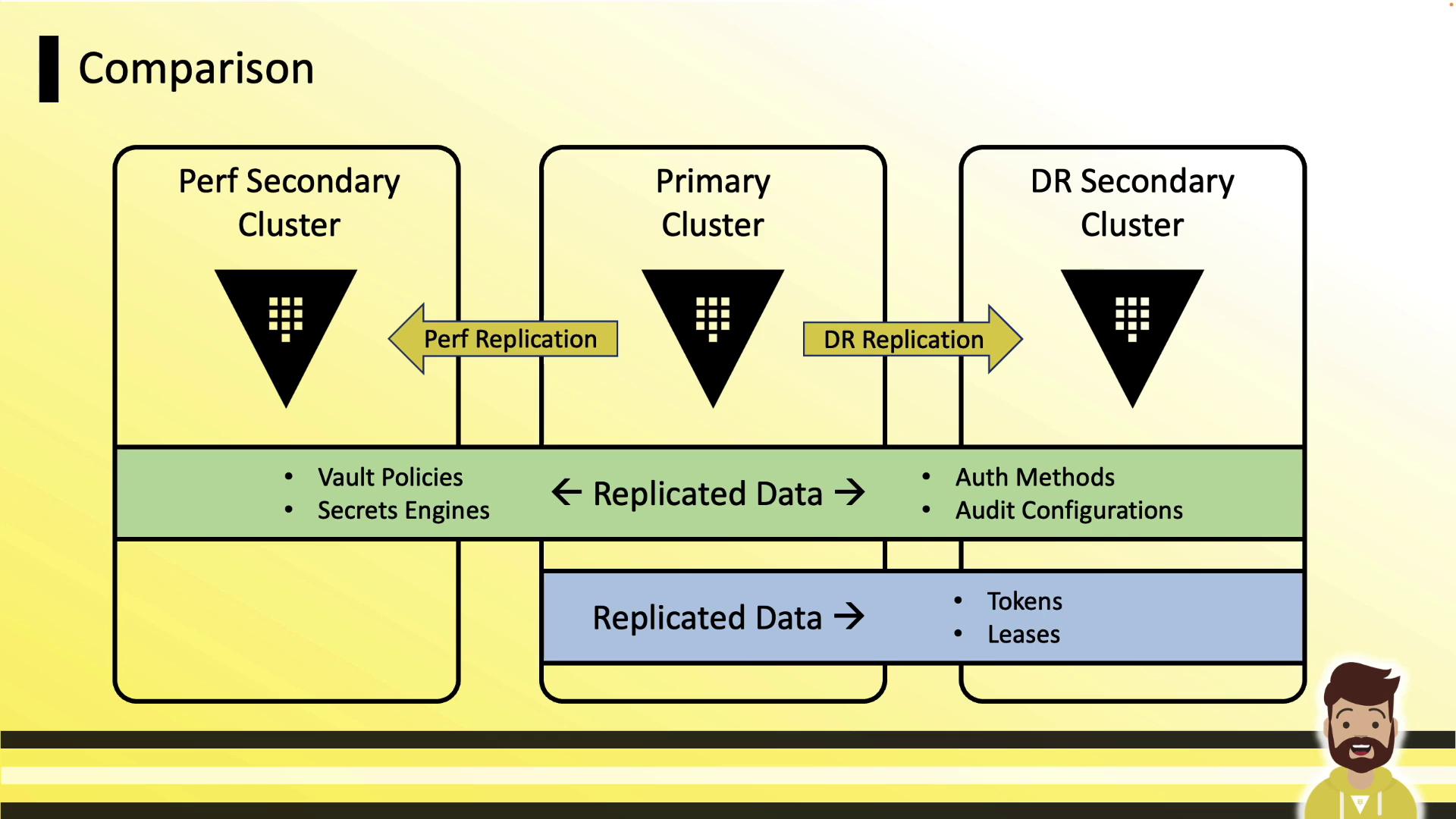
| Feature | Performance Replication | Disaster Recovery (DR) Replication |
|---|---|---|
| Data & Config | Policies, Secrets engines, Auth methods, KV data, Audit logs | Same as Performance + Tokens & Leases |
| Read Traffic | Served locally | Not served (warm standby) |
| Write Traffic | Forwarded to primary | Not served |
| Tokens & Leases | Not replicated | Replicated |
| Typical Use Case | Global read scaling | Fast failover and seamless client ops |
Replication Comparison
Here’s how a performance secondary, primary, and DR secondary differ. Only DR replication includes tokens and leases in the secondary:
DR Secondary Characteristics
A DR secondary acts as a warm standby. It accepts replication logs but:
- Does not serve any client operations (reads or writes).
- Keeps most API paths disabled—even for admin or root tokens—until you promote it.

Reference Architectures
Choose the topology that fits your environment:
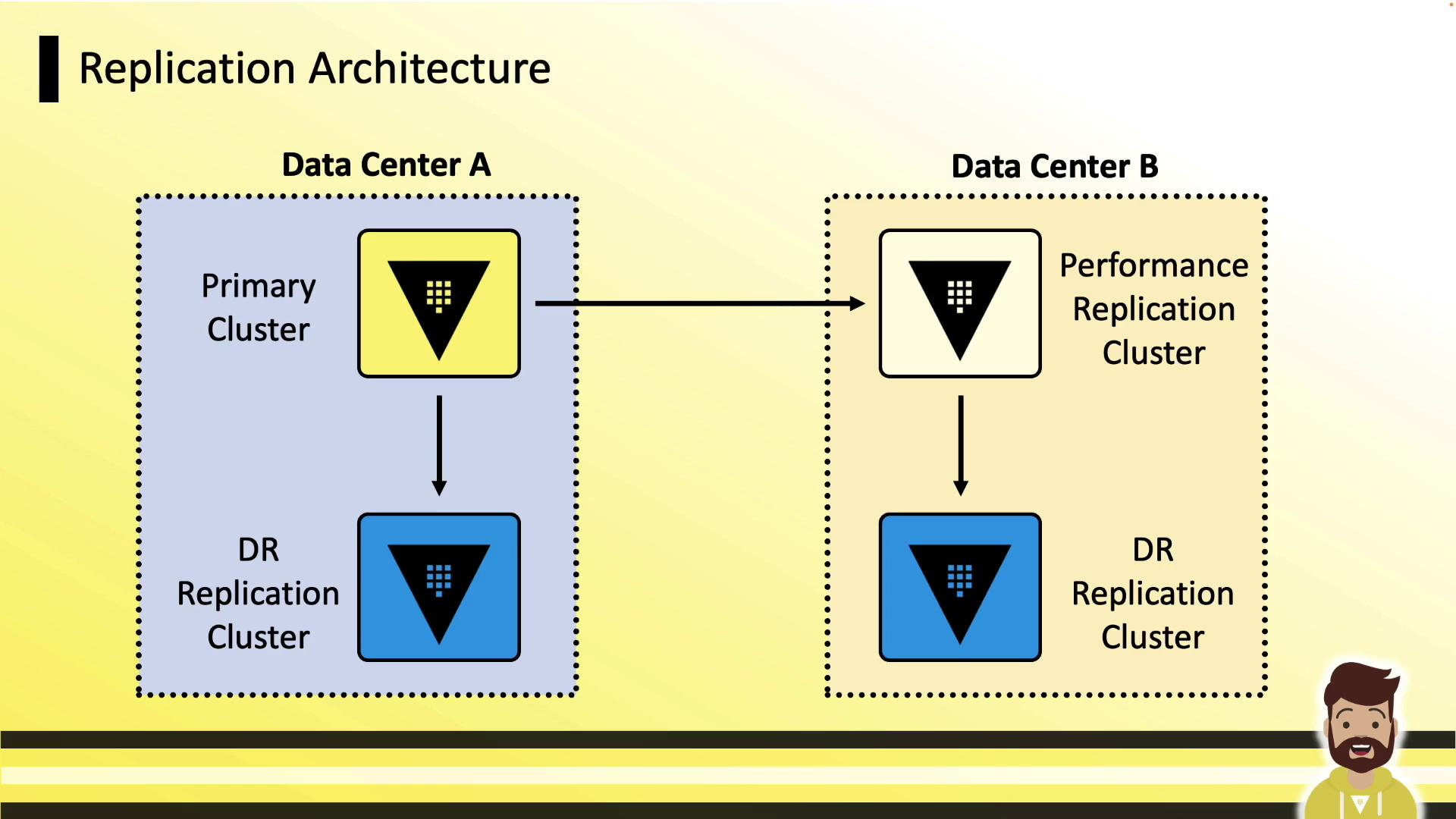
Two Data Centers
- Data Center A: Primary + local DR secondary
- Data Center B: Performance secondary + local DR secondary
- Clients talk to their local cluster; on failure, promote the DR node.
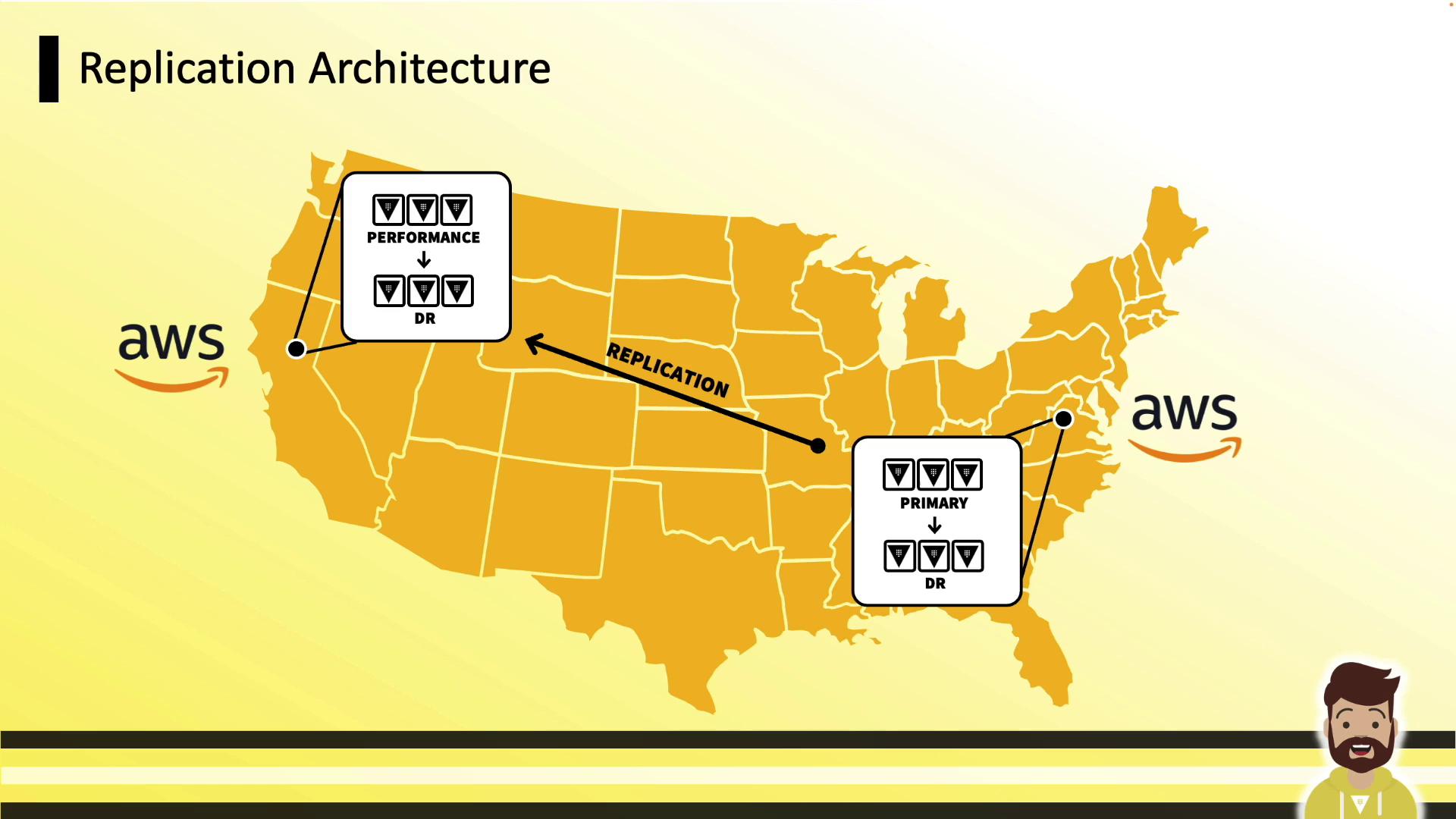
AWS Regions
- Northern Virginia: Primary + DR
- Northern California: Performance + DR
- Ideal for multi-region AWS deployments.
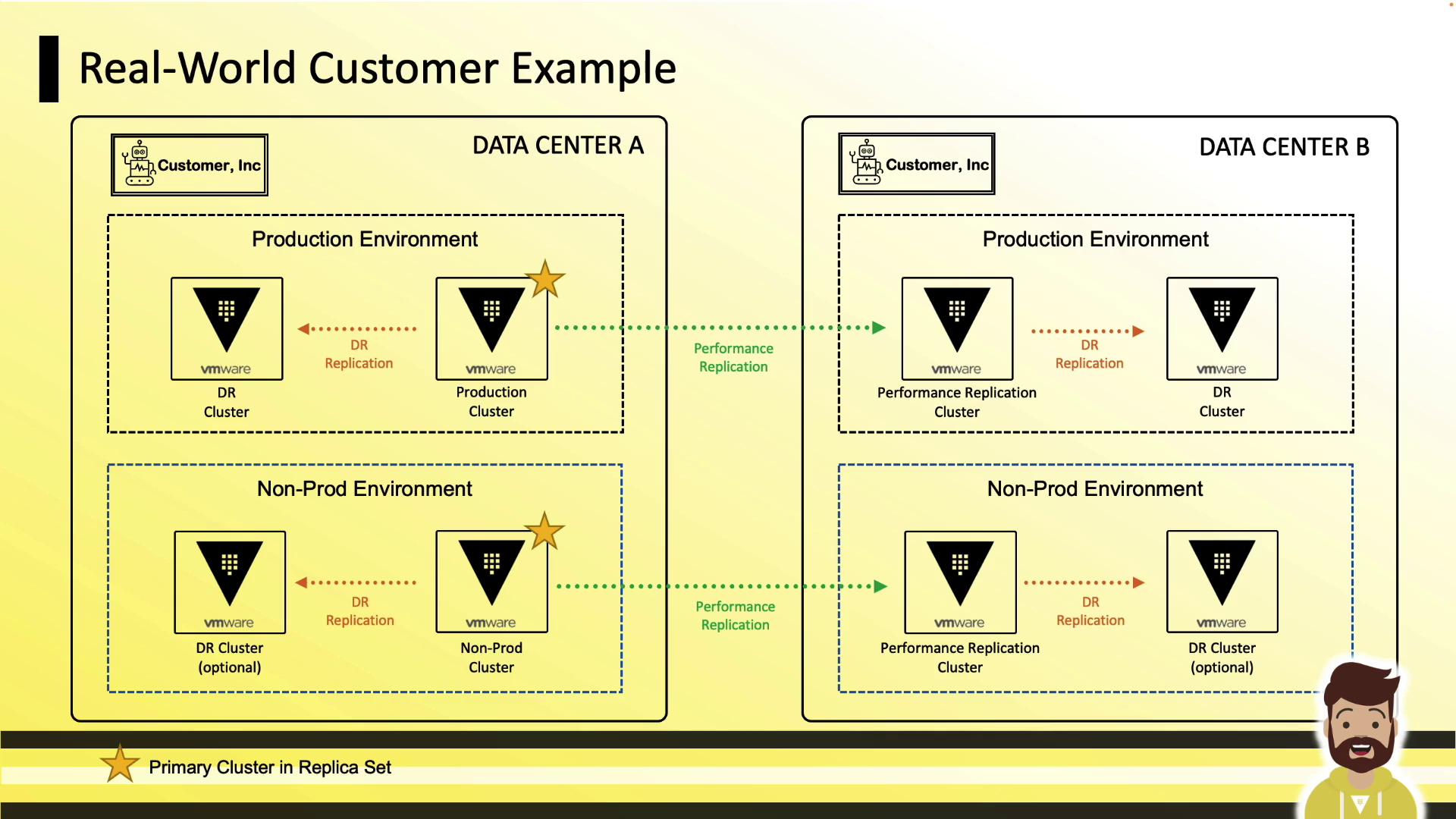
On-Prem VMware Example
- Data Center A: Production primary + DR
- Data Center B: Performance + DR
- Separate non-prod environment mirroring production for QA/testing.
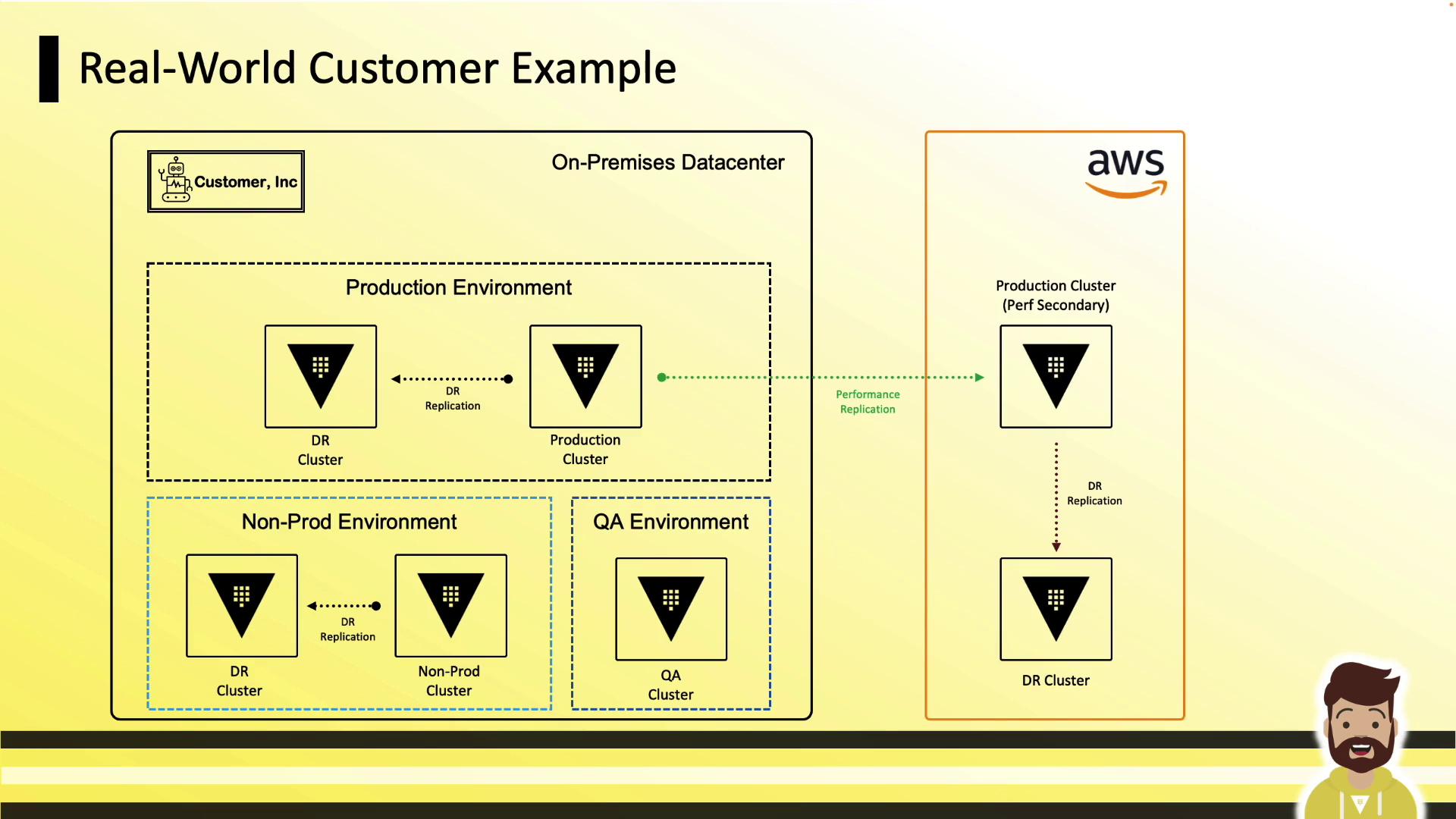
On-Prem to AWS Example
- On-prem DC: Production primary + DR
- AWS: Performance + DR
- Dedicated non-prod and QA clusters.
Networking Requirements
- Bidirectional Vault-to-Vault on ports 8200 (cluster bootstrap/API) and 8201 (replication/Raft forwarding).
- DNS resolution between clusters must be configured.
Warning
Open these ports only between trusted Vault clusters. Exposing replication ports publicly can lead to security risks.
Enabling DR Replication
Follow these three steps to set up DR replication via the CLI:
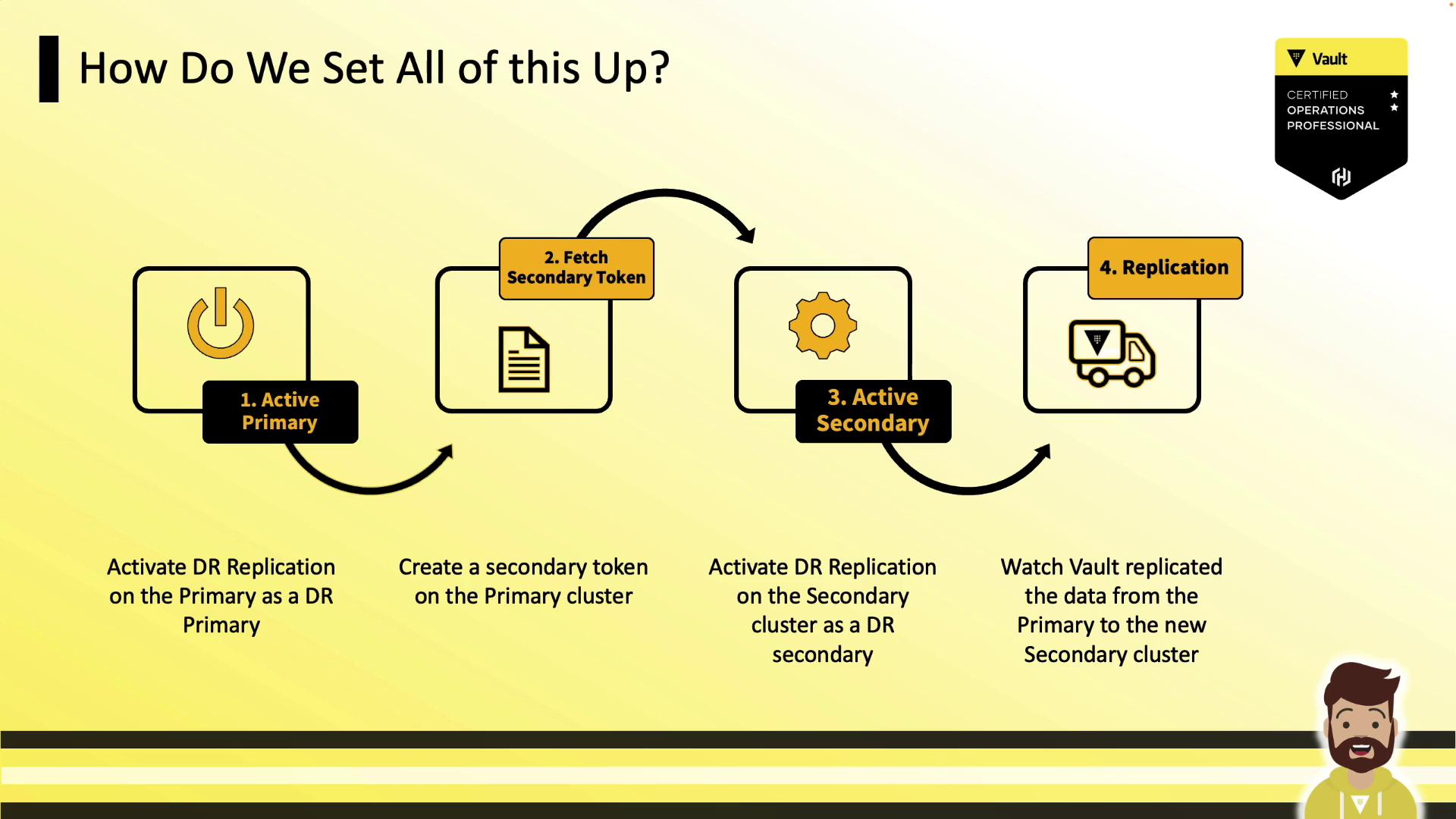
1. Activate DR on the Primary
Vault generates an internal CA and mutual-TLS certificates for secure inter-cluster links. If you’re behind a TLS-terminating load balancer, pass through port 8201.
vault write -f sys/replication/dr/primary/enable
2. Generate the Secondary Token
Create a one-time, response-wrapped token to authorize the DR secondary. It includes the CA cert, client cert/key, and primary’s API address.

vault write sys/replication/dr/primary/secondary-token id="us-east-2-dr"
Inspect the unwrapped token to see embedded details:
{
"data": {
"ca_cert": "...",
"client_cert": "...",
"client_key": { "type": "p521", "x": "...", "y": "...", "d": "..." },
"cluster_id": "0d127970-99ce-152f-0311-3b081d126d43",
"id": "secondary",
"primary_cluster_addr": "https://vault-pr.hvcop.com:8201"
}
}
Warning
Treat the secondary token like a password. It’s single-use and grants high privileges.
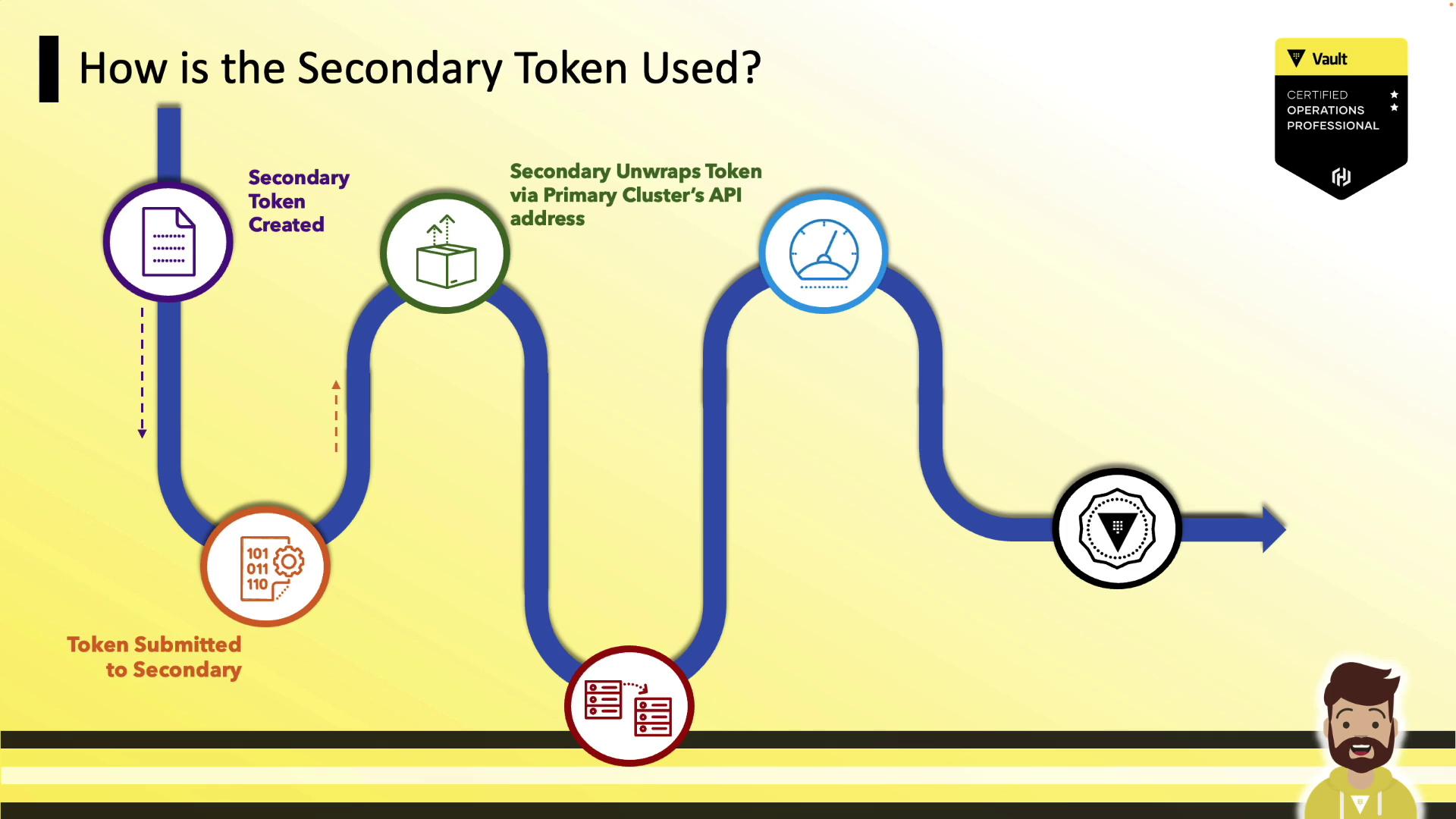
How the Token Is Used
- The secondary submits the wrapped token to the primary API (
:8200). - It unwraps the token and retrieves certs and cluster info.
- Replication over port 8201 then begins automatically.

3. Activate DR on the Secondary
vault write sys/replication/dr/secondary/enable token="<response-wrapped-token>"
Once the secondary connects, replication starts immediately.
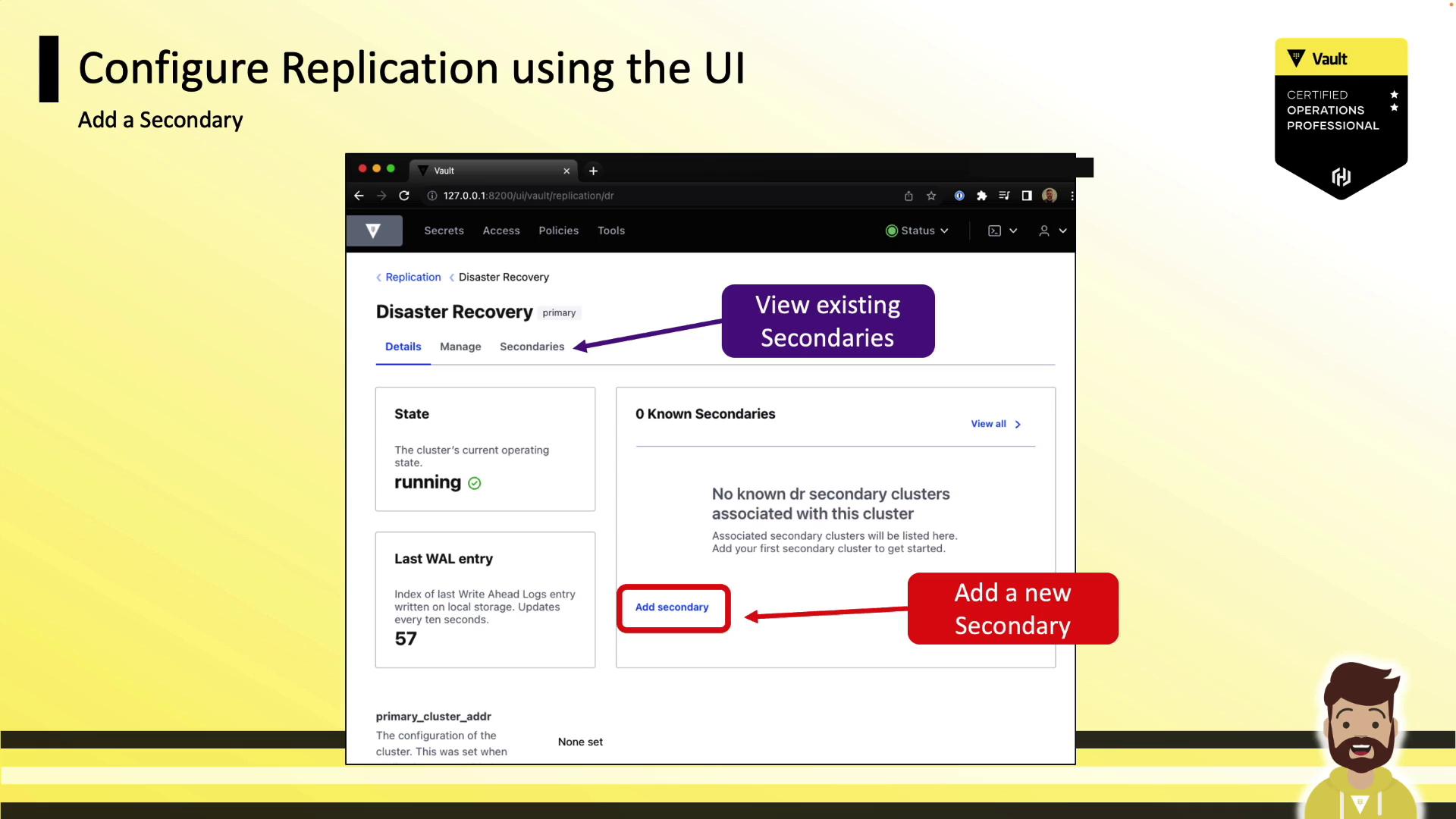
Configuring DR via the UI
You can also enable DR replication through Vault’s web interface:
Primary
- Navigate to Status → Replication → Enable Replication
- Choose Disaster Recovery – Primary, then click Enable
- Click Add Secondary, assign a name, and Generate Token. Copy the token.
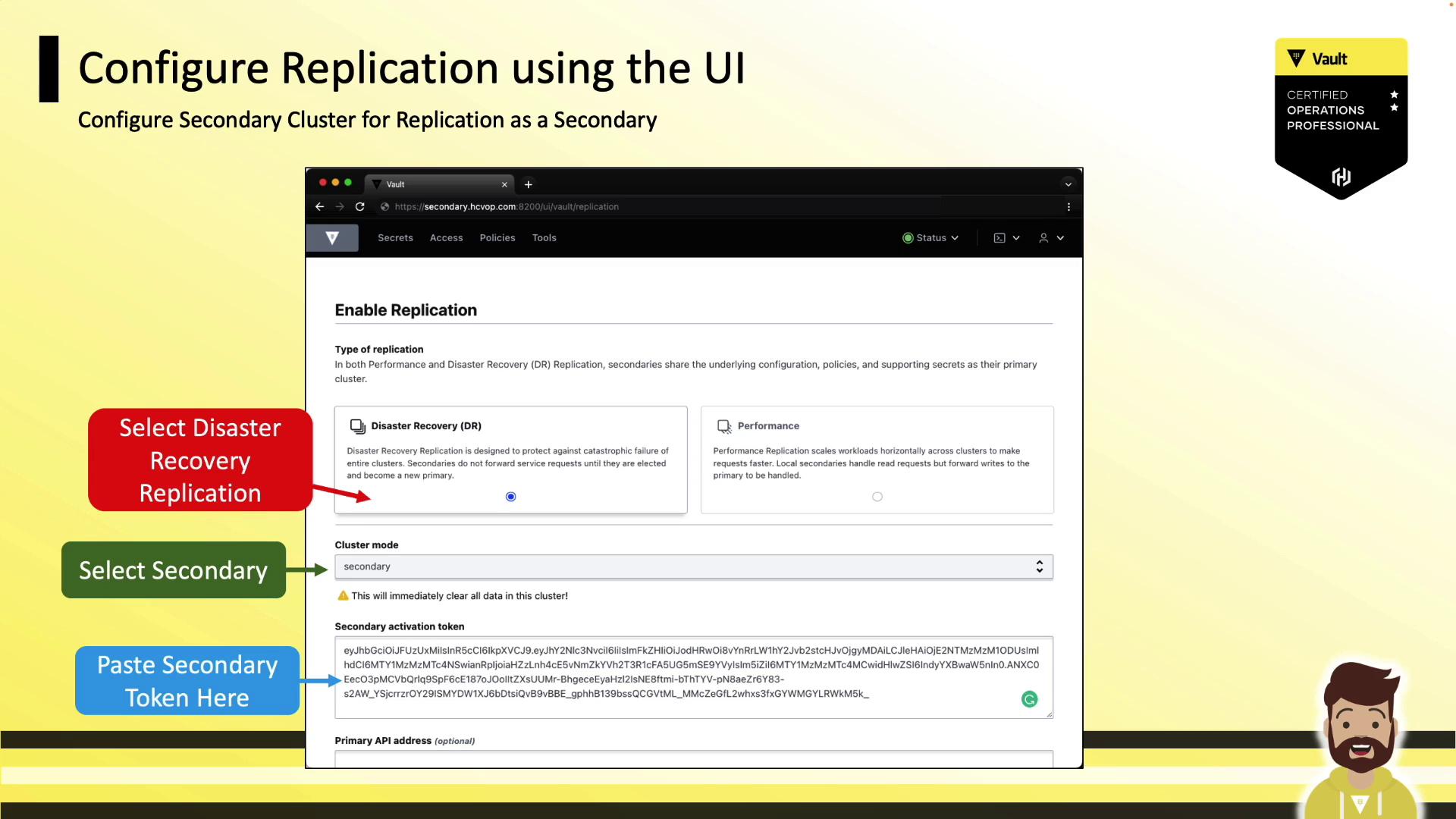
Secondary
- Go to Status → Replication → Enable Replication
- Select Disaster Recovery – Secondary
- Paste the activation token and click Enable
Monitoring Replication
Use the Vault CLI to verify replication health and status:
vault read -format=json sys/replication/status
vault read -format=json sys/replication/performance/status
vault read -format=json sys/replication/dr/status
sys/replication/status: Shows both performance and DR replicationsys/replication/performance/status: Performance onlysys/replication/dr/status: DR only
Now you’re ready to deploy DR replication in your Vault Enterprise environment or practice these steps for the Vault Certified Operations Professional exam.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content