Jenkins Pipelines
AWS Lambda and Advanced Deployment Techniques
Manual Lambda Deployment
In this lesson, we'll manually deploy our application to AWS Lambda while exploring each step in detail. Later, these steps will be automated through a Jenkins pipeline stage.
Below is an overview of the AWS resources created during this Lambda deployment.
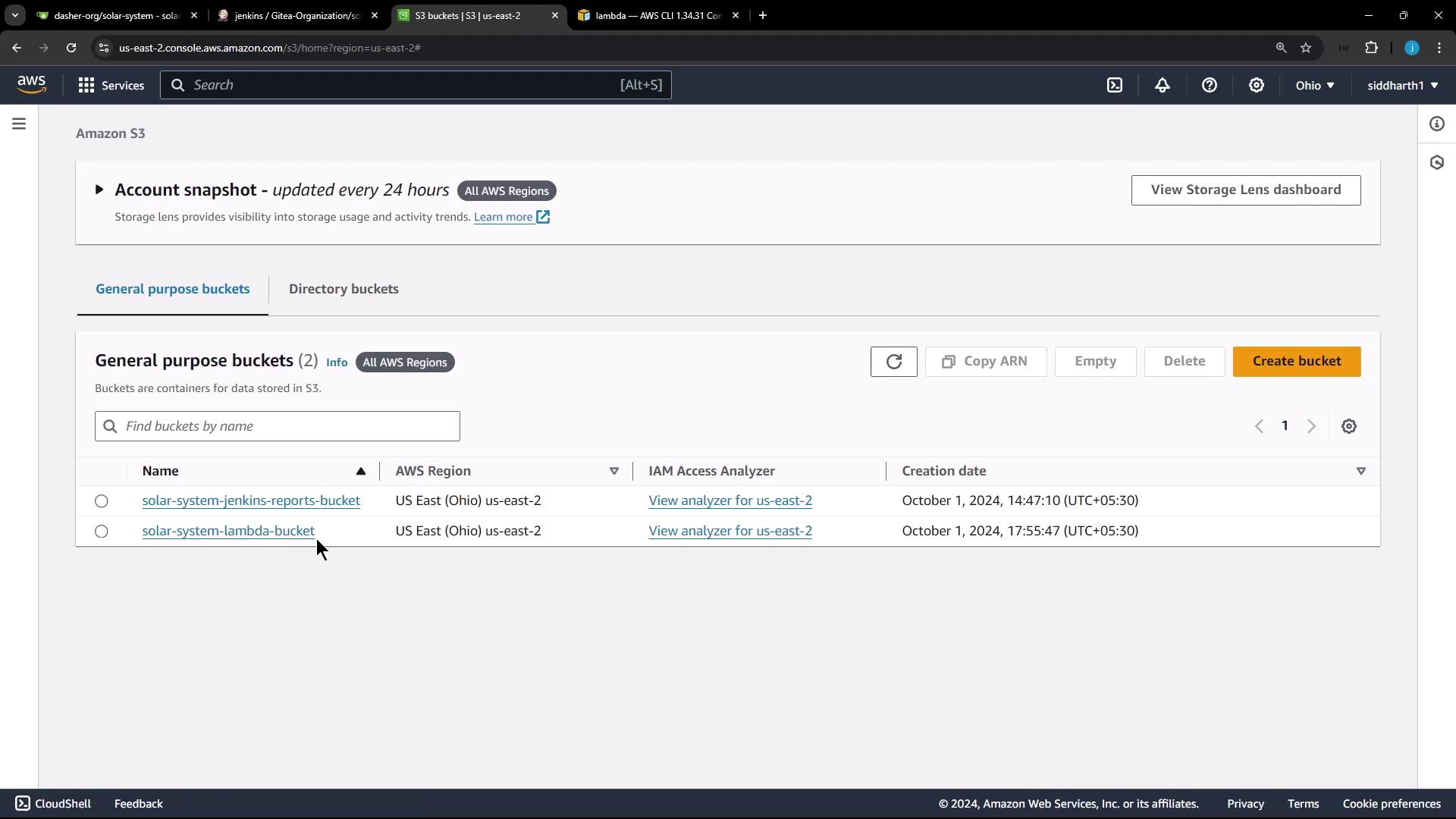
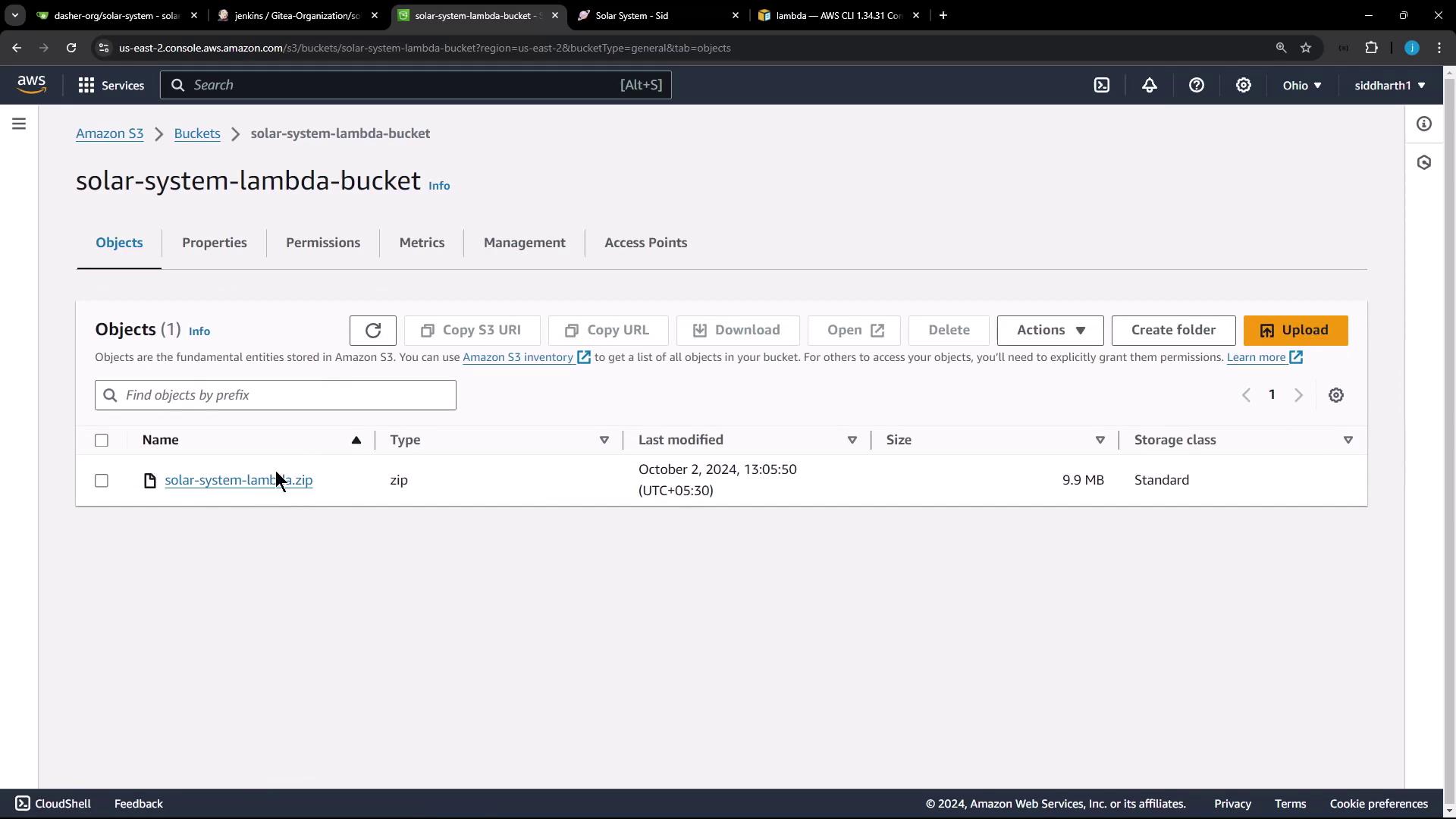
AWS S3 Bucket
First, we create a ZIP archive of the application and upload it to an S3 bucket. For this deployment, an S3 bucket named Solar System Lambda Bucket is already available in the US East 2 region.
AWS Lambda Function
Next, we update an existing Lambda function. The function, named solar system function, is configured with a ZIP package type and uses the Node.js 20.x runtime.
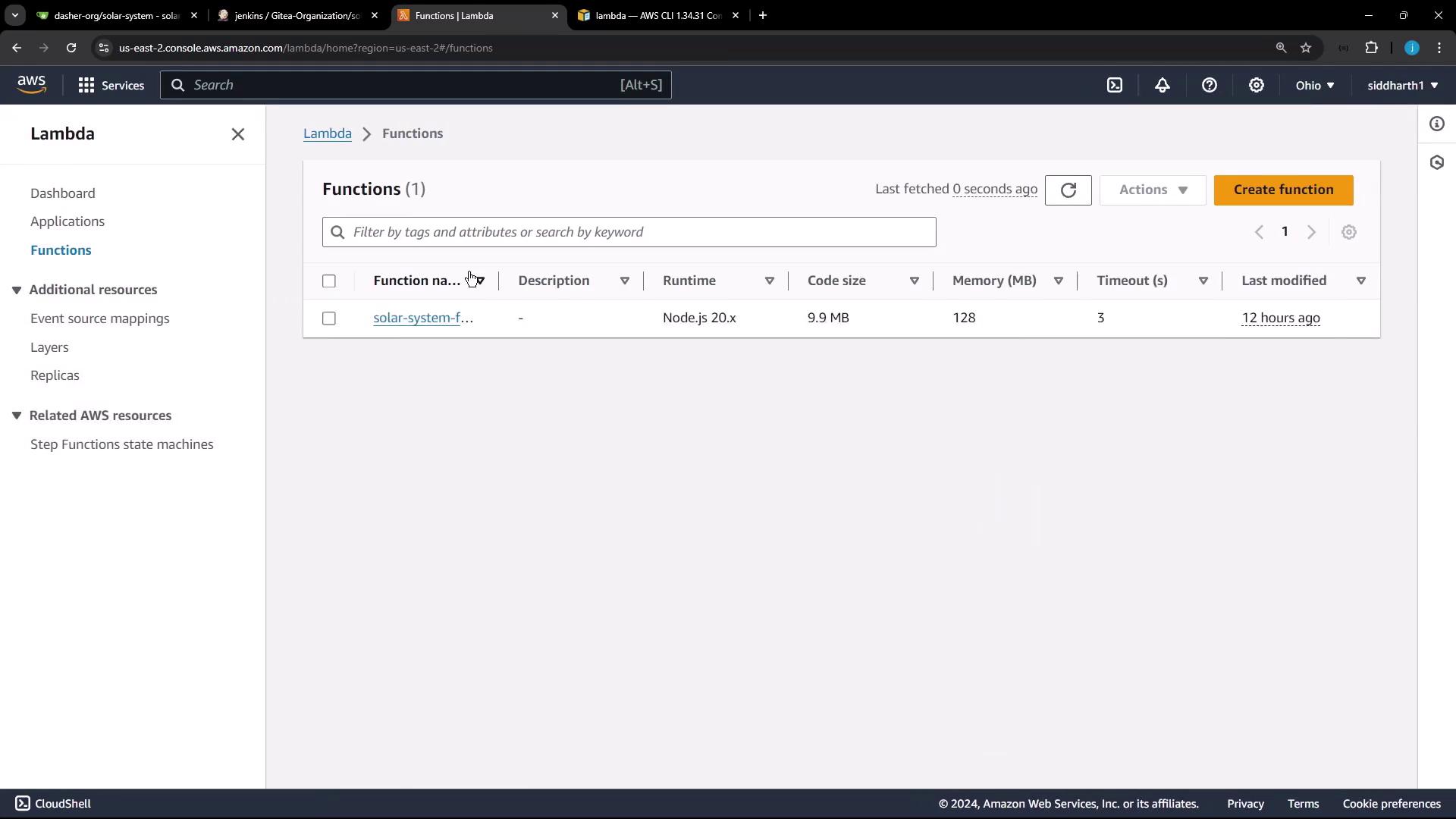
The function configuration shows the deployed code and important properties. When scrolling down, you can view details such as the package size (approximately 10 MB), runtime settings, and code source.
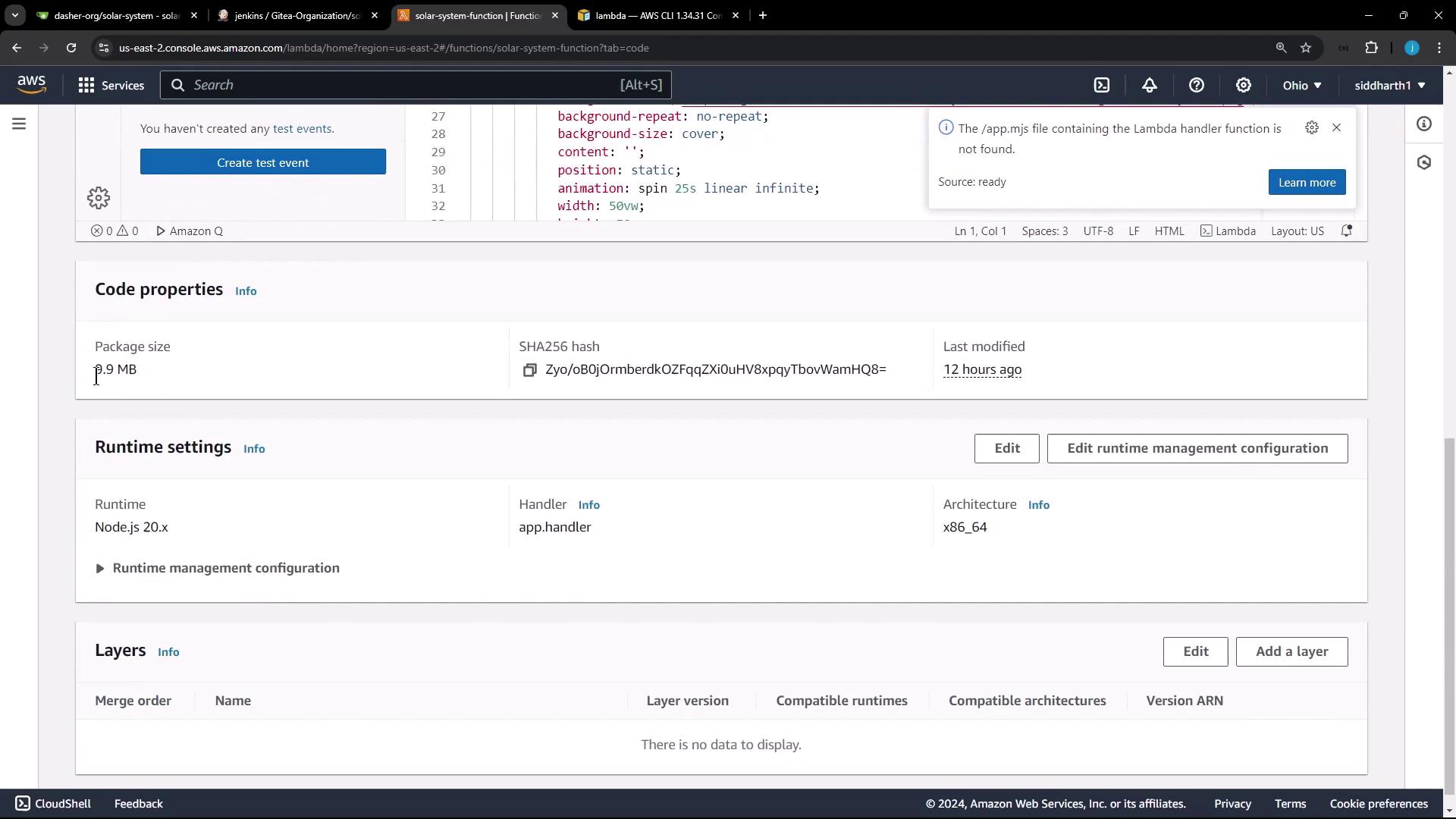
Runtime Settings:
- Runtime: Node.js 20.x
- Handler:
app.handler(usingapp.js)Note
If your application uses
index.jsas the entry point, update the handler toindex.handler.
Reviewing the Application Configuration
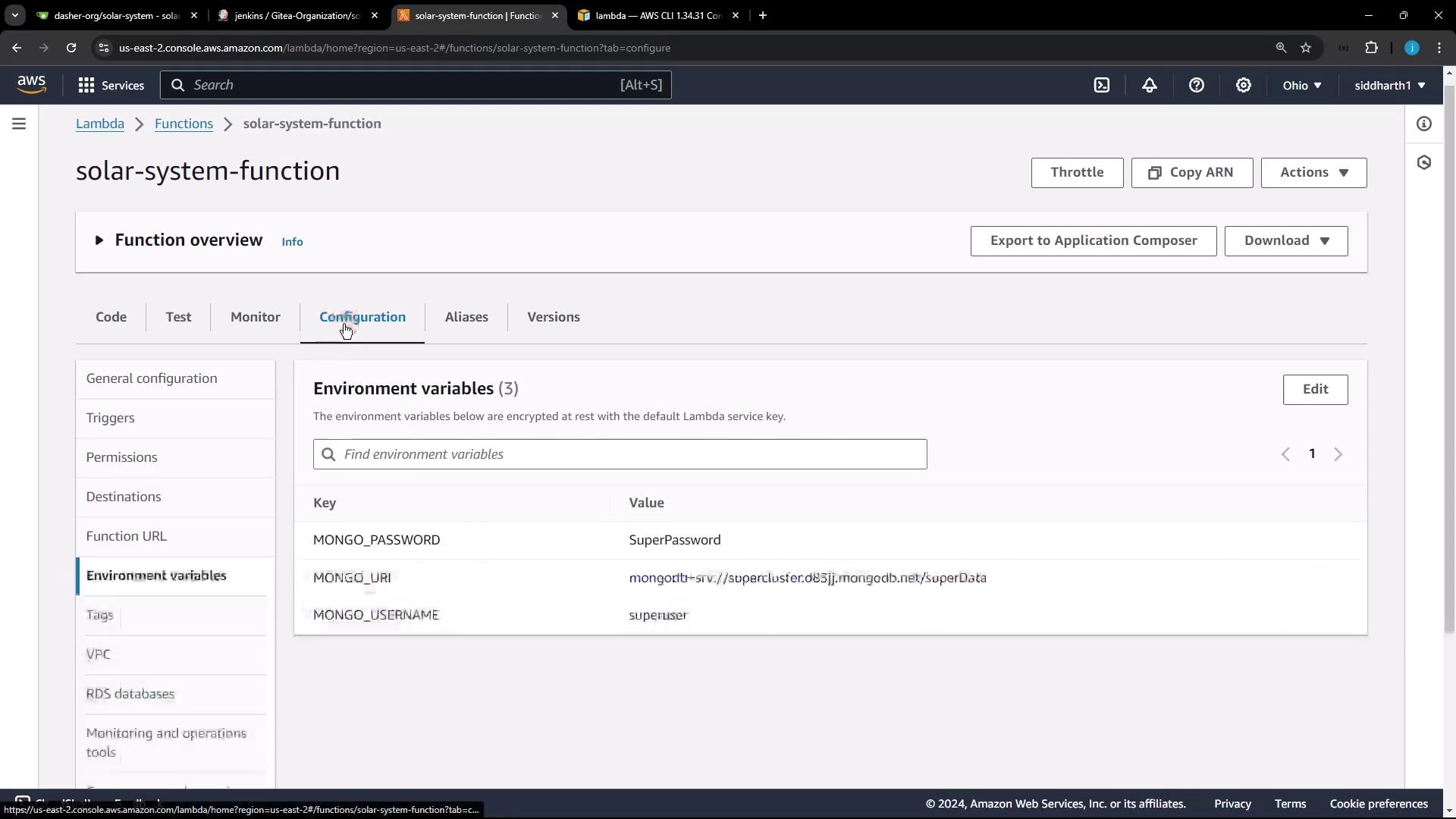
In the configuration tab, you may notice that environment variables (such as the Mongo password, URI, and username) are hardcoded. This practice is discouraged in production deployments and will be removed in the pipeline deployment.
Accessing the function URL in a browser will display the currently deployed application (version 3.0).
Manual Deployment Process
To update our Lambda function, follow these steps:
- Clone the Solar System repository and work on the main branch.
- Ensure that necessary dependencies (for example,
serverless-http) are added to yourpackage.json.
Example Code Snippets in app.js
Below is an example snippet from the deployed app.js file:
const path = require('path');
const fs = require('fs');
const express = require('express');
const OS = require('os');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const cors = require('cors');
const serverless = require('serverless-http');
const app = express();
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, '/')));
app.use(cors());
mongoose.connect(process.env.MONGO_URI, {
user: process.env.MONGO_USERNAME,
pass: process.env.MONGO_PASSWORD,
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
}, function(err) {
if (err) {
console.error(err);
}
});
Before deploying to Lambda, update the code by commenting out the HTTP server listener and exporting the Lambda handler using the serverless adapter.
Original snippet:
app.listen(3000, () => { console.log("Server successfully running on port - " +3000); })
module.exports = app;
//module.exports.handler = serverless(app)
Updated snippet for Lambda deployment:
//app.listen(3000, () => { console.log("Server successfully running on port - " +3000); });
//module.exports = app;
module.exports.handler = serverless(app);
Building and Zipping the Application
After updating the code for Lambda compatibility, perform the following steps:
Install Dependencies
Run the following command to install dependencies and create thenode_modulesdirectory:npm installUpdate index.html (Version Upgrade)
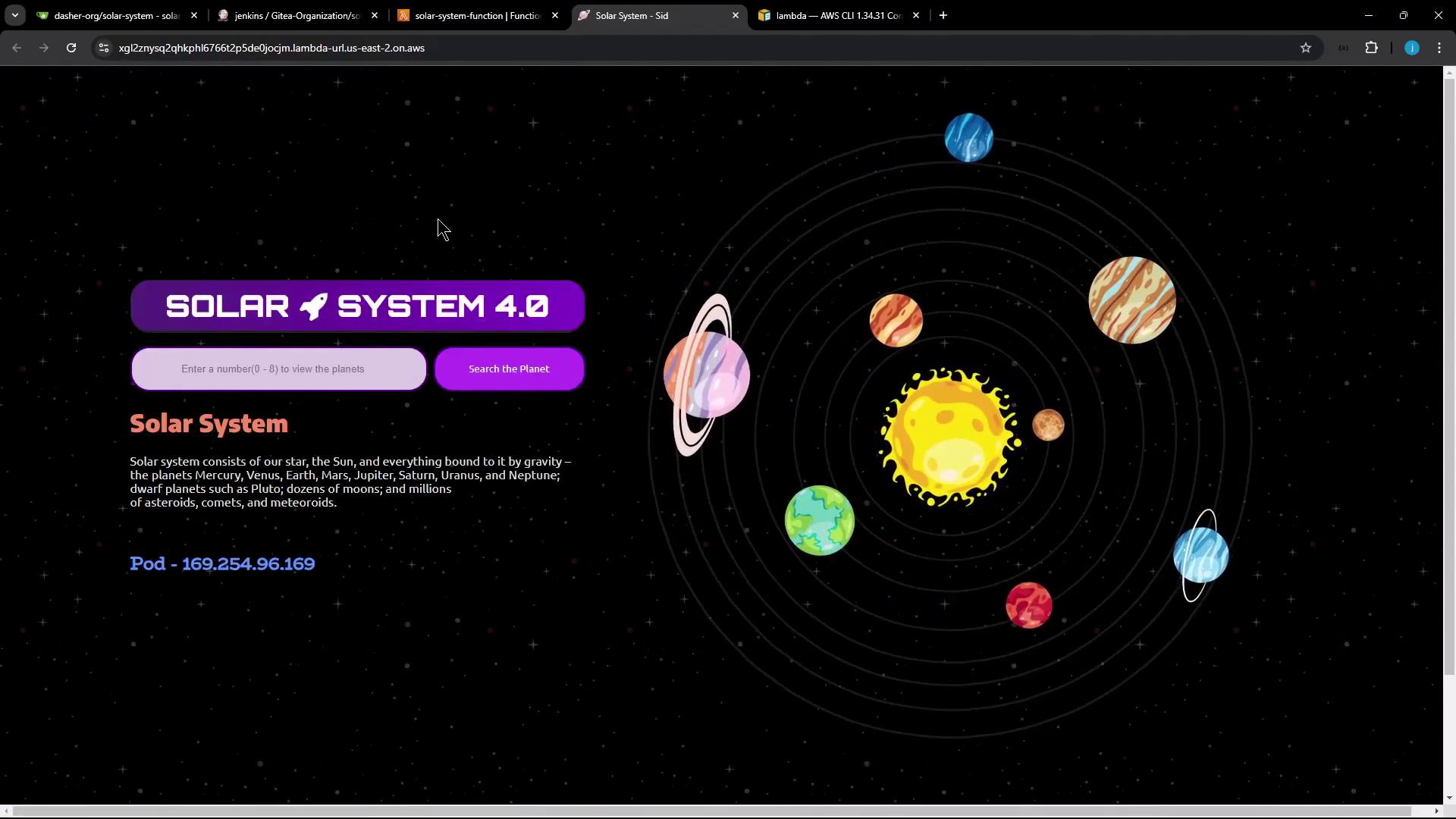
For example, update the version from 3.0 to 4.0:<button style="px 1px 3px"> SOLAR <i class="fa fa-rocket"></i> SYSTEM 4.0 </button>Zip the Required Files
Only include necessary files such asapp.js,package.json,package-lock.json,index.html, and thenode_modulesdirectory:zip -qr solar-system-lambda.zip app* package* index.html node* ls
Uploading to S3 and Updating Lambda
Follow these steps to update your Lambda function with the new deployment package:
Copy the Zip File to S3
Use the AWS CLI to upload the zip file to your S3 bucket:aws s3 cp solar-system-lambda.zip s3://solar-system-lambda-bucket/solar-system-lambda.zipUpdate the Lambda Function Code
Execute the following command to update the function:aws lambda update-function-code --function-name solar-system-function --s3-bucket solar-system-lambda-bucket --s3-key solar-system-lambda.zipVerify the Update
Retrieve the function URL configuration with:aws lambda get-function-url-config --function-name solar-system-functionAn example JSON output:
{ "FunctionName": "solar-system-function", "FunctionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-2:604513242291:function:solar-system-function", "Runtime": "nodejs20.x", "Role": "arn:aws:iam::604513242291:role/service-role/solar-system-function-role-gs891r31", "Handler": "app.handler", "CodeSize": 1032346, "Description": "", "Timeout": 3, "MemorySize": 128, "LastModified": "2024-10-07T36:54:0000Z", "CodeSha256": "IHF6tIDbZEqY8SMORN+v58xBD54U+liWCPII1YLb30U=", "Version": "$LATEST", "Environment": { "Variables": { "MONGO_USERNAME": "superuser" } } }
After refreshing the function URL, you should see the updated version (Solar System 4.0).
Final Recap and Next Steps
To summarize, these are the steps for a manual deployment to AWS Lambda:
- Prepare your application:
Updateapp.jsby commenting out the HTTP listener and exporting the Lambda handler. - Install dependencies:
Runnpm installto create thenode_modulesdirectory. - Update static files:
Modify files such asindex.html(e.g., version label upgrade). - Zip the necessary files:
Use thezipcommand to include only required files and directories. - Upload the zip to S3:
Useaws s3 cpto transfer the ZIP file. - Update the Lambda function code:
Executeaws lambda update-function-codewith the appropriate S3 parameters. - Verify the deployment:
Check the new deployment by retrieving the function URL configuration.
You can view the following table for a summary of key commands:
| Step | Command Example |
|---|---|
| Install Dependencies | npm install |
| Update Version in index.html | <button style="px 1px 3px"> SOLAR <i class="fa fa-rocket"></i> SYSTEM 4.0 </button> |
| Create Zip Archive | zip -qr solar-system-lambda.zip app* package* index.html node* |
| Upload Zip to S3 | aws s3 cp solar-system-lambda.zip s3://solar-system-lambda-bucket/solar-system-lambda.zip |
| Update Lambda Function | aws lambda update-function-code --function-name solar-system-function --s3-bucket solar-system-lambda-bucket --s3-key solar-system-lambda.zip |
| Verify Update | aws lambda get-function-url-config --function-name solar-system-function |
Below is an example set of commands to automate the updates in app.js and package the application:
# Comment out the server listener and update the export for AWS Lambda
sed -i 's/app\.listen(3000)/\/\/app.listen(3000)/g' app.js
sed -i 's/module.exports = app;/\/\/module.exports = app;/g' app.js
sed -i 's/\/\/module.exports.handler = serverless(app);/module.exports.handler = serverless(app);/g' app.js
tail -5 app.js
# Install dependencies if not already installed
npm install
# Zip the required files
zip -qr solar-system-lambda.zip app* package* index.html node*
# Copy the zip file to the S3 bucket and update the Lambda function code
aws s3 cp solar-system-lambda.zip s3://solar-system-lambda-bucket/solar-system-lambda.zip
aws lambda update-function-code --function-name solar-system-function --s3-bucket solar-system-lambda-bucket --s3-key solar-system-lambda.zip
# Retrieve function URL configuration for verification
aws lambda get-function-url-config --function-name solar-system-function
Next Steps
Subsequent automation of these tasks will be integrated into a Jenkins pipeline stage for a seamless deployment process.
Thank you.
Watch Video
Watch video content