Non-compliance can result in severe penalties, data exposure, and reputational damage.
| Framework | Scope | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | EU personal data protection | Encrypt data at rest, restrict data access |
| HIPAA | US healthcare PHI | TLS encryption, strict access controls, secure secrets |
| PCI DSS | Payment card data | Encrypt in transit & at rest, auditing, strong auth |
| NIST | Cybersecurity best practices | Risk assessments, security controls, periodic audits |
| CIS Benchmarks | IT system hardening | Secure configs, RBAC, network policies, logging |
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
The GDPR is an EU regulation that protects individuals’ personal data and privacy rights. In a web application context, GDPR compliance often includes:- Encrypting user data stored in your MySQL database (data at rest)
- Ensuring only authorized back-end services can access personal data
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA is a U.S. regulation focused on protecting sensitive patient health information (PHI). For applications handling patient data, you must:- Encrypt all data transfers (front-end ↔ back-end ↔ database) using TLS
- Implement strict access controls to prevent unauthorized access
- Securely configure Kubernetes Secrets for application use
Ensure your TLS certificates are managed via a secure certificate authority and rotated regularly.
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard)
The PCI DSS applies to any system processing payment card data. Key requirements include:- Encrypting cardholder data in transit and at rest
- Enforcing strong access controls
- Monitoring and auditing all access to payment information

NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology)
NIST publishes the Cybersecurity Framework to improve the security and resilience of information systems. For web applications, typical NIST controls involve:- Conducting regular risk assessments to identify vulnerabilities
- Implementing security controls (firewalls, IDS/IPS)
- Performing periodic security audits
CIS Benchmarks (Center for Internet Security)
CIS provides detailed benchmarks for securing IT systems, including Kubernetes. These guidelines cover:- Secure configuration of control plane components (API server, etcd, kubelet, controller-manager, scheduler)
- Authentication and authorization (enforce RBAC, disable anonymous access)
- Logging, monitoring, network policies, and pod security
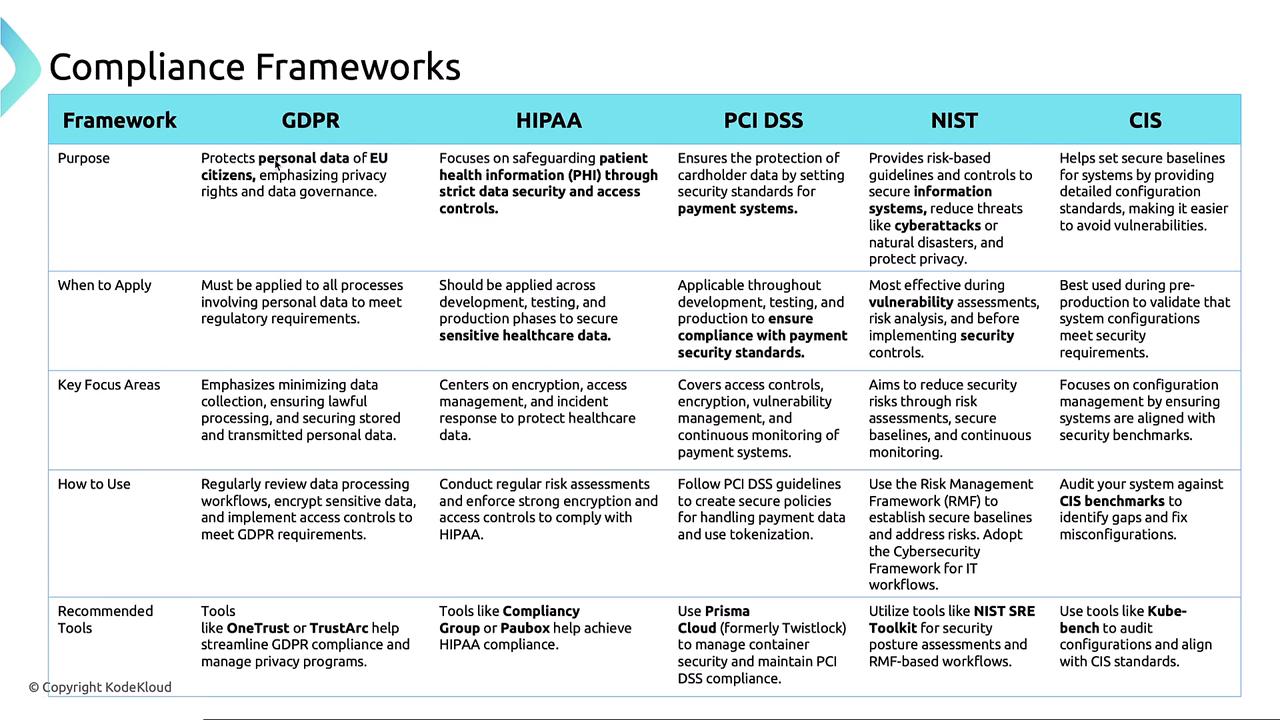
Below is a visual comparison of these frameworks—when they apply, their focus areas, and recommended tools:

- Compliance frameworks guide data protection, encryption, and access controls
- GDPR targets personal data of EU citizens
- HIPAA safeguards protected health information (PHI)
- PCI DSS secures payment card data
- NIST offers risk assessment and security control guidelines
- CIS Benchmarks provide granular, automated checks for Kubernetes security