
Securing the Underlying Hosts
Before diving into Kubernetes-specific features, it is vital to secure the physical or virtual hosts that form the cluster. Ensure all host access is protected by:- Disabling root access
- Disabling password-based authentication
- Enforcing SSH key-based authentication
- Implementing other critical security measures

Kubernetes-Specific Security Measures
Focusing specifically on Kubernetes, the core component is the kube-apiserver. This component is the central point of contact for operations, whether accessed via the kubectl utility or directly through its API. Its security is paramount, so consider these key questions:- Who can access the cluster?
- What actions can they perform once access is granted?

Authentication
Access to the API server is managed through robust authentication mechanisms. Methods include:- Static files with user IDs and passwords
- Tokens and certificates
- External authentication providers (e.g., LDAP)
- Machine-to-machine interactions managed through service accounts

Authorization
Once authenticated, the system determines valid actions through authorization. Kubernetes primarily uses Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), where permissions are assigned based on roles or group memberships. Additional methods include Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) and webhooks for extended flexibility.
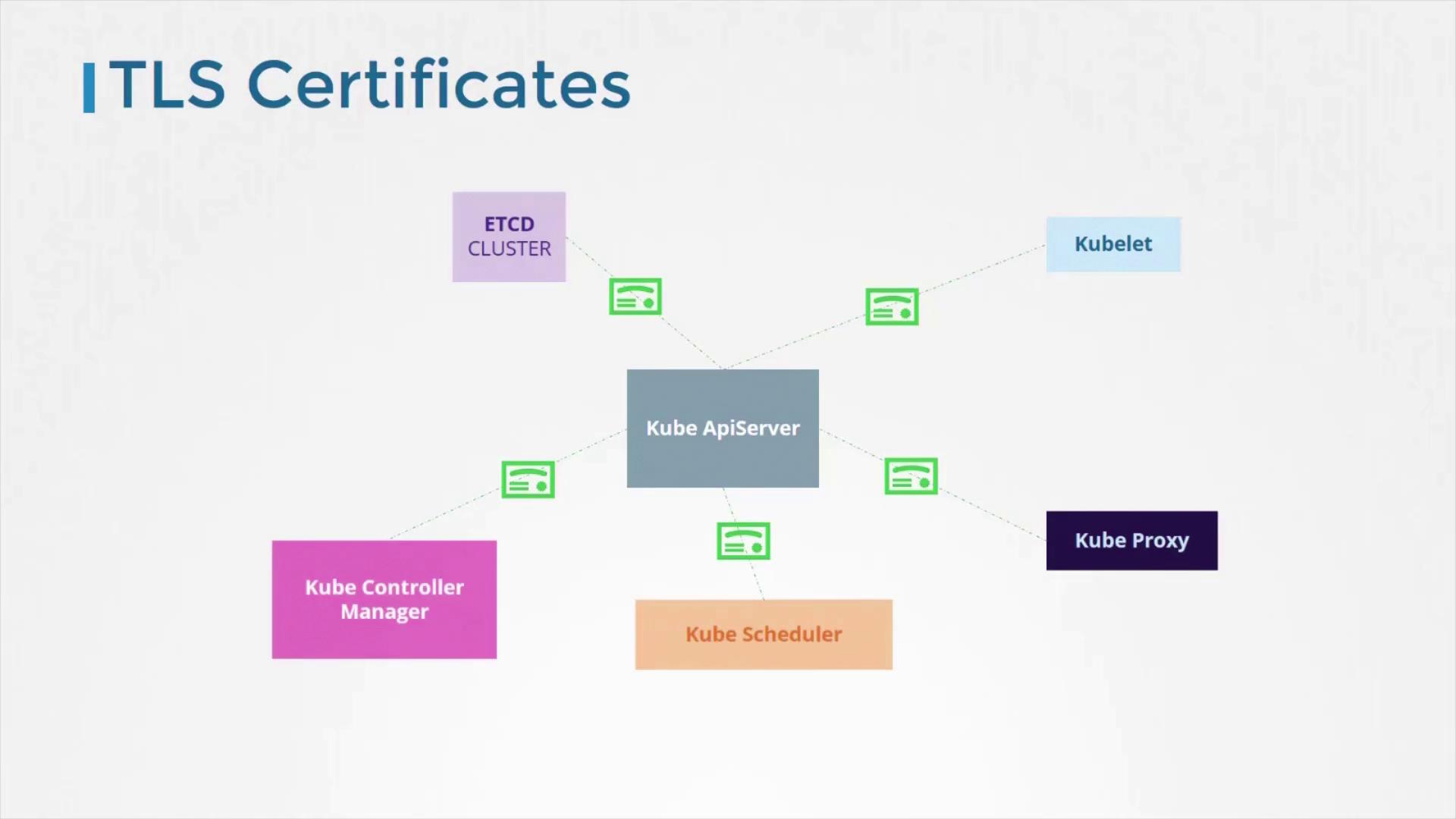
All communications between essential cluster components—such as the etcd cluster, kube-controller-manager, scheduler, API server, and nodes (kubelet and kube-proxy)—are secured with TLS encryption. This ensures that every interaction within the cluster remains confidential and tamper-proof.
TLS Encryption
An entire section of Kubernetes documentation is dedicated to configuring TLS certificates. These certificates secure intra-cluster communication, safeguarding sensitive data exchanged between:- Kube ApiServer
- ETCD Cluster
- Kubelet
- Additional components
Network Policies
By default, pods within the cluster can communicate freely. However, to tighten security, you can implement network policies, which restrict communication between pods and enhance overall cluster security.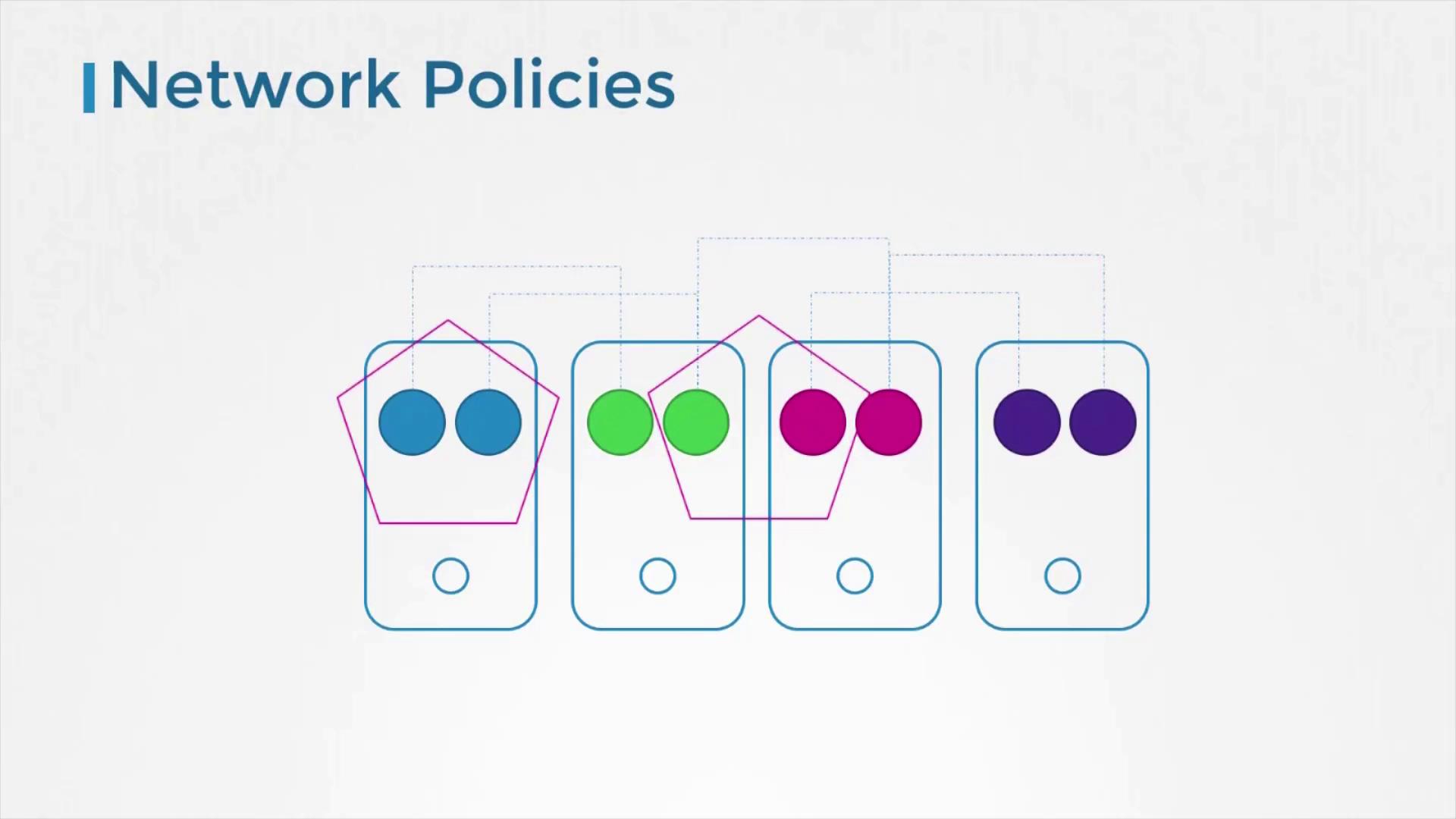
This high-level overview has introduced the key security primitives in Kubernetes. In the upcoming sections, we will explore each component in greater depth to help you build a secure and resilient Kubernetes cluster. For additional insights, consider exploring the following resources: