kubectl CLI communicates with the Kubernetes API server and demonstrate two secure methods—kubectl proxy and kubectl port-forward—for accessing cluster APIs and Services locally. You’ll see how kubeconfig provides authentication, how to launch a local HTTP proxy, and how to forward ports from your machine to in-cluster endpoints.
1. Interacting with the Kubernetes API
By default,kubectl uses credentials in your ~/.kube/config (kubeconfig) to authenticate against the API server:
Comparison of Access Methods
| Method | Command | Authentication | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| kubectl CLI | kubectl get nodes | kubeconfig | Standard cluster management |
| Direct API Curl | curl https://<api>:6443 | Client certs | Scripting or debugging API interactions |
| kubectl proxy | kubectl proxy | kubeconfig | Local HTTP proxy for API & services |
2. Using kubectl proxy
The kubectl proxy command starts a local HTTP server (default port 8001) that forwards requests to the API server using your kubeconfig credentials:
http://localhost:8001:
By default,
kubectl proxy listens only on the loopback interface (127.0.0.1) for security.Avoid exposing the proxy on public IPs without proper authentication controls.
3. Accessing In-Cluster Services via Proxy
You can also reach Services of typeClusterIP inside the cluster through the proxy. For example, to access an NGINX Service in the default namespace:
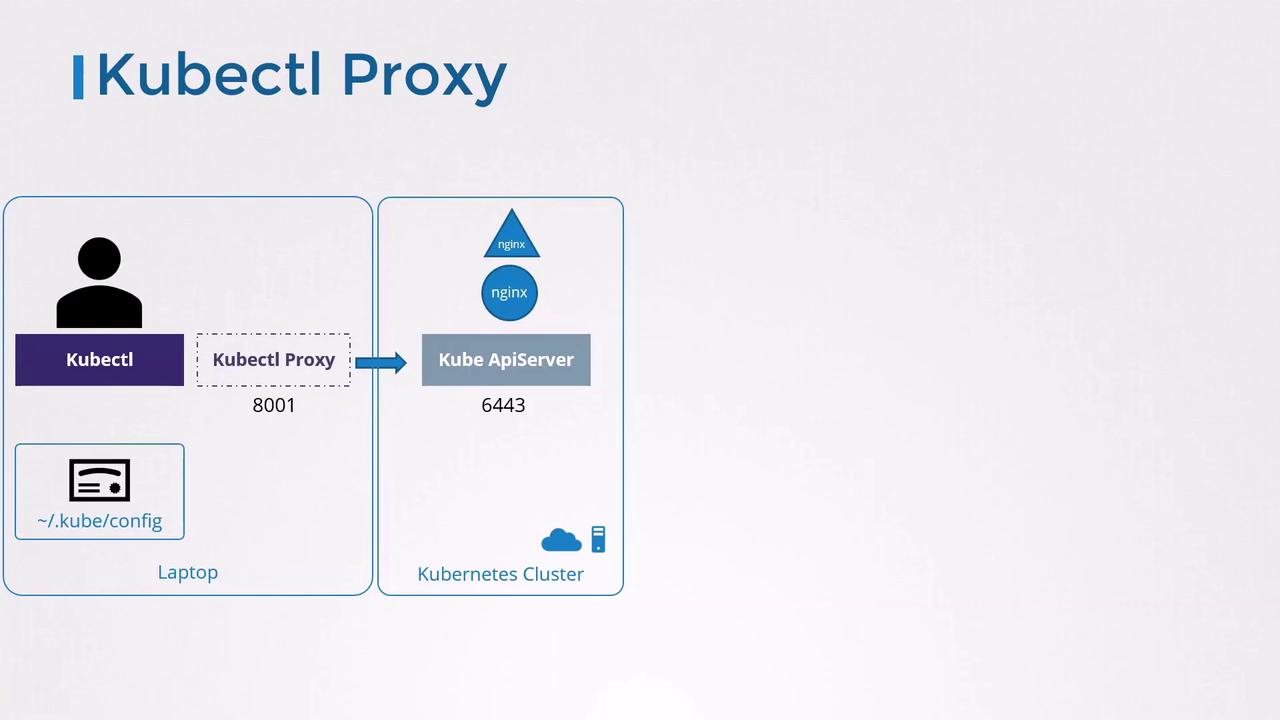
kubectl proxy, the in-cluster Service appears as if it’s running locally.
4. Port Forwarding with kubectl port-forward
An alternative to proxying is port forwarding, which maps a local port directly to a Pod or Service port:
- Local endpoint:
http://localhost:8080 - Cluster endpoint: Service
nginxport80
http://localhost:8080 sends traffic through the API server to the nginx Service.