HashiCorp Certified: Vault Operations Professional 2022
Understand the Hardware Security Module HSM Integration
Benefits of Auto Unsealing with HSM
In this lesson, we explore how integrating a Hardware Security Module (HSM) for auto unsealing Vault boosts security, simplifies operations, and helps meet compliance requirements.

An HSM is a network-attached, tamper-resistant device that generates, manages, and protects cryptographic keys. Common use cases include:
- Encrypting/decrypting data
- Digital signatures
- Strong authentication
- Secure key storage
If tampering is detected, the HSM can zeroize its keys to prevent unauthorized access. Enterprises with strict security needs—such as banks, telcos, or PCI-DSS environments—often deploy on-premises HSMs. Cloud providers also offer dedicated and shared HSM services, for example:
- AWS CloudHSM
- Azure Dedicated HSM
- AWS KMS (shared HSM-backed)
- Azure Key Vault (shared HSM-backed)
Vault Enterprise HSM Support
Vault Enterprise integrates with any HSM that supports the PKCS#11 standard. Key features include:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Root Key Protection | Encrypts Vault’s root key within the HSM instead of deriving it from Shamir shares. |
| Auto Unseal | Vault auto-decrypts its root key by calling the HSM on startup. |
| Seal Wrapping | Wraps secret data for FIPS 140-2 compliance using an additional HSM layer. |
| Entropy Augmentation | Feeds Vault’s internal RNG with HSM-generated entropy for stronger cryptographic operations. |
To use these features, download the Vault Enterprise HSM–enabled binary (suffix +ent+hsm) from releases.hashicorp.com.
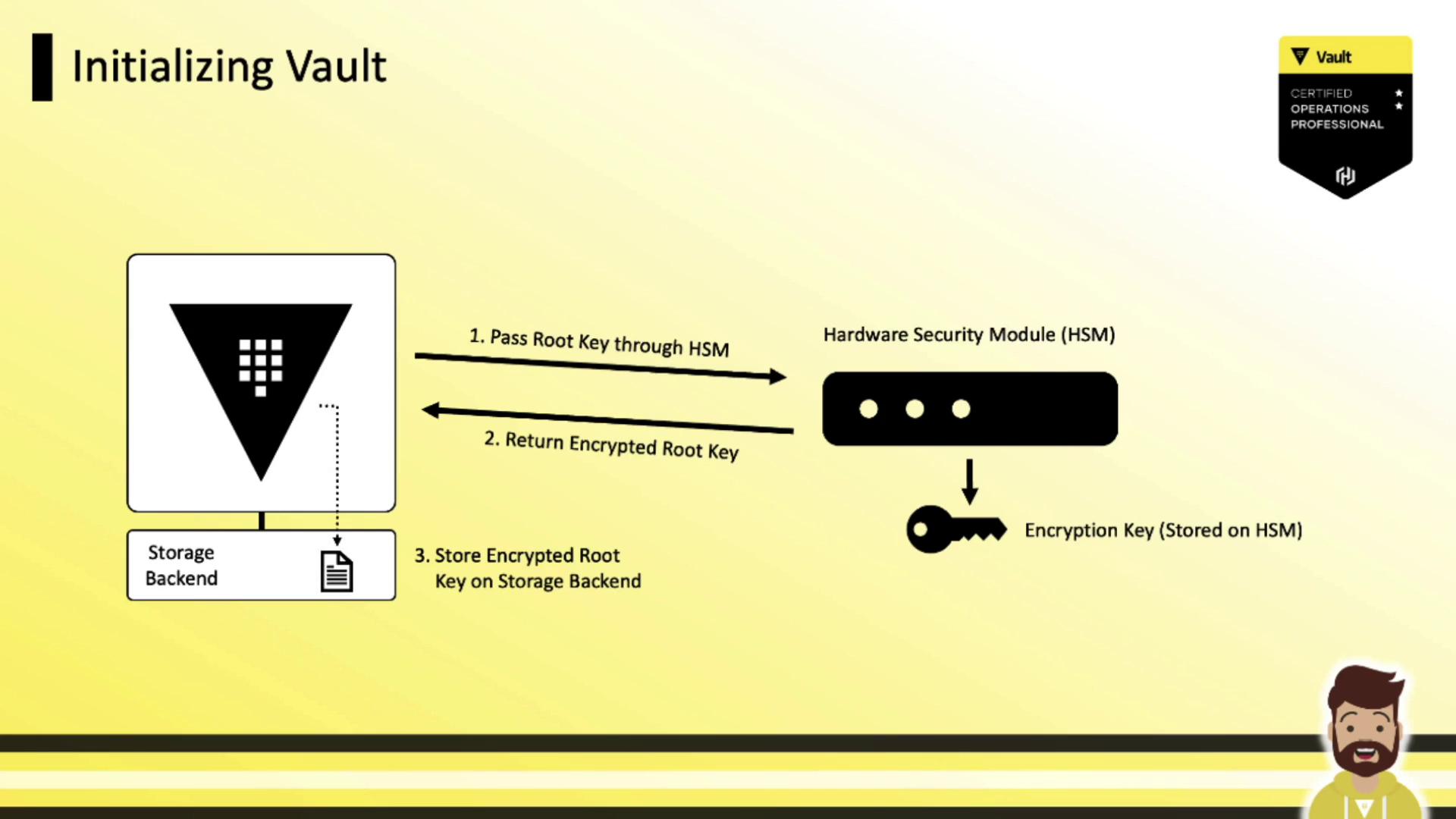
HSM in Vault Initialization
When initializing Vault with HSM auto unseal:
- Vault generates the root key.
- Vault submits the root key to the HSM.
- The HSM encrypts it with its internal key and returns ciphertext.
- Vault stores the encrypted root key on its backend.
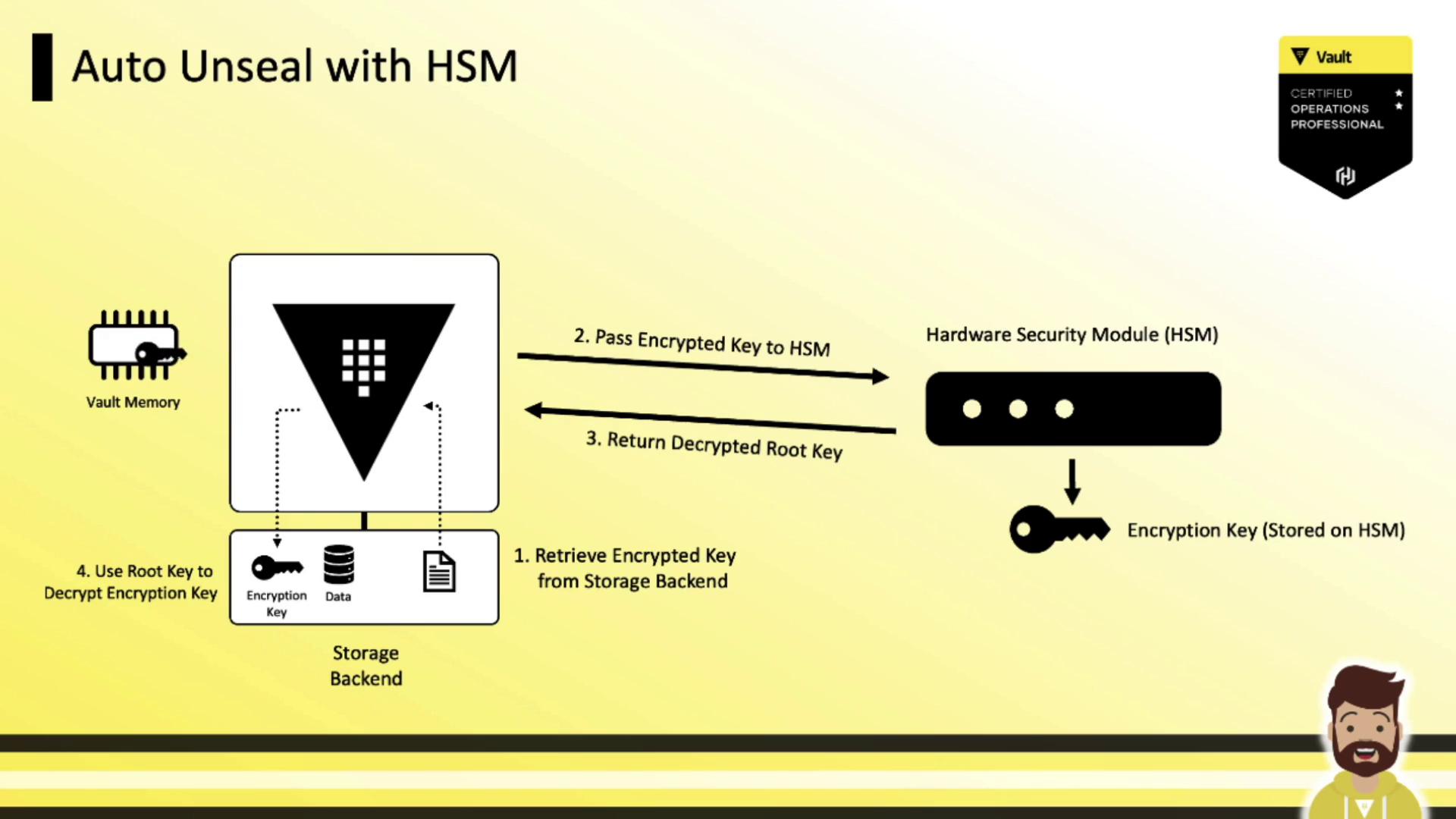
Auto Unseal Flow
On each Vault restart, auto unseal follows these steps:
- Retrieve the encrypted root key from the storage backend.
- Send the ciphertext to the HSM for decryption.
- Receive the plaintext root key from the HSM.
- Use the root key to decrypt Vault’s data-encryption key.
- Keep the data-encryption key in memory to handle storage encryption/decryption.
This workflow mirrors cloud HSM services (AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault) but keeps traffic on-premises when using a local HSM.
Configuring the PKCS#11 Seal Stanza
Add a seal "pkcs11" block to your Vault HCL configuration to enable HSM auto unseal:
seal "pkcs11" {
lib = "/usr/vault/lib/libCryptoki2_64.so"
slot = "2305843009213693953"
pin = "AAAA-BBBB-CCCC-DDDD"
key_label = "vault-hsm-key"
hmac_key_label = "vault-hsm-hmac-key"
}
Warning
Avoid embedding sensitive values (like the HSM PIN) directly in a world-readable file.
Vault supports environment variables for all PKCS#11 parameters so you can inject secrets at runtime without exposing them on disk.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content